Yes, in a technical sense, biomass can replace coal, but this substitution is not a simple one-to-one solution. Power plants can either be retrofitted to burn a mix of coal and biomass—a process called co-firing—or be fully converted to run on biomass alone. However, the environmental benefits, economic viability, and scalability of this replacement are highly contested and depend entirely on the source of the biomass and the timeline of its carbon cycle.
While biomass offers a pathway to repurpose existing coal infrastructure and reduce immediate fossil fuel consumption, it is not a universal solution. Its viability as a true replacement is severely limited by questionable carbon neutrality claims, logistical complexity, and competition for land use.

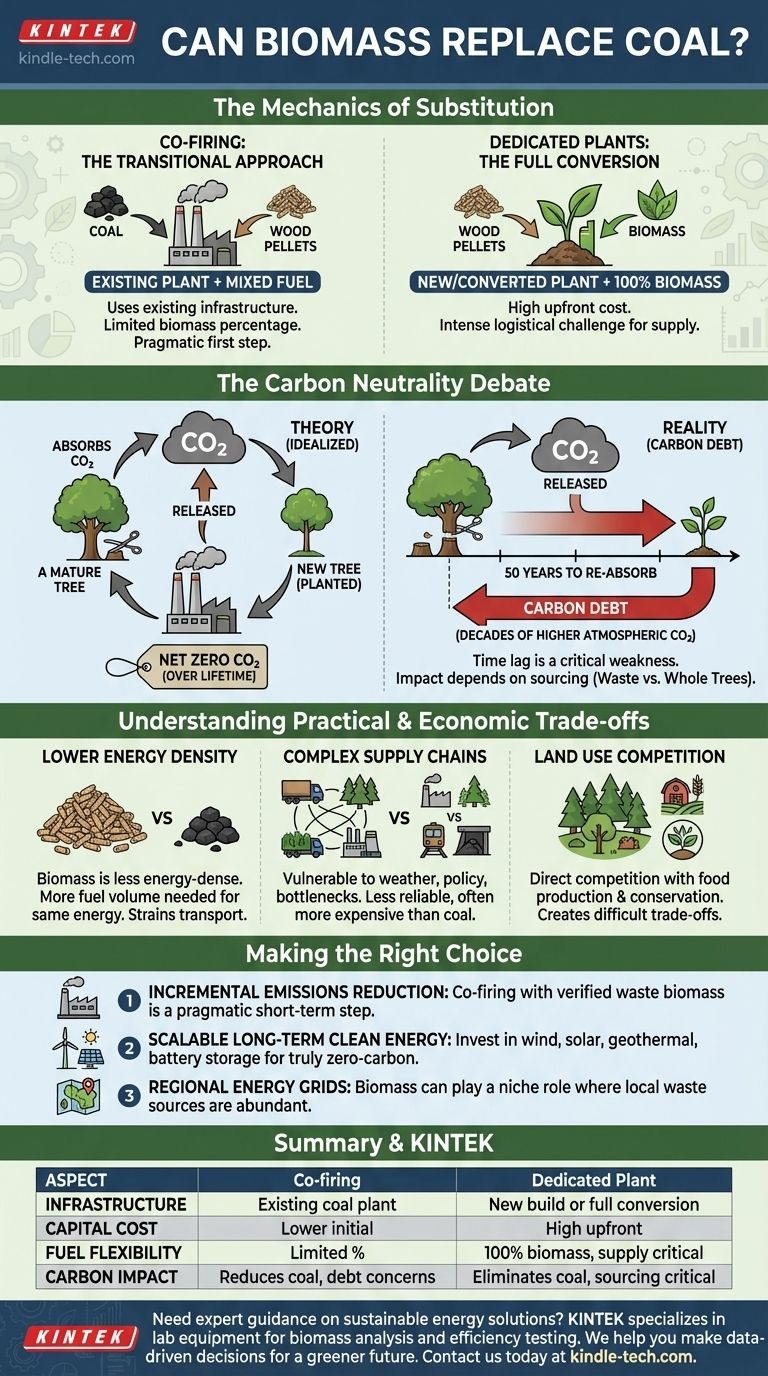
The Mechanics of Substitution
The concept of using biomass for power generation hinges on its ability to be burned to create steam, which then drives turbines, similar to a conventional coal plant. The practical application, however, varies significantly.
Co-firing: The Transitional Approach
Co-firing involves blending biomass, typically in the form of processed wood pellets, with coal in an existing power plant. This is often seen as a pragmatic first step to reduce a plant's carbon footprint.
