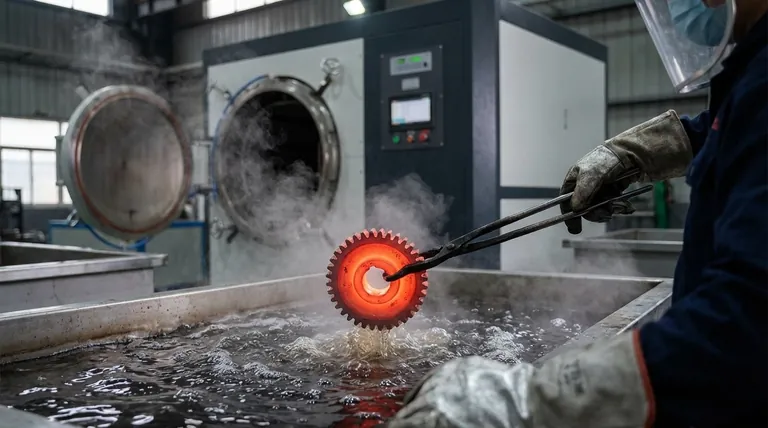
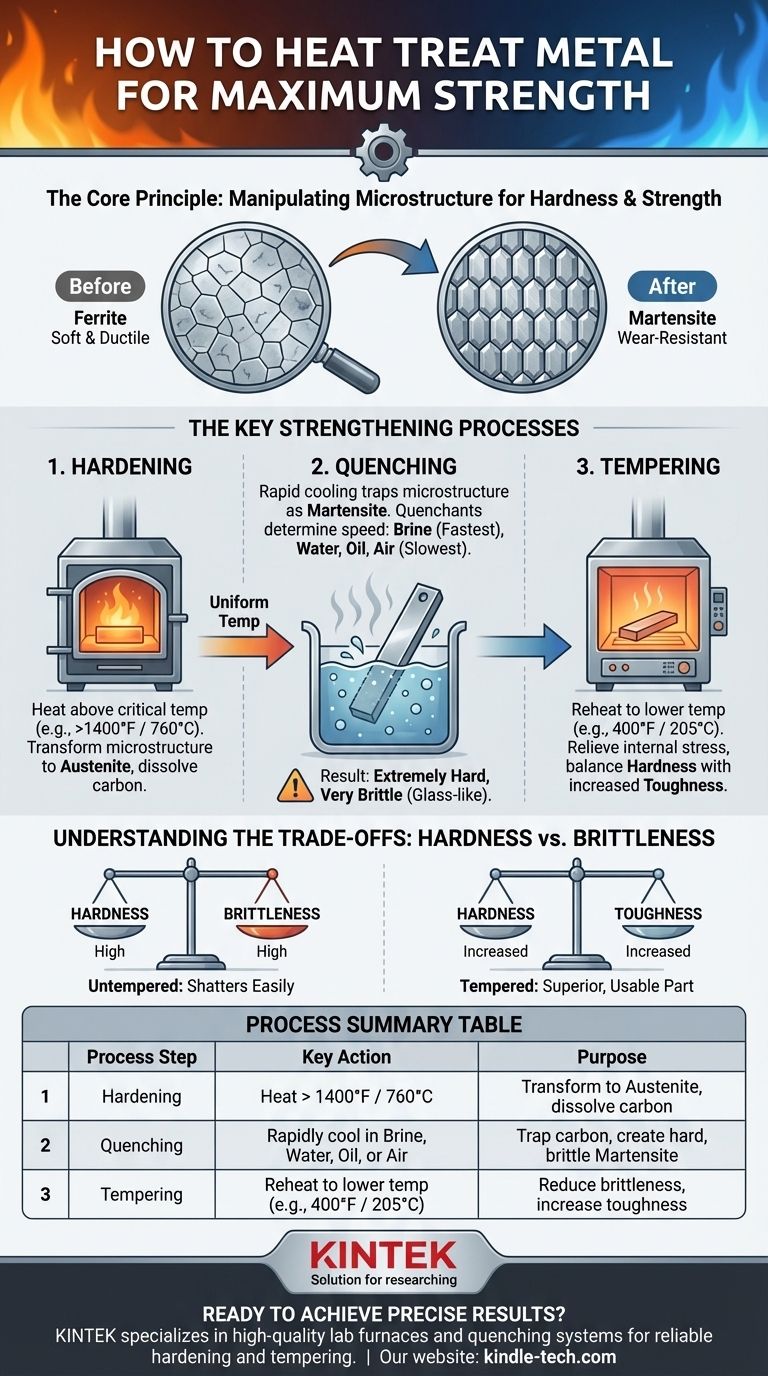
To make a metal stronger, you must heat it to a specific, critical temperature and then cool it very rapidly. This process, known as hardening and quenching, fundamentally changes the metal's internal crystal structure, locking it into a much harder, more wear-resistant state. This is followed by a lower-temperature heating called tempering to reduce the brittleness that quenching creates.
The core principle of strengthening metal through heat treatment is not just about heating and cooling; it's about precisely manipulating the metal's internal microstructure to achieve a new balance of properties, typically trading flexibility for a significant increase in hardness and strength.

