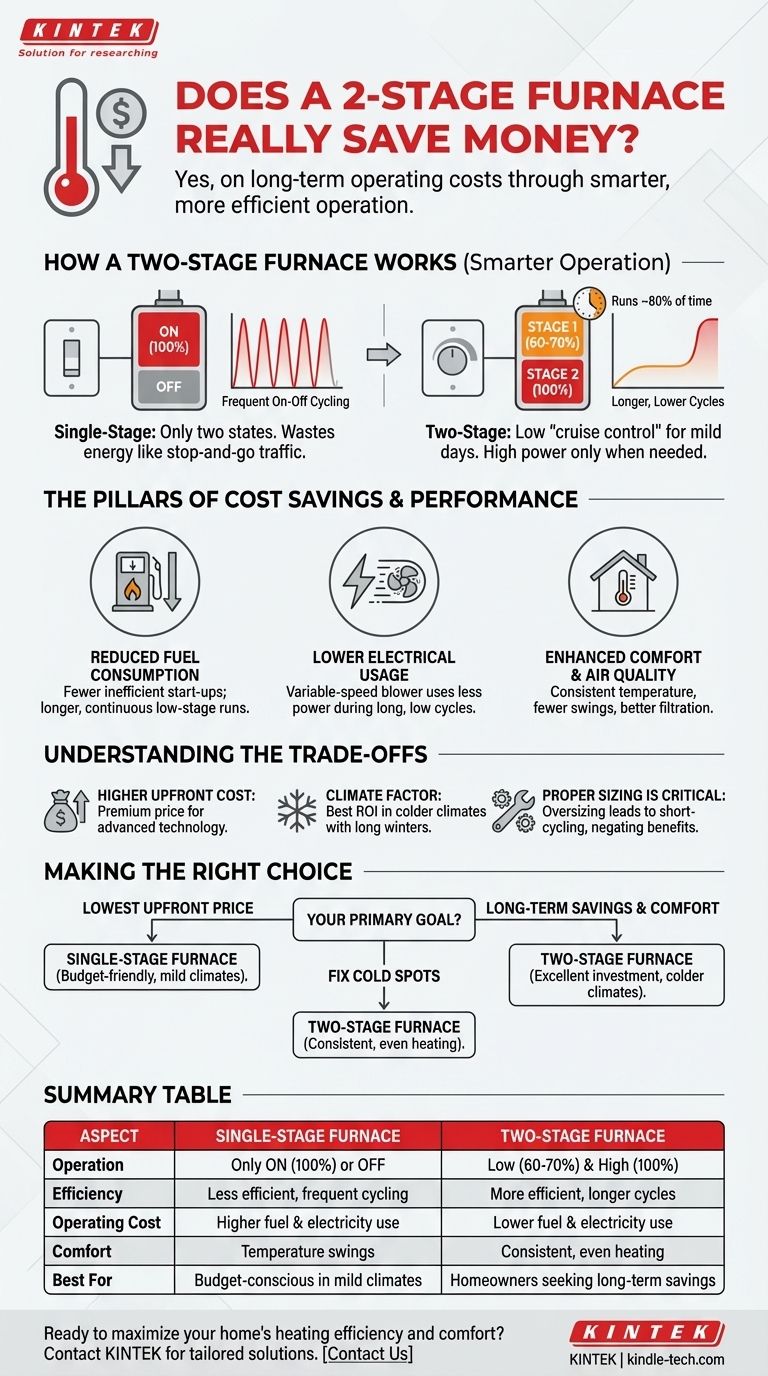
Yes, a two-stage furnace saves money on operating costs, but whether it's a worthwhile investment depends on several factors. Its primary financial benefit comes from reducing fuel and electricity consumption by running at a lower, more efficient capacity for most of the time, which also leads to less wear and tear on the system.
The core principle of a two-stage furnace is not about being more powerful, but about being smarter. By operating longer at a lower setting, it avoids the energy waste associated with the frequent on-and-off cycling of a traditional single-stage unit, much like a car getting better gas mileage on the highway than in stop-and-go city traffic.

