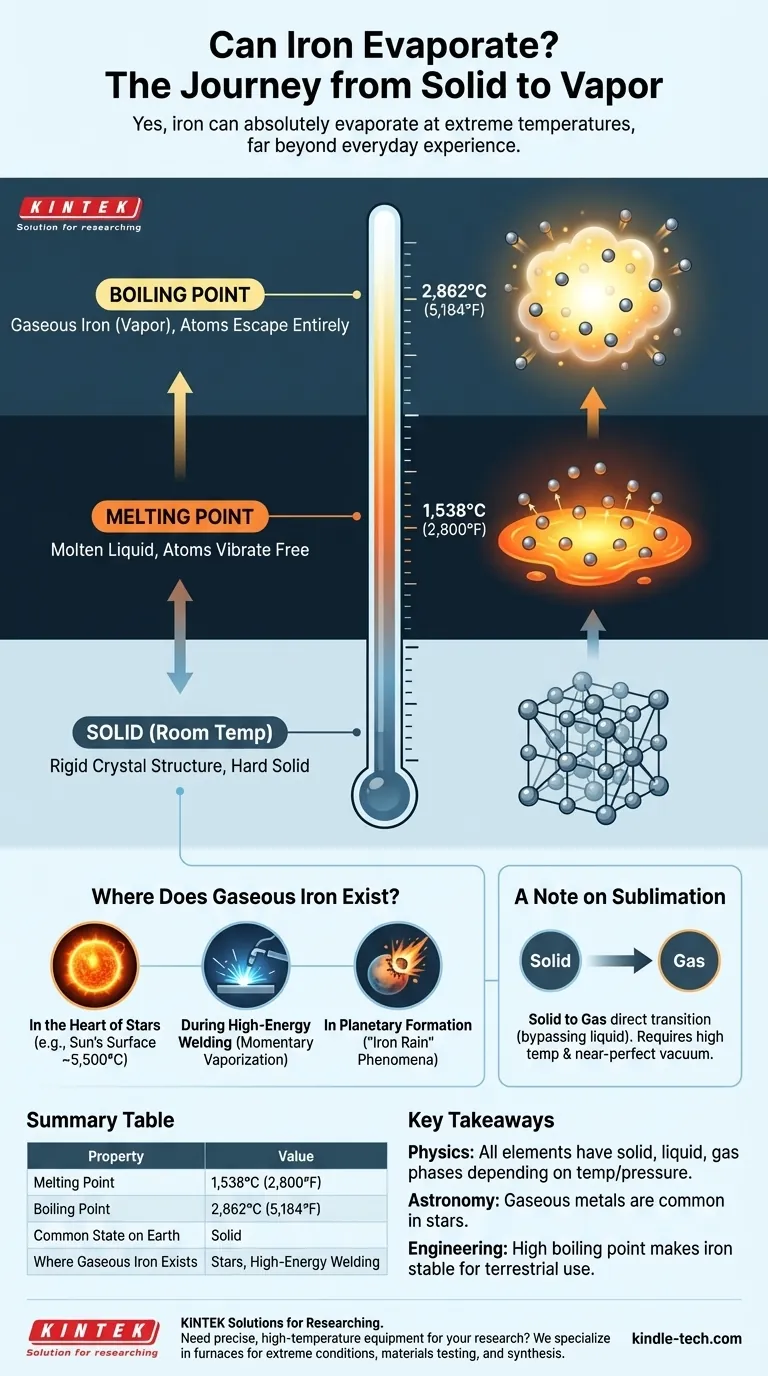
Yes, iron can absolutely evaporate. Like virtually all matter, iron can exist as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. However, the conditions required to turn solid iron into a gas, or vapor, involve temperatures so extreme that they are far outside the realm of everyday human experience.
The core principle is that any element will transition into a gas if it is heated to its boiling point. For iron, this temperature is an incredibly high 2,862°C (5,184°F), which is why we perceive it as a permanently solid material under all normal conditions.

Understanding the Journey to Iron Vapor
To grasp how iron evaporates, it's best to think of the same process that water goes through, but at a much higher temperature scale. The state of any matter—solid, liquid, or gas—is determined by the energy and movement of its atoms.
First Step: From Solid to Liquid
Before iron can boil, it must first melt. At room temperature, the iron atoms are locked into a rigid crystal structure, which is what makes it a hard solid.
As you add immense heat, the atoms vibrate more and more violently until they break free from this structure. This happens at iron's melting point of 1,538°C (2,800°F), turning it into a molten liquid.
Second Step: From Liquid to Gas
To evaporate, or boil, the iron atoms need even more energy to completely overcome the forces holding them together as a liquid.
When the temperature reaches iron's boiling point of 2,862°C (5,184°F), the atoms escape entirely, forming a superheated cloud of individual iron atoms. This is iron vapor, or gaseous iron.
Where Does Gaseous Iron Actually Exist?
While you will never see a puddle of iron evaporating on a hot day, this process is common in certain extreme environments in the universe and in specialized industrial applications.
In the Heart of Stars
The most common place to find gaseous iron is inside stars, including our Sun. The surface of the Sun is about 5,500°C (9,940°F), well above iron's boiling point. Here, iron exists as a component of the solar plasma.
During High-Energy Welding
On a much smaller and more controlled scale, the intense heat of an industrial welding arc can momentarily vaporize a tiny amount of the metal being welded. This iron vapor immediately cools and re-solidifies as part of the weld.
In Planetary Formation
During the formation of our solar system, massive impacts between celestial bodies would have generated enough energy to vaporize rock and iron. This could have led to phenomena like "iron rain" on protoplanets as the vapor cooled and condensed.
A Note on Sublimation
There is another path to a gaseous state called sublimation, where a material turns directly from a solid to a gas, bypassing the liquid phase entirely. This is what dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) does at room temperature.
Theoretically, iron can also sublimate. However, this would require a combination of very high temperatures and extremely low pressure (a near-perfect vacuum). Under any normal atmospheric pressure, the rate of sublimation for iron is practically zero.
Key Takeaways for Understanding Matter
- If your primary focus is basic physics: Remember that all elements can exist in solid, liquid, and gas phases; it is only a question of reaching the right temperature and pressure.
- If you are interested in astronomy: Recognize that gaseous metals, including iron, are a common and important component of stars and play a key role in cosmic events.
- If you are thinking about engineering: Appreciate that the incredibly high boiling point of iron is the fundamental property that makes it a stable and reliable material for nearly all terrestrial applications.
Ultimately, knowing that even something as strong as iron can be turned into a gas reinforces the universal physical laws that govern all matter.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1,538°C (2,800°F) |
| Boiling Point | 2,862°C (5,184°F) |
| Common State on Earth | Solid |
| Where Gaseous Iron Exists | Stars, High-Energy Welding |
Need precise, high-temperature equipment for your research or industrial processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces that can handle extreme conditions for materials testing and synthesis. Whether you're studying phase transitions or developing new alloys, our reliable solutions help you achieve accurate and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's high-temperature needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- How can the temperature rise of a furnace be reduced if it is too high? Fix Airflow Issues for Safe & Efficient Heating
- Which method of heat transfer can work through vacuum? Unlock the Power of Thermal Radiation
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials



















