At its core, industrial hydraulics is a method for multiplying force. Systems use a confined, incompressible fluid—typically oil—to transfer power from one point to another, enabling the precise control and movement of immense loads. This principle is fundamental to applications ranging from the massive presses that shape car bodies to the delicate flight controls of a modern aircraft.
The essential reason industry relies on hydraulics is its unmatched power density. No other technology can pack as much force and torque into such a compact and durable package, making it the default choice for heavy-duty work.

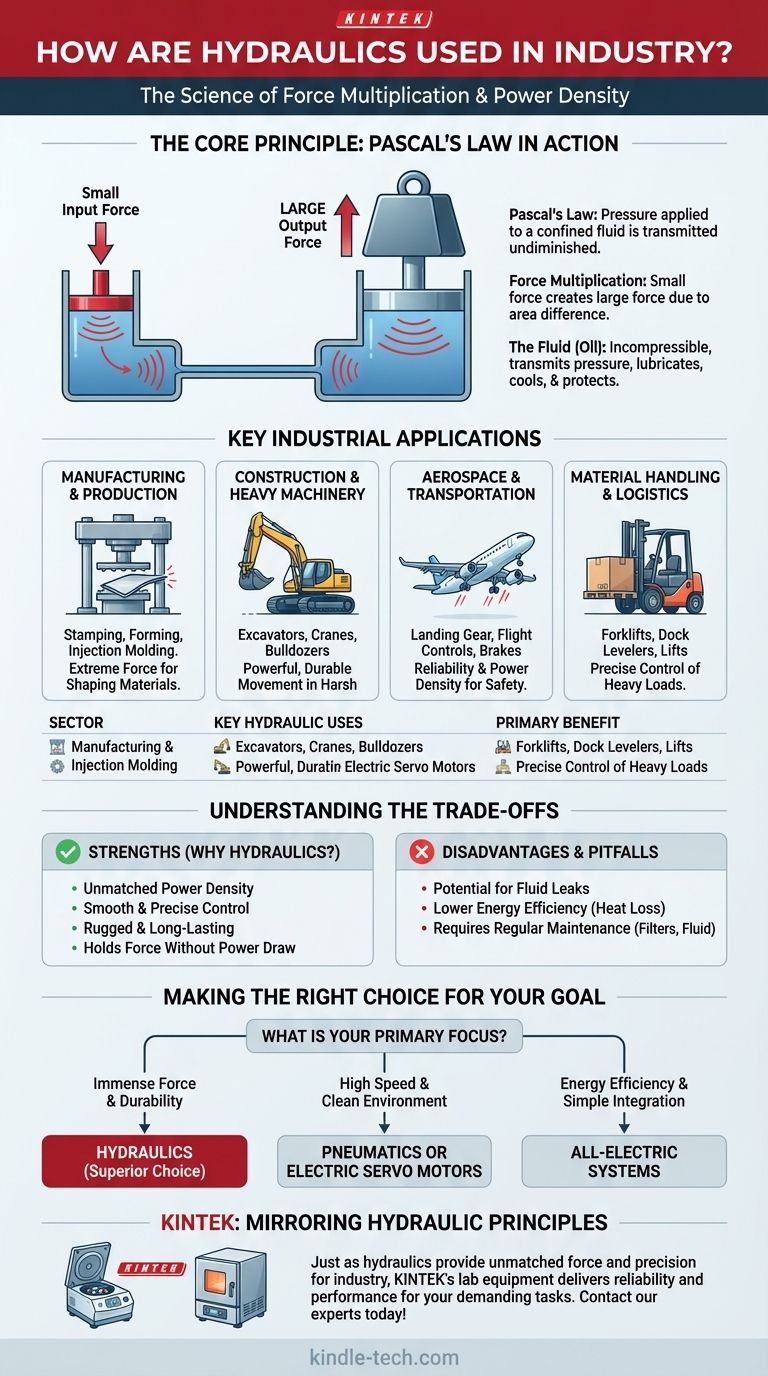
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law in Action
To truly understand industrial hydraulics, you must first grasp the physical law that governs it: Pascal's Law.
