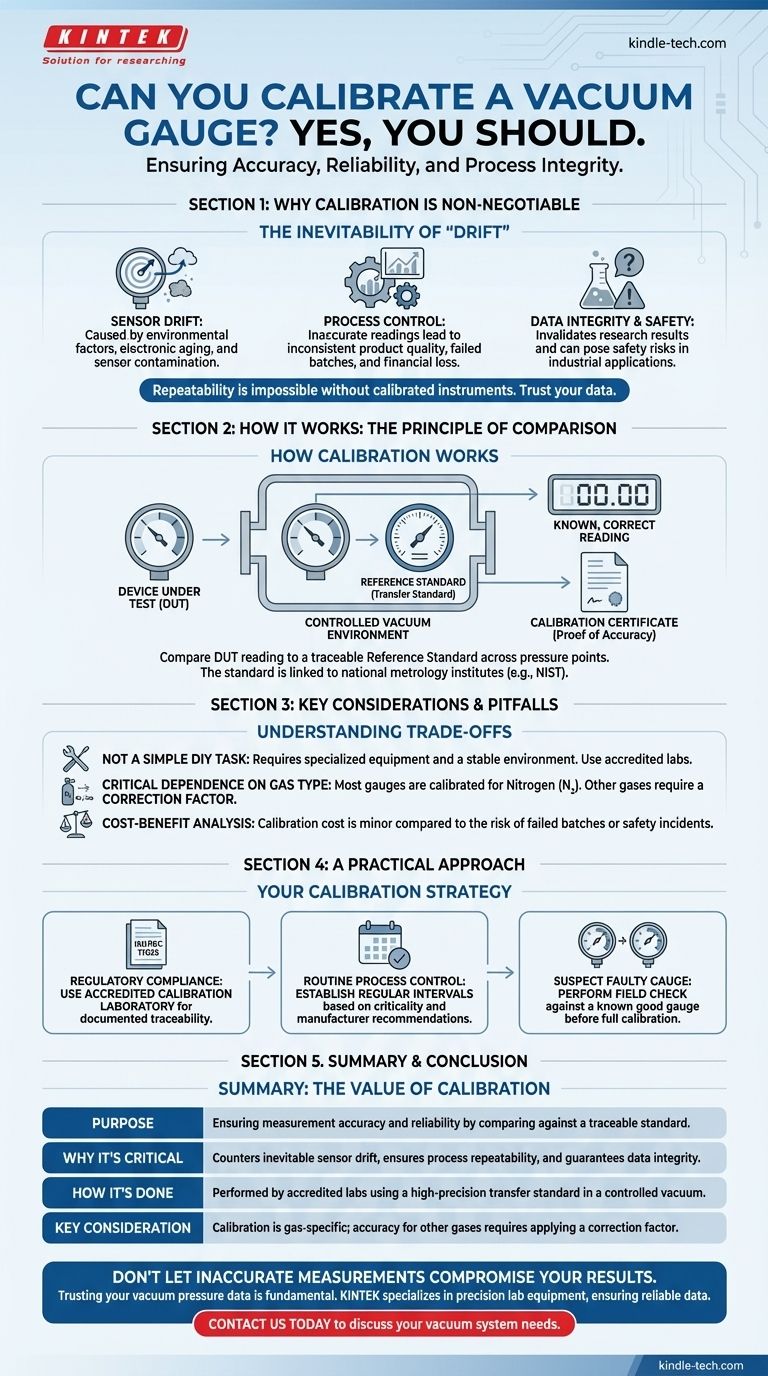
Yes, you can and absolutely should calibrate a vacuum gauge. It is a fundamental process required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your measurements. Over time, all gauges experience "drift" due to environmental factors, electronic aging, and sensor contamination, making regular calibration essential for any application where pressure values are critical.
The core principle of calibration is straightforward: you compare the reading of your gauge against a reference standard—a separate, more accurate instrument whose own calibration is traceable to a national metrology institute. This process verifies your gauge's accuracy and provides the data needed for any necessary adjustments.

Why Calibration is Non-Negotiable
A vacuum gauge is not a static device. Its accuracy degrades over its service life. Understanding why this happens reveals why calibration is a mandatory part of professional vacuum practice, not an optional one.
The Inevitability of "Drift"
Drift is the gradual loss of accuracy in an instrument. In vacuum gauges, it's caused by several factors, including the contamination of the sensor by process gases or oil vapors, the aging of electronic components, and physical wear on the sensor itself (like filament degradation in a hot cathode gauge).
