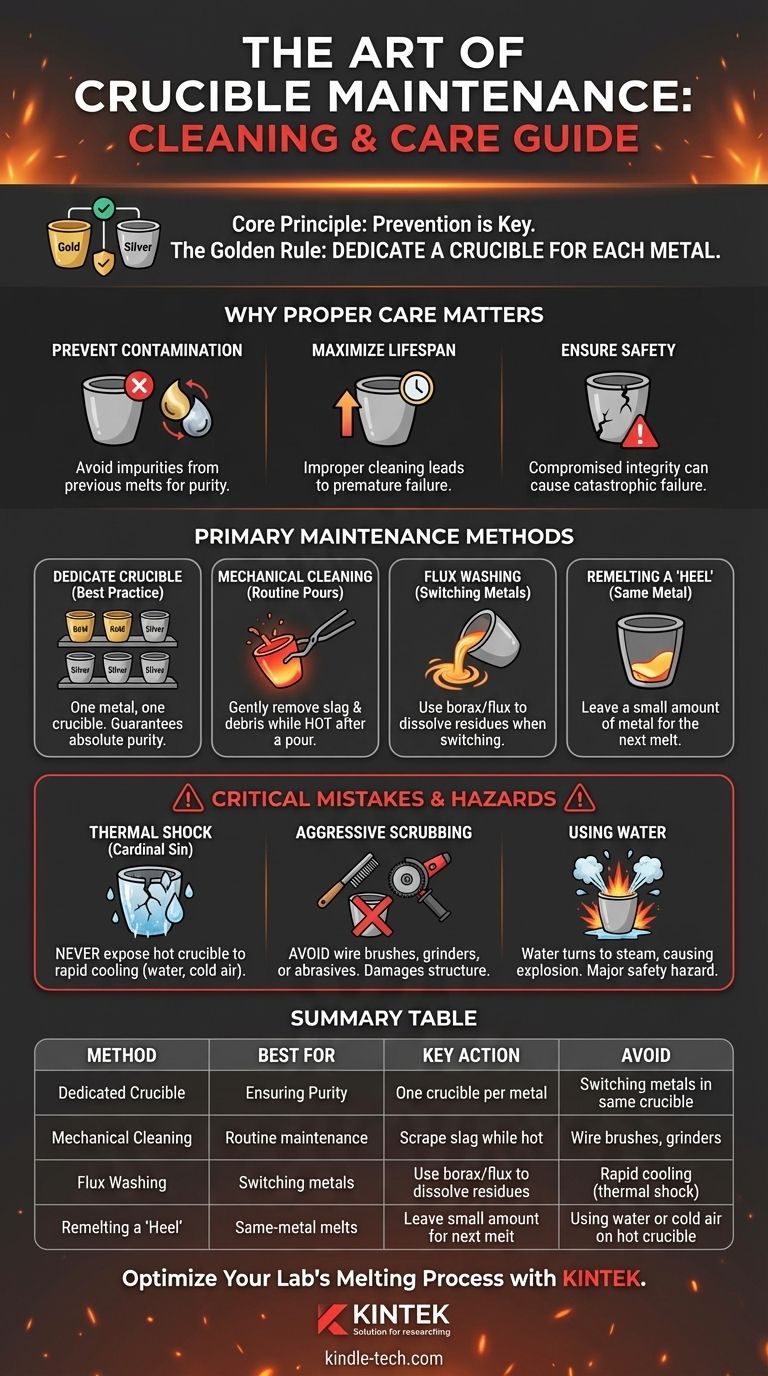
The most effective way to "clean" a melting crucible is not to scrub it, but to carefully remove slag and residual material after a pour while the crucible is still hot. The specific method depends on the crucible material (graphite, ceramic, clay) and the metal being used, but the universal goal is to avoid damaging the crucible's structure through mechanical force or thermal shock.
The core principle of professional crucible management is not cleaning, but prevention. The industry-standard practice is to dedicate a specific crucible to each metal or alloy you work with, eliminating the primary source of cross-contamination and the need for aggressive cleaning.

Why Proper Crucible Care Is Foundational
A crucible is not just a container; it is a critical piece of equipment whose integrity directly impacts the quality and safety of your work. Understanding why you clean it clarifies how to do it correctly.
Preventing Metal Contamination
Any residue left from a previous melt can act as an impurity in your next one. For example, remnants of brass (a copper-zinc alloy) can contaminate a subsequent melt of fine silver, altering its purity and working properties.
This cross-contamination is the single biggest reason to maintain crucible hygiene, especially when working with precious metals or alloys with tight specifications.
Maximizing Crucible Lifespan
Crucibles are consumables, but their lifespan is determined by their treatment. Improper cleaning is a leading cause of premature failure.
