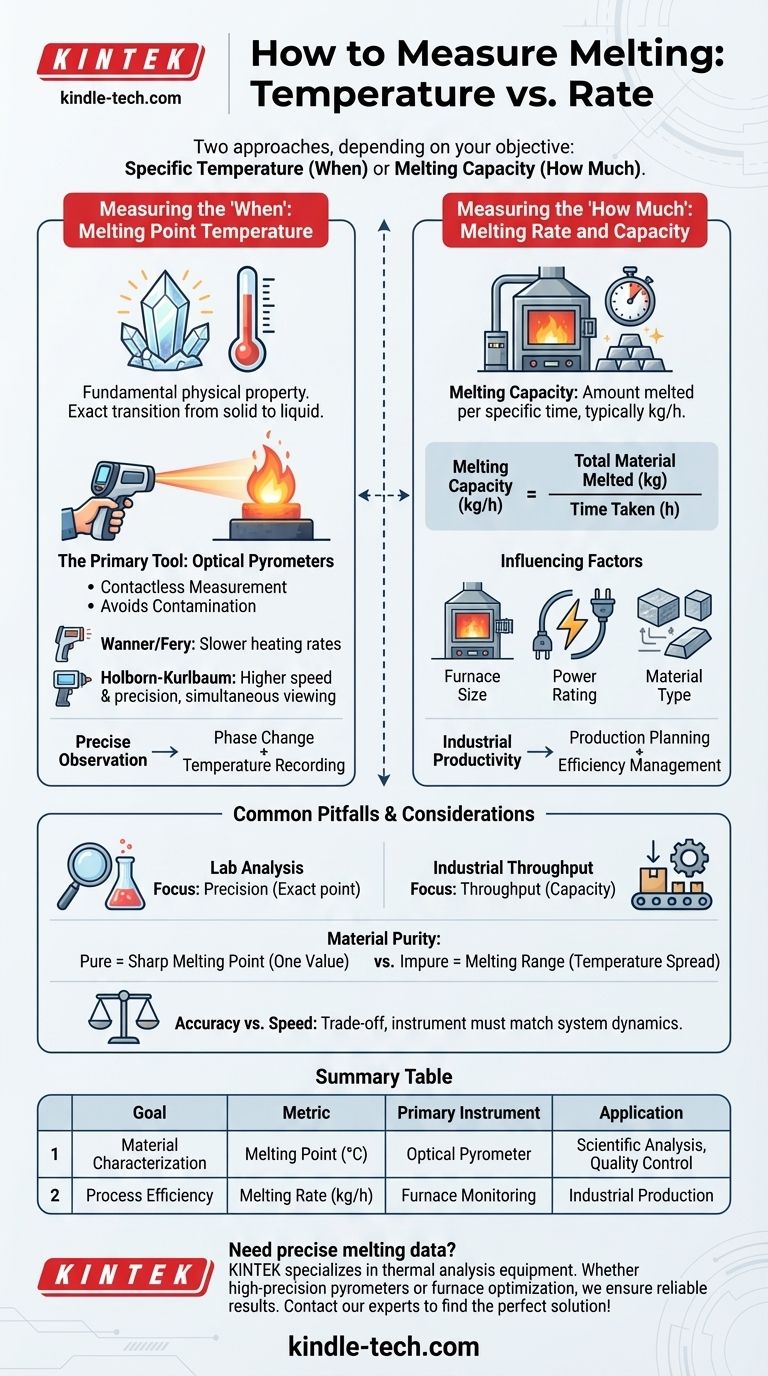
To measure melting, you must first decide which property you are measuring: the specific temperature at which a substance melts, or the rate at which a volume of material can be melted. For temperature, specialized optical instruments called pyrometers are used to ensure accuracy. For rate, the focus is on melting capacity, typically measured in kilograms per hour, which is critical for industrial processes.
The method for measuring melting depends entirely on your objective. For scientific analysis and material characterization, you measure the melting point temperature. For industrial production and efficiency, you measure the melting rate or capacity.