The primary advantage is the use of existing infrastructure, minimizing upfront capital costs. However, the percentage of biomass that can be added is often limited without significant and costly modifications to the boiler and fuel handling systems.
Dedicated Plants: The Full Conversion
A dedicated biomass plant burns only biomass. These can be new facilities designed for this purpose or, more commonly, retired coal plants that have been fully converted.
While a full conversion eliminates coal entirely, it requires substantial investment. It also concentrates the immense logistical challenge of sourcing and transporting a massive, continuous supply of biomass fuel to a single location.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate: Is Biomass Truly Green?
The central argument for biomass is that it is "carbon neutral." This claim requires careful and critical examination, as the reality is far more complex.
The Theoretical Carbon Cycle
The theory is that burning wood releases carbon dioxide (CO2) that the tree absorbed from the atmosphere during its lifetime. If a new tree is planted to replace it, that new tree will re-absorb an equivalent amount of CO2 over its life.
In this idealized loop, the net CO2 added to the atmosphere is zero, unlike burning fossil fuels, which releases carbon that was sequestered millions of years ago.
The Reality of "Carbon Debt"
This theory breaks down when considering time. When a 50-year-old tree is burned, its stored carbon is released into the atmosphere almost instantly. A newly planted sapling will take 50 years to re-absorb that same amount of carbon.
This creates a "carbon debt." For several decades, the atmospheric CO2 concentration is higher than it would have been, contributing to warming during a critical period. This time lag is the single greatest weakness in the carbon neutrality argument.
The Critical Impact of Sourcing
The environmental outcome is entirely dependent on the biomass source. Using waste products—like sawdust from lumber mills or agricultural residues—is broadly considered sustainable as it adds no new harvesting pressure.
Conversely, harvesting whole trees specifically for fuel can lead to deforestation, habitat loss, and a significant carbon debt. If old-growth forests are cleared for fuel, the environmental impact is profoundly negative.
Understanding the Practical and Economic Trade-offs
Beyond the carbon debate, replacing coal with biomass introduces significant logistical and financial hurdles that cannot be ignored.
Lower Energy Density
Biomass is far less energy-dense than coal. A ton of wood pellets produces significantly less energy than a ton of coal.
This means more fuel by volume and weight must be harvested, processed, transported, and stored to generate the same amount of electricity, placing a much larger strain on transportation infrastructure.
Complex and Costly Supply Chains
The coal supply chain is mature and highly efficient. In contrast, sourcing the vast quantities of biomass needed for a large power plant requires an enormous and continuous harvesting and processing operation.
This supply chain is vulnerable to weather, local land-use policies, and transportation bottlenecks, making it less reliable and often more expensive than coal.
Land Use Competition
Scaling up biomass production raises a critical question: where does the land come from?
Growing energy crops or trees for fuel can compete directly with agriculture for food production or with the need to conserve natural forests for biodiversity and carbon sequestration. This creates a difficult and often untenable trade-off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass is not a silver bullet for decarbonization. It should be seen as a niche fuel with a limited, transitional role rather than a direct, scalable replacement for coal.
- If your primary focus is incrementally reducing emissions at an existing coal plant: Co-firing with verified waste biomass can be a pragmatic short-term step, provided the supply chain is genuinely sustainable.
- If your primary focus is building scalable, long-term clean energy: Investing in wind, solar, geothermal, and battery storage offers a far more effective and truly zero-carbon solution without the negative land-use and carbon-debt implications.
- If you are assessing regional energy grids: Biomass may play a role where a sustainable source of waste (like from forestry or agricultural industries) is abundant and localized, but it cannot be the foundation of a national energy strategy.
Ultimately, understanding the profound limitations of biomass is crucial for making sound decisions in the transition to a truly sustainable energy future.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Co-firing (Mixed Fuel) | Dedicated Biomass Plant |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Uses existing coal plant | Requires new build or full conversion |
| Capital Cost | Lower initial investment | High upfront cost |
| Fuel Flexibility | Limited % of biomass possible | 100% biomass, but supply chain intensive |
| Carbon Impact | Reduces coal use, but carbon debt concerns | Eliminates coal, but sourcing is critical |
Need expert guidance on sustainable energy solutions for your laboratory or facility? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to support your research into alternative energy sources, including biomass analysis and efficiency testing. Our team can help you select the right tools to evaluate fuel properties, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions for a greener future. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your energy transition goals with precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















