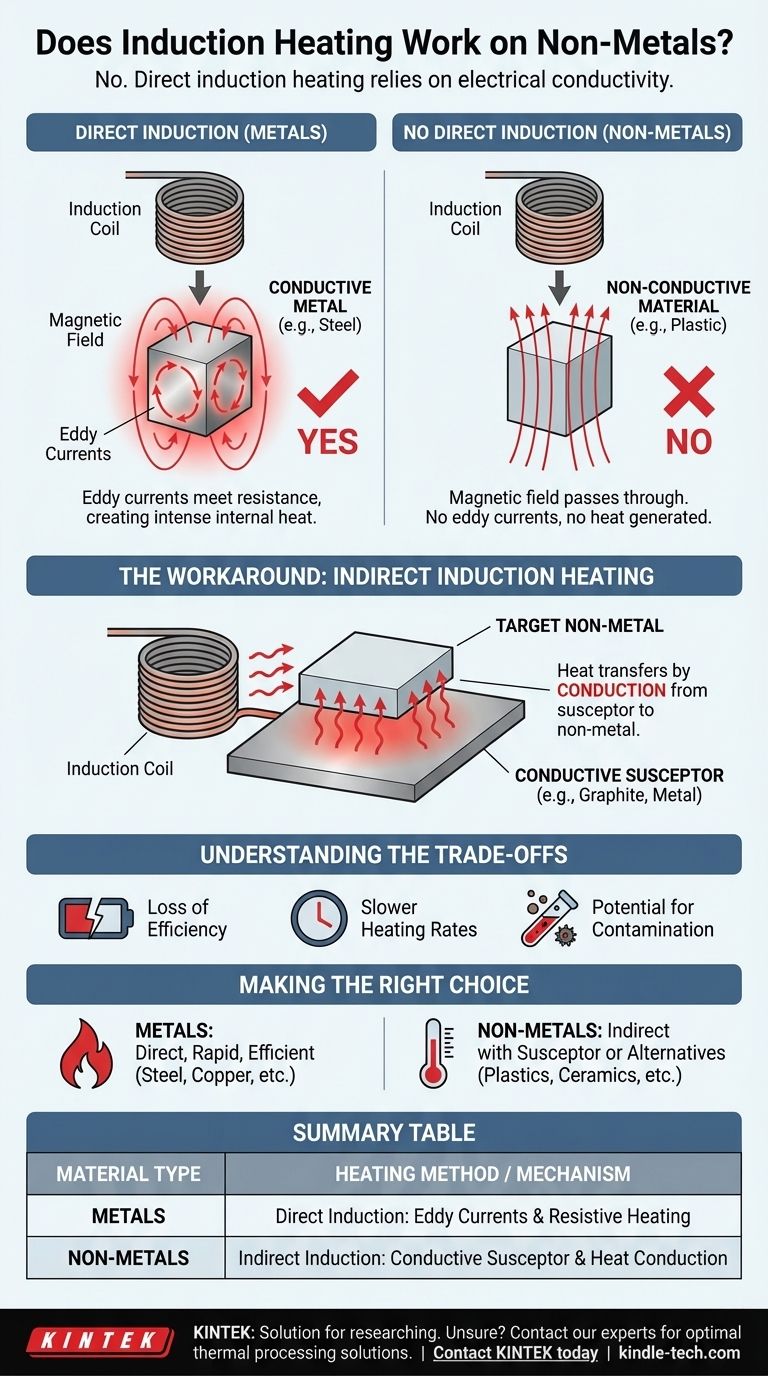
No, direct induction heating does not work on non-metals. This process relies entirely on a material's ability to conduct electricity. Because non-metals like plastics, ceramics, and glass are electrical insulators, the magnetic fields used in induction heating pass through them without generating heat.
The power of induction heating is fundamentally linked to a material's electrical conductivity. It is an exceptionally efficient method for metals, but non-metals can only be heated indirectly by using a conductive intermediary to absorb and transfer the energy.
The Core Principle: Why Conductivity is Key
To understand the limitation, we must first understand how induction heating functions. It is a non-contact process that uses electromagnetism to generate heat within a material itself.
The Role of a Magnetic Field
An induction heater uses a coil of wire through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
Generating "Eddy Currents"
When an electrically conductive material, such as a metal, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The metal has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates friction for the moving electrons, which manifests as intense and rapid heat. The higher the material's resistance, the more heat is generated.
Why Non-Metals Don't Respond
The entire process hinges on the ability to generate eddy currents, which non-metals simply cannot support.
The Lack of Free Electrons
Metals are defined by a "sea" of free-moving electrons that are not tightly bound to any single atom. These are the charge carriers that form the eddy currents. Non-metals have their electrons tightly bound, preventing electrical current from flowing.
No Path for Current
Because non-metals are electrical insulators, the magnetic field passes through them harmlessly. It cannot induce the necessary eddy currents because there are no free electrons to move.
The Result: No Heating
If no eddy currents are generated, there is no internal electrical resistance to create heat. The non-metallic material remains at its ambient temperature.
The Workaround: Indirect Induction Heating
While you cannot heat a non-metal directly, you can use the principles of induction to heat it indirectly.
The "Susceptor" Concept
This method involves placing the non-metallic material in contact with a conductive object, known as a susceptor. This susceptor is typically a metal graphite container or plate.
Heating the Go-Between
The induction coil heats the metal susceptor directly through the process described above. The non-metal, which is immune to the magnetic field, is ignored.
Transferring Heat by Conduction
As the susceptor becomes hot, it transfers its thermal energy to the non-metallic material through direct contact, a process known as conduction. A perfect real-world example is an induction stove heating a metal pot, which in turn cooks the food inside it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using an indirect heating method introduces complexities and inefficiencies that must be considered.
Loss of Efficiency
Indirect heating is inherently less efficient. Energy is lost during the heat transfer from the susceptor to the target material, meaning more power is required to achieve the desired temperature.
Slower Heating Rates
The two-step process of heating the susceptor first and then waiting for that heat to conduct into the non-metal is significantly slower than the near-instantaneous heating that occurs with direct induction.
Potential for Contamination
In high-purity applications, the susceptor itself can become a source of contamination. Careful material selection is critical to ensure the susceptor does not react with or degrade the material being heated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heating method depends entirely on the material you are working with.
- If your primary focus is rapid, precise heating of metals: Induction is one of the most direct and efficient technologies available for materials like steel, iron, copper, aluminum, and gold.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials: You must either use indirect induction with a susceptor or consider alternative technologies like convection, infrared, or resistance heating.
Understanding this fundamental requirement of conductivity is the key to successfully applying induction technology.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Direct Induction Heating Possible? | Primary Heating Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Metals (e.g., Steel, Copper) | Yes | Internal generation of eddy currents and resistive heating. |
| Non-Metals (e.g., Plastics, Ceramics, Glass) | No | Requires a conductive susceptor for indirect heating via conduction. |
Unsure which heating method is right for your materials? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. Whether you're working with conductive metals or insulating non-metals, we can guide you to the optimal lab equipment solution for precise and efficient thermal processing.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover how our specialized heating systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide



