Force Multiplication Explained
Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
Imagine a sealed system with two pistons: a small input piston and a large output piston. Pushing on the small piston with a modest force creates pressure in the fluid. This same pressure acts on the larger piston, but because the larger piston has more surface area, the resulting output force is magnified significantly.
This is the essence of force multiplication, allowing a small motor or a simple lever to generate the force needed to lift a bulldozer or bend a steel beam.
The Role of Hydraulic Fluid
The fluid, usually a specially formulated oil, serves multiple purposes. It not only transmits pressure but also lubricates moving parts, dissipates heat, and protects components from corrosion.
The fluid's incompressibility is its most critical feature. Unlike air in a pneumatic system, oil does not compress under pressure, resulting in a very rigid and responsive system with minimal wasted motion.
Key Industrial Applications
The principle of force multiplication is applied across nearly every industrial sector for tasks that demand raw power and precise control.
Manufacturing and Production
Hydraulic presses are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. They are used for stamping, forming, and molding metal, plastic, and other materials with forces that can exceed thousands of tons.
Injection molding machines also rely on hydraulics to clamp molds shut with extreme force and inject molten plastic with high pressure.
Construction and Heavy Machinery
This is the most visible application of hydraulics. The arms, buckets, and blades of excavators, loaders, and bulldozers are all actuated by hydraulic cylinders.
Cranes use hydraulic systems to lift and position staggering loads, while dump trucks use a large hydraulic cylinder to raise their beds. The power and durability of hydraulics are essential in these harsh environments.
Aerospace and Transportation
In aviation, hydraulics are critical for operating landing gear, flight control surfaces like flaps and rudders, and braking systems. The reliability and power density of these systems are paramount for safety.
Automotive service lifts, car braking systems, and the power steering in many vehicles are also common hydraulic applications.
Material Handling and Logistics
Forklifts use hydraulics to lift and tilt heavy pallets with precision. Warehouse loading docks often feature hydraulic levelers, and many industrial elevators or lifts operate on hydraulic power.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hydraulics vs. Alternatives
While powerful, hydraulics is not the only solution. Its advantages and disadvantages must be weighed against pneumatic (air-powered) and all-electric systems.
The Strengths of Hydraulics
The primary advantage is power density. Hydraulic systems deliver more force for their size and weight than any alternative.
They also offer exceptionally smooth and precise control, can hold a force or torque constant without drawing much power, and are known for their ruggedness and long service life.
The Disadvantages and Common Pitfalls
Hydraulic systems can be messy. Fluid leaks are a significant concern, posing both environmental and safety hazards (e.g., slip and fall).
They can also be less energy-efficient than modern electric systems. Much of the energy input is lost as heat, often requiring coolers to be added to the system.
Finally, they require regular maintenance, including changing filters, checking hoses for wear, and monitoring fluid levels and quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct power system—hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric—depends entirely on the specific requirements of the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is immense force and durability: Hydraulics is almost always the superior choice for heavy lifting, pressing, and clamping.
- If your primary focus is high speed and a clean environment: Pneumatics or electric servo motors are often better for rapid, repetitive tasks like product assembly.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and simple integration: All-electric systems are gaining ground, especially in applications that don't require extreme force.
By understanding the fundamental trade-offs, you can leverage the unique power of hydraulics for the challenges it was designed to solve.
Summary Table:
| Application Sector | Key Hydraulic Uses | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Stamping presses, injection molding | Extreme force for shaping materials |
| Construction | Excavators, cranes, bulldozers | Powerful, durable movement in harsh conditions |
| Aerospace | Landing gear, flight controls | Reliability and power density for safety |
| Material Handling | Forklifts, dock levelers | Precise control of heavy loads |
Need robust equipment for your industrial processes? The principles of hydraulics—power density, durability, and precise control—are mirrored in the performance of KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables. Just as hydraulics provide unmatched force for industry, our solutions deliver reliability and precision for your laboratory's most demanding tasks. Let's discuss how we can support your specific needs. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance



















