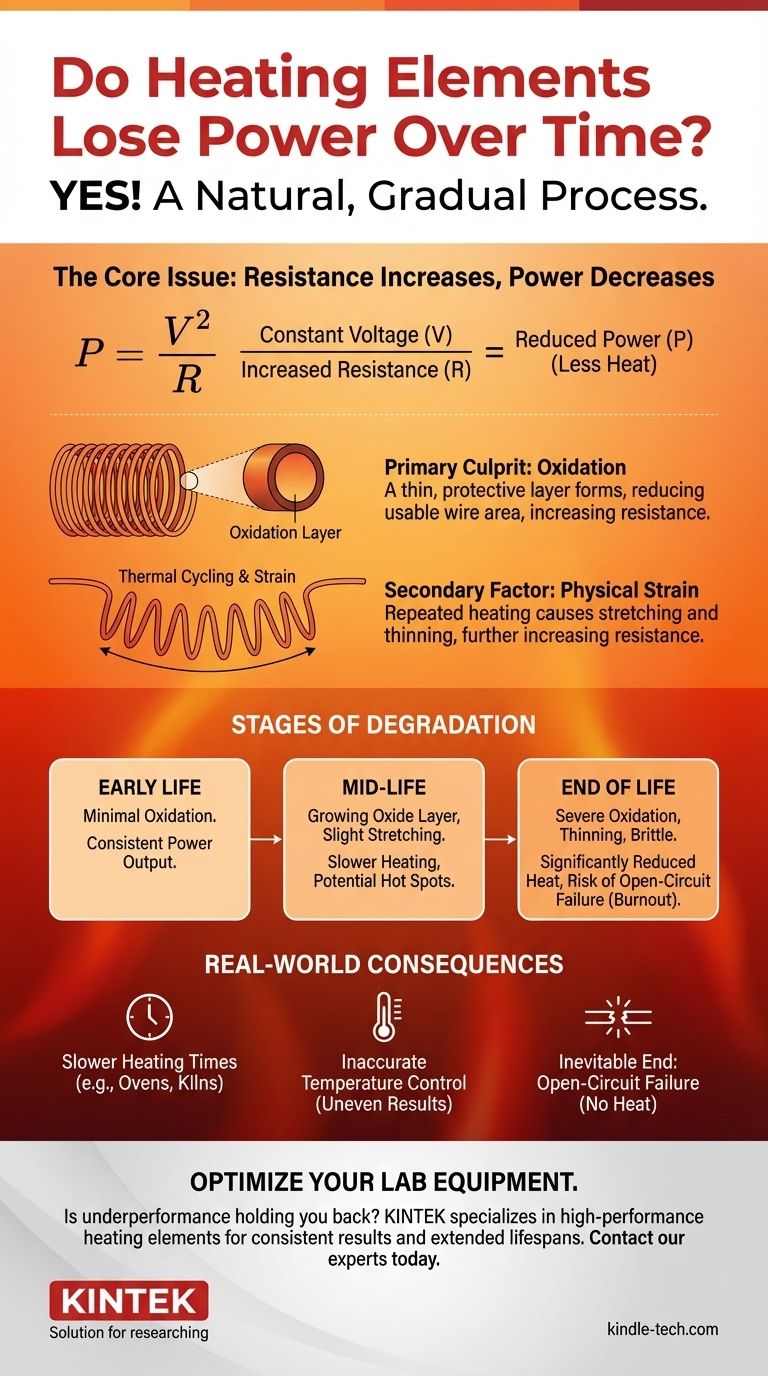
Yes, heating elements gradually lose power over their entire lifespan. This is not a defect but a natural and expected consequence of how they work. The process is slow and often goes unnoticed for years, but it is a fundamental aspect of their design and material science.
The core issue is that the element's electrical resistance increases over time. Because the voltage from your wall outlet is constant, Ohm's law dictates that an increase in resistance will inevitably lead to a decrease in power output, which you experience as less heat.