This drift means a gauge that was accurate a year ago may now provide readings that are significantly off, leading to incorrect assumptions about your vacuum system's performance.
The Impact on Process Control
For manufacturing processes like physical vapor deposition (PVD), freeze-drying, or semiconductor fabrication, the vacuum level is a critical process parameter. An uncalibrated gauge can lead to inconsistent product quality, failed batches, and significant financial loss.
Repeatability is impossible without calibrated instruments. If you cannot trust your measurements, you cannot guarantee your process outcome.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Safety
In a research environment, inaccurate pressure readings can invalidate experimental results, wasting time and resources. In some industrial applications, operating outside of a specific pressure range can even pose safety risks. Calibration provides the documented proof that your measurements are reliable and your system is operating as intended.
How Vacuum Gauge Calibration Works
While the concept is simple, the execution requires specialized equipment and a controlled environment. It is rarely a simple do-it-yourself task.
The Principle of Comparison
At its heart, calibration involves placing the gauge being tested (the Device Under Test, or DUT) and a reference standard in the same vacuum environment. You then compare the readings from the DUT to the known, correct readings from the reference standard across a range of pressure points.
The Role of a Transfer Standard
The reference gauge is known as a transfer standard. This is a high-precision instrument (like a capacitance diaphragm gauge) with exceptionally low drift and high accuracy. Crucially, this transfer standard must have its own traceable calibration, linking it in an unbroken chain back to a primary national standard, such as those maintained by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology).
The Calibration Certificate
A professional calibration service provides a certificate of calibration. This document is your proof of accuracy. It details the "as found" and "as left" readings, the uncertainty of the measurements, the transfer standards used, and the date the calibration was performed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While essential, calibration involves practical considerations and potential sources of error that you must manage.
This Is Not a Simple DIY Task
Accurate calibration requires a stable high-vacuum chamber, precision gas inlet systems, and an expensive, properly maintained transfer standard. For this reason, most organizations send their gauges to an accredited calibration laboratory that has the necessary equipment and expertise.
Critical Dependence on Gas Type
Many common gauges (such as Pirani or thermocouple gauges) are gas-sensitive; their output depends on the thermal conductivity of the gas in the system. They are typically calibrated for nitrogen (N₂).
If you use the gauge to measure a different gas, like argon (Ar) or helium (He), the reading will be inaccurate unless you apply the correct gas correction factor. A calibration must always specify the gas used.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
Sending a gauge for professional calibration involves cost and downtime. However, this cost is almost always minor compared to the potential cost of a failed production batch, a compromised research project, or a safety incident caused by relying on inaccurate data.
A Practical Approach to Gauge Calibration
Your strategy for calibration should align with your specific goals and requirements.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance or traceable research: You must use an ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibration laboratory. There is no substitute for the documented traceability this provides.
- If your primary focus is routine process control: Establish a regular calibration interval (e.g., annually) based on the manufacturer's recommendation and how critical the measurement is to your process quality.
- If you suspect a single gauge is faulty: Before incurring the cost of calibration, perform a simple field check by comparing its reading to a new or recently calibrated gauge under the same vacuum conditions. This can help isolate a truly defective unit.
Ultimately, regular calibration is what transforms a simple pressure indicator into a trusted instrument for scientific and industrial certainty.
Summary Table:
| Calibration Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures measurement accuracy and reliability by comparing against a traceable standard. |
| Why It's Critical | Counters inevitable sensor drift, ensures process repeatability, and guarantees data integrity. |
| How It's Done | Performed by accredited labs using a high-precision transfer standard in a controlled vacuum. |
| Key Consideration | Calibration is gas-specific; accuracy for other gases requires applying a correction factor. |
Don't let inaccurate measurements compromise your results.
Trusting your vacuum pressure data is fundamental to successful research and consistent process control. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of laboratories. Our expertise ensures your instruments provide the reliable data you depend on.
Contact us today to discuss your vacuum system needs and ensure your measurements are always accurate.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Can vacuum tubes be repaired? The Definitive Guide to Lifespan and Replacement
- What instrument is used to measure vacuum? Selecting the Right Gauge for Your Pressure Range
- What are the units for vacuum pressure? Torr, mbar, and Pascal Explained
- Which material should not be used inside vacuum chamber? Avoid Outgassing and Contamination
- What is the importance of leakage in a vacuum system? Prevent Contamination and Process Failure



















