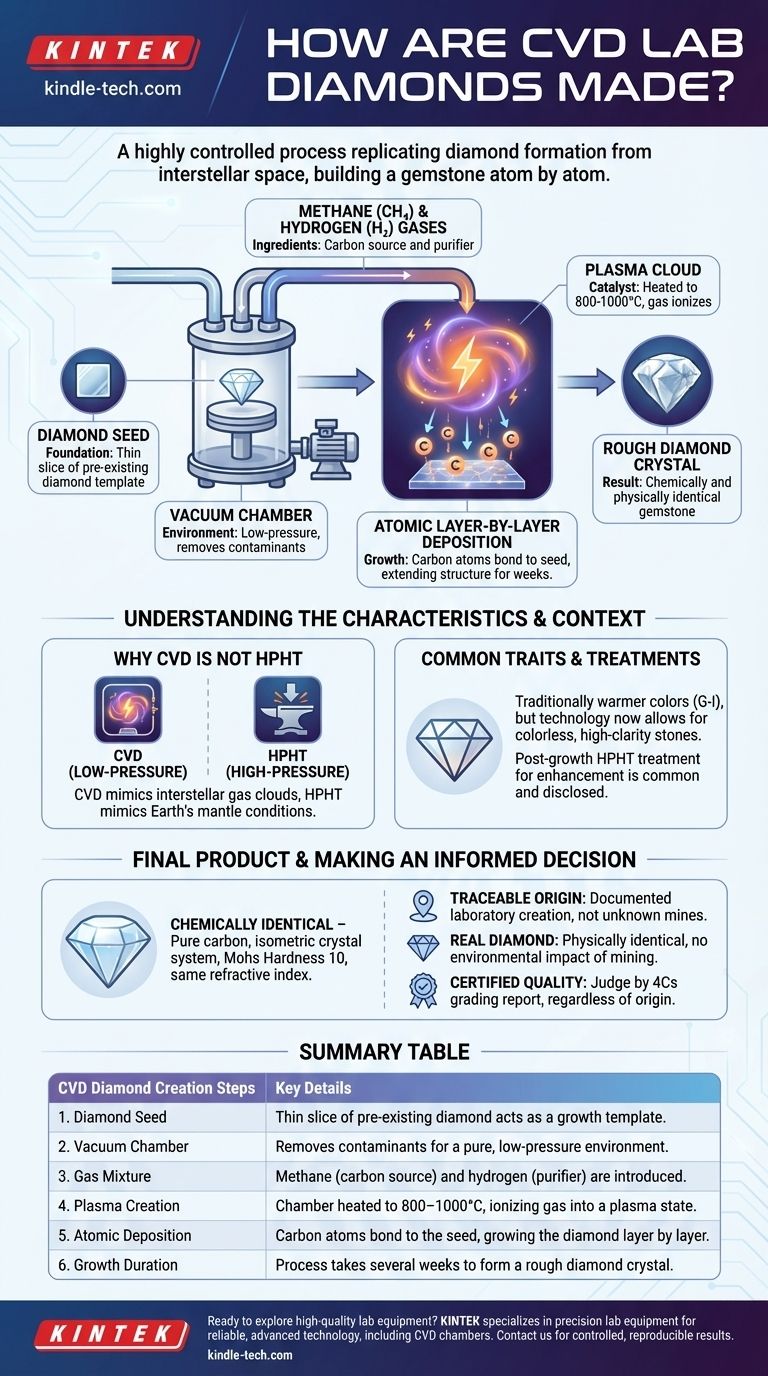
In essence, creating a diamond via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly controlled process that replicates diamond formation found in interstellar space. It begins by placing a thin diamond "seed" into a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a carbon-rich gas mixture (typically hydrogen and methane) and heated to extreme temperatures, creating a plasma that allows individual carbon atoms to rain down and bond to the seed, growing a new, larger diamond layer by atomic layer.
The core takeaway is not just the process, but the result. CVD does not create a synthetic imitation; it uses advanced technology to control the fundamental conditions of diamond growth, resulting in a gemstone that is chemically and physically identical to a mined diamond.

Deconstructing the CVD Process: From Gas to Gem
The CVD method is a feat of material science that builds a diamond atom by atom. Each stage is precisely engineered to ensure the carbon atoms arrange themselves into the strong, crystalline lattice that defines a diamond.
The Foundation: The Diamond Seed
The entire process begins with a "seed"—a minuscule, laser-cut slice of a pre-existing diamond. This seed acts as the template, or blueprint. Its existing crystal structure guides the new carbon atoms to align perfectly, ensuring the final product grows as a single diamond crystal rather than as graphite or other carbon forms.