The Principle: Changing the Crystal Structure
To understand how heat treatment works, you have to think of metal not as a solid block, but as a tightly packed structure of microscopic crystals. The size, shape, and arrangement of these crystals—its microstructure—determine its physical properties.
What is a Microstructure?
At room temperature, the carbon steel's crystals (called ferrite) are arranged in a relatively open, weak structure. This makes the metal ductile and easy to work with.
The Role of Heat
When you heat steel above a critical temperature (typically over 1400°F or 760°C), the crystals rearrange themselves into a new, denser structure called austenite. This new structure has the unique ability to dissolve carbon atoms from within the steel.
The Critical Role of Cooling
If you cool the steel slowly, the crystals will simply change back to their original soft state.
However, if you cool it extremely fast—a process called quenching—the carbon atoms get trapped. The crystals don't have time to revert to their soft form and are instead forced into a new, highly strained, and very hard structure called martensite. This martensitic structure is what gives hardened steel its strength and wear resistance.
The Key Strengthening Processes
The entire sequence of heating, quenching, and subsequent tempering is essential. Skipping a step results in a failed treatment.
Step 1: Hardening
This is the process of heating the metal into the austenite temperature range and holding it there long enough for the entire part to reach a uniform temperature. The specific temperature and time depend entirely on the type of metal alloy.
Step 2: Quenching
Quenching is the rapid cooling that traps the microstructure in its hardened martensite state. The speed of cooling is critical.
Different liquids, or quenchants, cool at different rates. Common quenchants include brine (fastest), water (fast), oil (slower), and air (slowest), each used for different types of steel and desired outcomes.
Step 3: Tempering
Immediately after quenching, the metal is extremely hard but also very brittle, like glass. An untempered part can shatter if dropped or struck.
Tempering is a mandatory follow-up step. It involves reheating the part to a much lower temperature (e.g., 400°F or 205°C) to relieve the internal stress from quenching. This process slightly reduces the overall hardness but dramatically increases the metal's toughness, making it useful.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Brittleness
Heat treatment is never about achieving a single property in isolation. It is always a balancing act.
The Hardness-Brittleness Spectrum
The primary trade-off in strengthening steel is between hardness and toughness. The harder you make the steel through quenching, the more brittle it becomes.
Think of a ceramic knife: it has an incredibly hard edge that stays sharp, but it will chip or shatter if you drop it. A softer butter knife will bend but not break. Hardened steel exists on this same spectrum.
Why Tempering is Non-Negotiable
Tempering allows you to dial in the exact balance you need. Higher tempering temperatures result in less hardness but more toughness. Lower tempering temperatures retain more hardness while adding just enough toughness to prevent shattering.
For this reason, a properly hardened and tempered part is almost always superior to a part that has only been quenched.
Clarifying Other Heat Treatments
The terms used in heat treating can be confusing. While hardening strengthens metal, other common processes are designed to soften it for different reasons.
What About Annealing?
Annealing is the opposite of hardening. It involves heating metal and then cooling it very slowly. This process creates a very soft, ductile, and stress-free state, which is ideal for making the metal easier to machine or form.
What About Stress Relieving?
This is a lower-temperature process used to remove internal stresses caused by manufacturing processes like welding or heavy machining. It doesn't significantly change the metal's hardness but prevents warping or cracking over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the final application of the metal part.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance (e.g., a cutting tool or file): You need to perform a full hardening and quenching cycle, followed by a very low-temperature temper to relieve only the most extreme brittleness.
- If your primary focus is balanced strength and toughness (e.g., a hammer or axe head): You will use a full hardening and quenching cycle, followed by a higher-temperature temper to trade some hardness for significant impact resistance.
- If your primary focus is preparing metal for machining or shaping: You will use annealing to make the metal as soft and stress-free as possible before any hardening is attempted.
By understanding these fundamental processes, you can control the internal structure of metal to achieve the precise properties your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Heat above critical temperature (e.g., >1400°F / 760°C) | Transform microstructure to austenite to dissolve carbon. |
| Quenching | Rapidly cool in brine, water, oil, or air | Trap carbon, creating a hard, brittle martensite structure. |
| Tempering | Reheat to a lower temperature (e.g., 400°F / 205°C) | Reduce brittleness by increasing toughness for a usable part. |
Ready to achieve precise heat treatment results in your lab? The right equipment is critical for controlling temperature and quenching rates. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and quenching systems designed for reliable hardening and tempering processes. Whether you're developing cutting tools or components requiring balanced strength and toughness, our solutions ensure repeatable outcomes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment equipment for your specific metalworking needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a hot air oven for a chemistry lab? Master Dry Heat Sterilization & Drying
- Is pyrolysis good or bad? A Balanced Look at the Waste-to-Energy Solution
- What is a sputtering machine? Achieve High-Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between THC extract and distillate? A Guide to Full-Spectrum vs. Pure Potency
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven assist in processing raw COF products? Master Material Activation
- What property does KBr have that makes it suitable for the infrared region? Unlock Clear IR Spectroscopy Analysis
- What is the difference between traditional sintering and selective laser sintering? Choose the Right Manufacturing Path
- Does heat treatment increase strength? Unlock Maximum Metal Performance for Your Components



