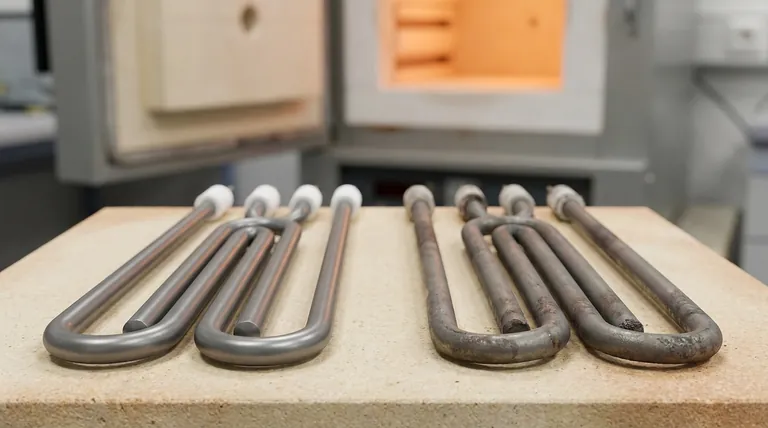

The Physics of an Aging Heating Element
To understand why power drops, we must first look at the physical changes happening to the element's wire, which is typically made from a material like Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy).
The Role of Resistance
A heating element works by converting electrical energy into heat. Its inherent electrical resistance is what makes this conversion possible. When new, this resistance is at a specific, engineered value to produce the desired amount of heat.
The Primary Culprit: Oxidation
Every time the element heats up, it reacts with oxygen in the air. This process, called oxidation, forms a thin, protective layer on the wire's surface.
While this layer protects the core metal from rapid decay, it slowly builds up over countless heating and cooling cycles. This effectively reduces the usable cross-sectional area of the metal wire, forcing the electrical current through a narrower path.
The Secondary Factor: Physical Strain
The reference to "elongation of the loops" points to a mechanical process. Extreme temperature changes cause the element to expand when hot and contract when cool.
Over time, this thermal cycling, combined with gravity, can cause the coiled wire to stretch, sag, or "creep." This stretching also thins the wire, further contributing to the problem.
How This Reduces Power Output
A thinner, more constricted wire has a higher electrical resistance. The relationship between power, voltage, and resistance is defined by the formula: Power = Voltage² / Resistance.
Since the voltage supplied by your electrical system is constant (e.g., 120V or 240V), if the Resistance (R) on the bottom of the equation goes up, the resulting Power (P) must go down. This directly translates to less heat production.
Understanding the Consequences of Degradation
This slow decline in power isn't just an academic concept; it has clear, real-world effects on any appliance that uses a resistive heating element.
Slower Heating Times
This is the most common symptom. An oven that used to preheat in 10 minutes might now take 15. A kiln may struggle to reach its target temperature, or a water heater may take longer to recover after use.
Inaccurate Temperature Control
As the element ages, it may not degrade uniformly. Some spots may oxidize or stretch more than others, leading to hot spots and cold spots. This can result in uneven cooking in an oven or inconsistent results in a kiln.
The Inevitable End: Open-Circuit Failure
Eventually, a spot on the wire becomes so thin and brittle from oxidation that it simply breaks. This creates an open circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity entirely.
At this point, the element is "burned out" and produces no heat whatsoever. This is the "ultimate failure" that marks the end of the element's normal life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Recognizing that heating elements are consumable parts allows you to plan for their eventual failure instead of being surprised by it.
- If your primary focus is diagnosing a slow appliance: A significantly longer heat-up time is a classic symptom of an aging element nearing the end of its life. Visually inspect it for sagging, bulging, cracks, or a dull, chalky appearance instead of a metallic one.
- If your primary focus is maintaining critical equipment (like a kiln): Proactively replace elements based on a maintenance schedule (e.g., usage hours) rather than waiting for an in-process failure that could ruin your work.
- If your primary focus is repairing an appliance: Replacing the heating element is often a straightforward and cost-effective repair that can restore the appliance to its original performance.
Understanding this degradation process transforms a frustrating failure into a predictable maintenance event.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Primary Cause | Effect on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Early Life | Minimal oxidation | Consistent power output |
| Mid-Life | Growing oxide layer, slight stretching | Slower heating times, potential hot spots |
| End of Life | Severe oxidation, wire thinning | Significantly reduced heat, risk of burnout |
Is your lab equipment underperforming due to aging heating elements? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including durable heating elements designed for consistent results. Our experts can help you select the right components to maintain precise temperature control and extend your equipment's lifespan. Contact us today to optimize your laboratory's heating systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance









