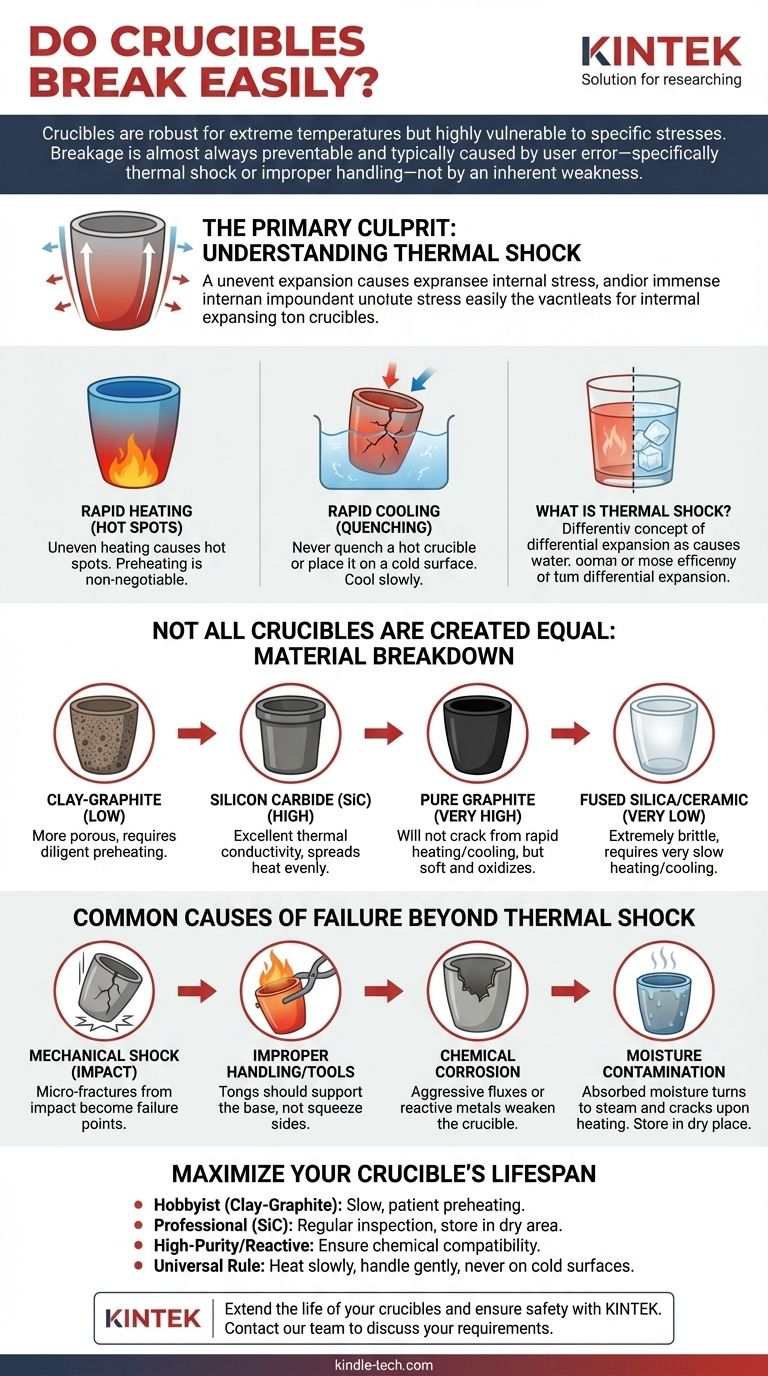
Crucibles are not designed to break easily, but their durability is entirely dependent on their material and how they are handled. While robust enough to withstand extreme temperatures far beyond what would destroy ordinary materials, they are highly vulnerable to specific types of stress, particularly sudden temperature changes known as thermal shock.
The question isn't whether a crucible is fragile like glass, but rather understanding what specific actions cause it to fail. Breakage is almost always preventable and is typically caused by user error—specifically thermal shock or improper handling—not by an inherent weakness in the crucible itself.
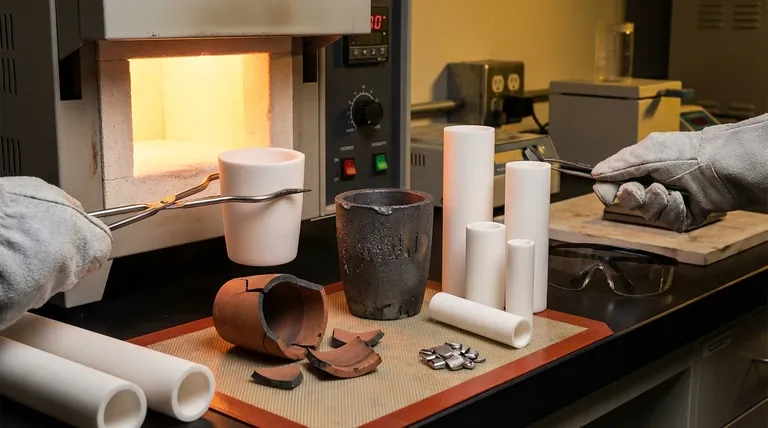

The Primary Culprit: Understanding Thermal Shock
The single greatest threat to a crucible's integrity is thermal shock. This phenomenon occurs when one part of the crucible expands or contracts faster than another, creating immense internal stress that results in cracking.
What is Thermal Shock?
Think of pouring boiling water into a thick, cold glass. The inside of the glass expands rapidly while the outside remains cold and contracted. The stress between these two layers can easily cause the glass to shatter. Crucibles experience this same stress, but at a much more extreme level.
How Heating Causes Cracks
When heat is applied too quickly or unevenly, "hot spots" develop. This is why preheating a crucible is non-negotiable. A slow, gentle, and empty first heating cycle (seasoning) removes any residual moisture and a gradual preheating before every use ensures the entire crucible comes up to temperature uniformly, preventing stress fractures.
The Danger of Rapid Cooling
The risk of thermal shock is just as high during cooling. Never quench a hot crucible in water or place it on a cold, damp, or thermally conductive surface like concrete or steel. This will almost certainly cause it to crack. It must be allowed to cool down slowly in the air or within the residual heat of the furnace.
Not All Crucibles Are Created Equal: A Material Breakdown
The type of crucible you use has the largest impact on its resistance to both thermal and mechanical shock.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are common for hobbyists and small-scale operations due to their lower cost. While effective, they are more porous and generally more susceptible to thermal shock if not handled with absolute care. They require diligent preheating.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Considered a significant upgrade, silicon carbide crucibles offer superior strength and excellent thermal conductivity. This high conductivity allows heat to spread through the material more quickly and evenly, making them far more resistant to the stresses of thermal shock.
Pure Graphite Crucibles
Graphite has outstanding resistance to thermal shock and will not crack from rapid heating or cooling. However, it is mechanically softer, can be scratched easily, and will oxidize (burn away) if held at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen for too long.
Fused Silica & Ceramic Crucibles
These are specialty crucibles, often used for melting precious metals like platinum or for laboratory analysis. They have very poor thermal shock resistance and are extremely brittle. They require a very slow, controlled heating and cooling ramp to prevent immediate failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Causes of Failure
Beyond thermal shock, several other factors contribute to crucible breakage. Recognizing them is key to prevention.
Mechanical Shock (Impact)
While not as common a cause of failure as thermal shock, dropping a crucible can be fatal. Any impact can create micro-fractures that are invisible to the naked eye. These tiny cracks become stress points that will inevitably fail during a future heating cycle.
Improper Handling and Tools
Using tongs that don't fit properly is a frequent mistake. Tongs should support the crucible from its base, not squeeze its sides. Squeezing a hot, softened crucible can easily deform or crack it.
Chemical Corrosion
Using the wrong crucible for the material being melted can cause it to fail. Aggressive fluxes or reactive metals can chemically eat away at the crucible's interior wall, thinning and weakening it from the inside out until it breaks.
Moisture Contamination
Storing a crucible in a damp environment is a critical error. Any moisture absorbed into the pores of the crucible will turn to steam instantly upon rapid heating, expanding violently and cracking the crucible from within. Always store crucibles in a warm, dry place.
How to Maximize Your Crucible's Lifespan
Following proper procedure is the most effective way to ensure your crucibles remain reliable and safe to use.
- If you are a hobbyist using clay-graphite: Your primary focus must be a slow, patient preheating process before every single use to avoid thermal shock.
- If you run a professional shop using silicon carbide: Emphasize regular visual inspection for small cracks or erosion and ensure all crucibles are stored in a designated dry area.
- If you work with high-purity or reactive materials: Prioritize selecting a crucible material that is chemically compatible with your charge to prevent internal degradation.
- For all users: The universal rule is to heat slowly, handle gently with proper tools, and never subject a hot crucible to a cold surface.
A crucible's lifespan is a direct reflection of the care and procedure used by its operator.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Thermal Shock Resistance | Key Handling Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Clay-Graphite | Low | Requires slow, careful preheating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High | Excellent for even heating |
| Pure Graphite | Very High | Soft, can oxidize in air |
| Fused Silica/Ceramic | Very Low | Requires extremely slow heating/cooling |
Extend the life of your crucibles and ensure the safety of your operations. The right crucible, handled correctly, is fundamental to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles designed for specific applications and materials. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your needs and provide guidance on best practices for handling and maintenance.
Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety



















