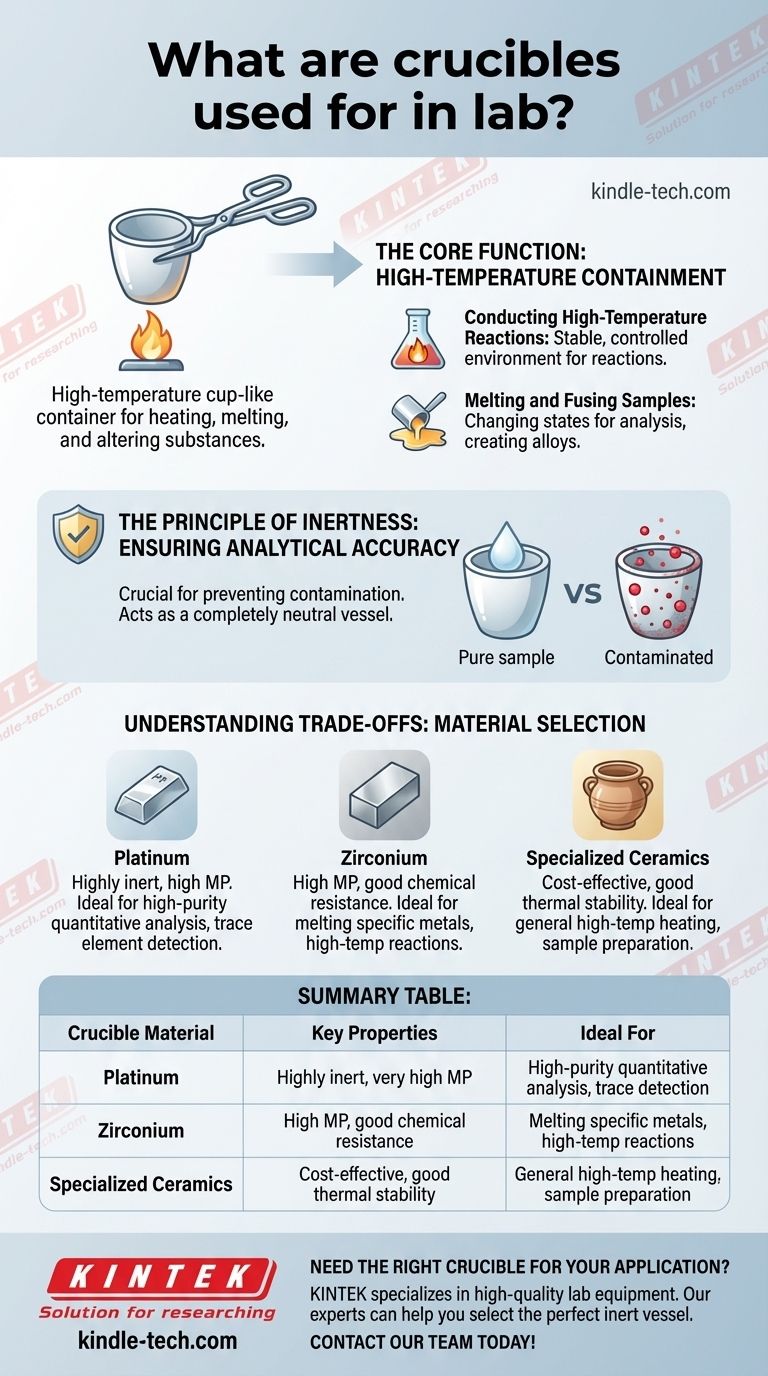
In a laboratory, a crucible is a specialized cup-like container engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures. They are primarily used for heating, melting, and chemically altering substances in processes like analytical chemistry, metallurgy, and materials science. Their fundamental purpose is to contain a sample securely while it is subjected to intense heat without the container itself reacting or breaking down.
The true value of a laboratory crucible isn't just its heat resistance, but its chemical inertness. Its job is to act as a completely neutral vessel, ensuring that the results of an experiment or analysis come purely from the sample, not from contamination from the container.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Containment
A crucible's most basic job is to hold materials at temperatures that would destroy standard glassware. This capability is foundational to several key laboratory and industrial processes.
Conducting High-Temperature Reactions
Many chemical reactions require significant thermal energy to proceed. Crucibles provide a stable, controlled environment for these high-temperature reactions, ensuring the process is contained safely and effectively.
Melting and Fusing Samples
Crucibles are essential for melting metals, creating alloys, or preparing samples for analysis by fusing them with a flux. This process changes the physical or chemical state of a material to make it suitable for further testing or use.
Why Crucibles Are Essential for Analytical Chemistry
In the context of precise scientific measurement, the role of the crucible becomes far more critical than simple containment. It is an instrument of accuracy.
The Principle of Inertness
The most important characteristic of a high-quality laboratory crucible is that it is chemically inert. This means it will not react with the substance being heated inside it.
This property is crucial for preventing contamination of the analyte—the substance being measured. Any reaction between the crucible and the sample would alter the sample's composition and invalidate the results.
Ensuring Analytical Accuracy
In fields like analytical chemistry, scientists often need to determine the exact amount of specific elements in a sample, sometimes at "trace" or "ultra-trace" levels (parts per million or billion).
At this scale, even the slightest contamination from the container can dramatically skew the final measurement. Using an inert crucible ensures that what is being measured is the sample and nothing else.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection
The choice of crucible material is a critical decision driven by the specific requirements of the experiment. There is no single crucible that is perfect for every task.
The Impact of Material Choice
Laboratory crucibles are typically made from materials like platinum, zirconium, or specialized ceramics. These materials are chosen for their high melting points and their resistance to chemical attack.
Platinum, for example, is extremely inert and has a very high melting point, making it ideal for the most sensitive analytical work, but it is also very expensive.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Using the wrong type of crucible can ruin an experiment. A material that is inert to one chemical might react strongly with another, or it may not be able to withstand the required temperature, leading to equipment failure and sample loss.
Therefore, selecting the crucible requires careful consideration of both the temperatures involved and the chemical properties of the sample being heated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Your experimental goal directly dictates the type of crucible you should use. The primary consideration is always the trade-off between performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity quantitative analysis: You must use a highly inert material like platinum to prevent sample contamination and ensure the highest possible accuracy.
- If your primary focus is melting a specific metal: You need a crucible made of a material that has a higher melting point than the metal and will not form an alloy with it.
- If your primary focus is general high-temperature heating: A less expensive ceramic crucible may be perfectly adequate, provided it can withstand the target temperature and has limited reactivity with your sample.
Ultimately, a crucible is a fundamental tool that enables the precise and reliable study of materials under extreme thermal conditions.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Platinum | Highly inert, very high melting point | High-purity quantitative analysis, trace element detection |
| Zirconium | High melting point, good chemical resistance | Melting specific metals, high-temperature reactions |
| Specialized Ceramics | Cost-effective, good thermal stability | General high-temperature heating, sample preparation |
Need the Right Crucible for Your Application?
Choosing the correct crucible is critical for the success and accuracy of your high-temperature processes. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles made from platinum, zirconium, and specialized ceramics. Our experts can help you select the perfect inert vessel to prevent sample contamination and ensure reliable results in your analytical chemistry, metallurgy, or materials science work.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your lab's precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the best type of crucible? The Answer Depends on Your Application's Needs
- Can a crucible withstand heat? Yes, with the right material and thermal properties.
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- Why is a PTFE crucible preferred for plasma etching? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Targeted Action
- What is the most durable crucible? Match the Right Crucible to Your Melting Application



