How a Two-Stage Furnace Actually Works
To understand the savings, you first need to understand the mechanism. A standard, single-stage furnace has only two states: off and on at 100% capacity. A two-stage furnace introduces an intermediate step.
Stage One: The Low-Burn "Cruise Control"
The first stage typically runs at about 60-70% of the furnace's total heating capacity. This is the mode your furnace will use for the vast majority of the time, estimated at around 80% of its total run time.
This low-fire setting is designed to gently maintain the desired temperature in your home on mild to moderately cold days.
Stage Two: The High-Burn "Full Power"
The second stage kicks in only when necessary, delivering 100% of the furnace's heating capacity. This is reserved for the coldest days of the year or for when the thermostat is turned up significantly, requiring a rapid increase in temperature.
The Pillars of Cost Savings and Performance
The financial and operational benefits stem directly from the furnace's ability to modulate its output.
Reduced Fuel Consumption
A furnace is least efficient during the first few minutes of a heating cycle. A single-stage unit that frequently starts and stops wastes significant fuel in this warm-up phase.
By running for longer, continuous periods on its lower stage, a two-stage furnace minimizes these inefficient start-up cycles, leading to more effective use of fuel over the course of a season.
Lower Electrical Usage
Many two-stage furnaces are paired with a variable-speed blower motor. Instead of running at full blast all the time, this motor adjusts its speed to match the heating stage.
Running the fan at a lower speed during the long first-stage cycles consumes significantly less electricity than a standard, fixed-speed motor.
Enhanced Comfort and Air Quality
While not a direct financial saving, the improvement in home comfort is a major part of the value proposition. The longer, gentler heating cycles eliminate the temperature swings common with single-stage units.
This continuous air circulation also means the air passes through your furnace filter more often, improving indoor air quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A two-stage furnace is not automatically the right choice for everyone. Objectively weighing the downsides against the benefits is critical.
The Higher Upfront Cost
The primary drawback is the initial purchase price. A two-stage furnace is more complex and will cost more than a comparable single-stage model. Your savings on utility bills are meant to pay back this premium over time.
Climate Is a Critical Factor
The colder your climate and the longer your heating season, the more a two-stage furnace will run and the faster you will recoup your initial investment. In very mild climates with short winters, the fuel savings may not be substantial enough to justify the higher cost.
Proper Sizing is Non-Negotiable
A common and costly mistake is installing an oversized furnace. If a two-stage furnace is too powerful for your home, it will heat the space too quickly even on its low setting. This forces it to short-cycle, just like a single-stage unit, completely negating its efficiency benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide, align the technology with your primary objective for a new furnace.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible purchase price: A correctly sized single-stage furnace remains the most budget-friendly option upfront.
- If your primary focus is long-term operating savings and better comfort: A two-stage furnace is an excellent investment, especially if you live in a region with a moderate to long heating season.
- If your home suffers from cold spots or uneven temperatures: The continuous air movement from a two-stage unit's longer run times is highly effective at creating a more consistent temperature throughout your home.
Ultimately, choosing a two-stage furnace is an investment in long-term efficiency and superior comfort over short-term savings.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Single-Stage Furnace | Two-Stage Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Only ON (100%) or OFF | Two modes: Low (60-70%) and High (100%) |
| Efficiency | Less efficient due to frequent cycling | More efficient with longer, gentler cycles |
| Operating Cost | Higher fuel and electricity use | Lower fuel and electricity consumption |
| Comfort | Temperature swings, uneven heating | Consistent temperature, reduced cold spots |
| Best For | Budget-conscious buyers in mild climates | Homeowners in colder climates seeking long-term savings |
Ready to maximize your home's heating efficiency and comfort? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables, including precision heating systems. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution tailored to your needs, whether for research, industrial applications, or environmental testing. Contact us today to learn how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and save on long-term operating costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What are the disadvantages of rotary kiln incinerator? High Costs and Operational Complexities



