Measuring the 'When': Melting Point Temperature
The melting point is a fundamental physical property of a crystalline solid. It is the exact temperature at which the material transitions from a solid to a liquid state under a given pressure.
The Primary Tool: Pyrometers
For measuring high melting point temperatures with the required accuracy, optical or radiation pyrometers are the recommended instruments.
These devices work by measuring the thermal radiation emitted by a hot object from a distance, making them ideal for environments where contact thermometers are impractical or would be destroyed.
Why Optical Pyrometers are Effective
Contactless measurement is crucial for melting processes. It avoids contaminating the material and prevents the measuring device from being damaged by extreme heat, ensuring a more accurate reading of the substance itself.
The instrument can be focused on the material, allowing for precise observation of the phase change while simultaneously recording the temperature.
Key Instruments for the Task
Different pyrometers are suited for different conditions. The Wanner or Fery optical pyrometers are effective for processes with slower heating rates.
For applications requiring more speed and precision, the Holborn-Kurlbaum type of Morse optical pyrometer is superior. It allows the observer to view the specimen and measure its temperature at the same time, making it highly efficient.
Measuring the 'How Much': Melting Rate and Capacity
In an industrial context, the focus shifts from a material's intrinsic properties to the performance of the equipment processing it. Here, the key metric is melting capacity.
Defining Melting Capacity
The melting capacity of a furnace is the amount of material it can melt within a specific time frame. This is almost always measured in kilograms per hour (kg/h).
This metric is a direct indicator of a furnace's productivity and is essential for planning and managing production schedules effectively.
Factors That Influence Melting Rate
A furnace's melting capacity is not a single, fixed number. It depends heavily on several factors.
Key variables include the furnace’s size, its power rating, and the specific type of material being melted, as different materials require different amounts of energy to change state.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Choosing the right measurement is only the first step. Understanding the context and potential sources of error is critical for obtaining meaningful data.
Lab Analysis vs. Industrial Throughput
The goals of a laboratory and a production floor are fundamentally different, and so are their measurements.
Lab analysis prioritizes precision in determining a material's exact melting point. Industrial operations prioritize throughput and efficiency, making melting capacity the dominant metric.
The Impact of Material Purity
Impurities in a material can significantly affect its melting behavior. A pure crystalline solid has a sharp, distinct melting point.
An impure substance, however, will typically melt over a range of temperatures, making a single "melting point" measurement less meaningful. This is a critical consideration in both quality control and material science.
Accuracy vs. Speed
As seen with different pyrometers, there is often a trade-off between the speed of measurement and its precision.
Rapidly heating a sample may be necessary for some processes, but it can also introduce errors or make it difficult to pinpoint the exact moment of phase transition. The choice of instrument must match the dynamics of the system being measured.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your objective dictates the correct approach to measurement.
- If your primary focus is material characterization or scientific analysis: Your goal is to determine the melting point temperature with high precision using an optical pyrometer.
- If your primary focus is industrial productivity or process optimization: Your goal is to measure the melting capacity (kg/h) of your furnace to manage production schedules and efficiency.
Ultimately, choosing the right measurement transforms a simple question of 'melting' into a powerful tool for discovery or production.
Summary Table:
| Measurement Goal | Key Metric | Primary Instrument | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Characterization | Melting Point Temperature (°C) | Optical Pyrometer | Scientific Analysis, Quality Control |
| Process Efficiency | Melting Rate/Capacity (kg/h) | Furnace Monitoring | Industrial Production, Throughput |
Need precise melting data for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables you need for accurate thermal analysis. Whether you require a high-precision pyrometer for material characterization or are optimizing your furnace's melting capacity, our expertise ensures you get reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- How does the combination of thermocouples and temperature control systems affect the study of reduction kinetics?
- Why are glassy carbon crucibles selected for high-temperature molten salt corrosion? Achieve Unmatched Data Accuracy
- What is the function of a high-temperature test furnace in RAFM steel testing? Replicate Nuclear Reactor Conditions
- What is the test for refractory material? Essential Tests for High-Temperature Performance
- What is a thermistor on a heat press? The Key to Consistent, Professional Transfers



