Aggressive scraping can gouge the crucible walls, creating weak points. More importantly, rapid temperature changes (thermal shock) from improper cooling or cleaning methods will cause cracks, rendering the crucible useless and dangerous.
Ensuring a Safe Melt
A crucible with compromised structural integrity, whether from a crack or a deep gouge, can fail catastrophically during a melt. A crucible failure that releases molten metal is an extremely hazardous event.
The Primary Methods for Crucible Maintenance
True cleaning is rare. What is more common is routine maintenance between melts of the same metal or a more thorough process when switching metals is unavoidable.
The Gold Standard: The 'Dedicated Crucible' Method
The safest and most professional approach is to avoid the problem entirely. By dedicating one crucible to one specific metal (e.g., one for sterling silver, one for 14k yellow gold, one for bronze), you never have to worry about cross-contamination.
Simply label your crucibles clearly and store them separately. This is the only way to guarantee absolute purity.
Mechanical Cleaning (For Routine Pours)
This is the most common form of maintenance between melts of the same metal. The goal is to remove the glassy layer of slag (impurities that float to the surface) and any loose debris.
Immediately after your pour, while the crucible is still glowing red, use long-handled tongs to gently scrape the interior with a graphite or steel rod. The slag should be brittle and pop off easily. Tap the crucible gently upside down to dislodge any loose bits.
Flux Washing (For Deeper Cleaning)
When you must switch metals, a flux wash is the most effective method. Flux, such as borax, is a chemical agent that cleans and protects metal during melting.
Heat the empty crucible until it is red hot. Add a small amount of borax or a specialized crucible cleaning flux. It will melt into a liquid glass, dissolving and bonding with many of the remaining metallic residues. Swirl the molten flux around to "wash" the interior walls, then pour it out like you would a metal melt.
Remelting a "Heel"
For some processes, it is common to leave a small amount of metal (a "heel") in the bottom of the crucible after a pour.
When you perform the next melt of the same metal, this heel melts first and incorporates any minor surface oxidation or debris into the larger melt, where it can be skimmed off as slag.
Critical Mistakes and Trade-offs
Understanding what not to do is as important as knowing what to do. Most crucible damage is caused by user error during the cleaning phase.
The Cardinal Sin: Thermal Shock
Never expose a hot crucible to water, cold air, or any rapid cooling. The extreme temperature gradient will crack graphite and shatter ceramic almost instantly.
Always allow your crucible to cool down slowly, ideally inside the kiln or furnace, or on a heat-resistant surface away from drafts.
The Myth of 'Scrubbing' a Crucible
Never use wire brushes, grinders, sandpaper, or other aggressive abrasives. This practice physically damages the crucible structure, creating weak spots.
For glazed ceramic or clay-graphite crucibles, this will remove the protective vitrified layer, exposing the porous material beneath and drastically shortening its life.
The Hazard of Using Water
Water should be considered an enemy of your crucible. It can be absorbed into the porous structure of graphite or clay.
If a water-logged crucible is heated, that trapped moisture will turn into steam and expand violently, causing the crucible to explode. This is a severe safety hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to crucible care should be dictated by the desired outcome of your work.
- If your primary focus is purity and professional results: Dedicate one crucible for each specific metal or alloy you use; this is the only truly reliable method.
- If you absolutely must reuse a crucible for a different metal: Perform a thorough mechanical cleaning followed by a flux wash to remove as much old residue as possible.
- If you are performing routine melts of the same metal: Rely on gentle mechanical scraping of slag after each pour and allow the crucible to cool slowly.
Proper crucible maintenance is a simple discipline that protects your investment, ensures the quality of your work, and keeps you safe.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Action | Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Crucible | Ensuring purity | Use one crucible per metal type | Switching metals in the same crucible |
| Mechanical Cleaning | Routine maintenance | Scrape slag while crucible is hot | Wire brushes, grinders |
| Flux Washing | Switching metals | Use borax to dissolve residues | Rapid cooling (thermal shock) |
| Remelting a 'Heel' | Same-metal melts | Leave a small amount of metal for next melt | Using water or cold air on hot crucible |
Ready to optimize your lab's melting process? Proper crucible care is essential for safety and purity. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable crucibles designed for specific metals and alloys. Let our experts help you choose the right tools to maximize your crucible's lifespan and ensure contamination-free results. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a PTFE crucible preferred for plasma etching? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Targeted Action
- What is the most durable crucible? Match the Right Crucible to Your Melting Application
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What is the best type of crucible? The Answer Depends on Your Application's Needs
- Is a crucible a lab equipment? A Guide to High-Temperature Containers for Labs and Foundries



