The Environment: The Vacuum Chamber
The diamond seed is placed inside a vacuum chamber. This step is critical for removing any atmospheric contaminants, like nitrogen, that could interfere with the growth process or introduce defects into the diamond's crystal structure. The chamber allows for a low-pressure, highly controlled environment.
The Ingredients: Carbon-Rich Gases
A specific mixture of gases, primarily methane (CH₄) and hydrogen (H₂), is introduced into the chamber. Methane serves as the source for the carbon atoms that will build the new diamond. Hydrogen plays a crucial purifying role, selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon that might try to form.
The Catalyst: Creating the Plasma
The chamber is heated to extreme temperatures, typically between 800°C and 1000°C. This intense heat energizes the gases and breaks their molecular bonds, stripping electrons from the atoms. This process, called ionization, transforms the gas into a plasma—a super-heated cloud of carbon and hydrogen ions.
The Growth: Atomic Layer-by-Layer Deposition
Within the plasma, freed carbon atoms "rain down" onto the cooler diamond seed. As they land on the seed's surface, they bond to its existing crystal lattice, extending the structure one atom at a time. This methodical, layer-by-layer growth continues for several weeks, slowly building the rough diamond crystal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Characteristics
While CVD produces a real diamond, the method imparts certain tendencies and requires an understanding of its context compared to other diamond creation techniques.
Why CVD is Not HPHT
CVD should not be confused with the other primary method for creating lab diamonds, High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT). HPHT mimics the brute-force conditions deep within the Earth's mantle. In contrast, CVD is a more finessed process that mimics the low-pressure, high-energy environment of diamond formation in interstellar gas clouds.
Common Traits of CVD Diamonds
Historically, the CVD process tended to produce diamonds with slightly warmer colors (often in the G-I color range). However, as technology has advanced, manufacturers have gained greater control, making it possible to produce high-clarity, colorless CVD diamonds. The process is also flexible, allowing for growth over larger surface areas.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
It is a common and accepted practice for some CVD-grown diamonds to undergo a treatment process after they are grown, such as HPHT, to improve their color or clarity. This is simply a final step to enhance the gem's quality and is always disclosed in a professional diamond grading report.
How This Translates to a Final Product
Understanding the science of CVD is key to appreciating the nature of the final gemstone you see in a piece of jewelry.
A Chemically Identical Diamond
The output of the CVD process is not a diamond simulant like cubic zirconia. It is pure carbon crystallized in an isometric cubic system. It has the same chemical composition, refractive index, hardness (a 10 on the Mohs scale), and density as a diamond mined from the earth.
Speed and Control
The primary advantage of CVD is control. What nature does over billions of years under chaotic conditions, science can now accomplish in a matter of weeks in a controlled laboratory setting. This allows for a predictable supply chain with documented origins for every single stone.
Making an Informed Decision
Choosing a diamond is a personal decision, and understanding its origin is a modern consideration.
- If your primary focus is a traceable, controlled origin: CVD offers a transparent creation story from a documented laboratory, not an unknown mine.
- If your primary focus is owning a "real" diamond without the environmental impact of mining: CVD produces a gemstone that is physically and chemically identical to a mined diamond.
- If you are concerned about quality: Judge a CVD diamond the same way you would any diamond—by its certified grading report (the 4Cs), which details its specific qualities regardless of its origin.
Ultimately, understanding the CVD process empowers you to see the final gem not as a substitute, but as the product of remarkable scientific achievement.
Summary Table:
| CVD Diamond Creation Steps | Key Details |
|---|---|
| 1. Diamond Seed | Thin slice of pre-existing diamond acts as a growth template. |
| 2. Vacuum Chamber | Removes contaminants for a pure, low-pressure environment. |
| 3. Gas Mixture | Methane (carbon source) and hydrogen (purifier) are introduced. |
| 4. Plasma Creation | Chamber heated to 800–1000°C, ionizing gas into a plasma state. |
| 5. Atomic Deposition | Carbon atoms bond to the seed, growing the diamond layer by layer. |
| 6. Growth Duration | Process takes several weeks to form a rough diamond crystal. |
Ready to explore high-quality lab equipment for your research or production needs? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that require reliable, advanced technology—just like the CVD chambers used to create flawless diamonds. Whether you're in materials science, gemology, or chemical research, our solutions ensure controlled, reproducible results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating



















