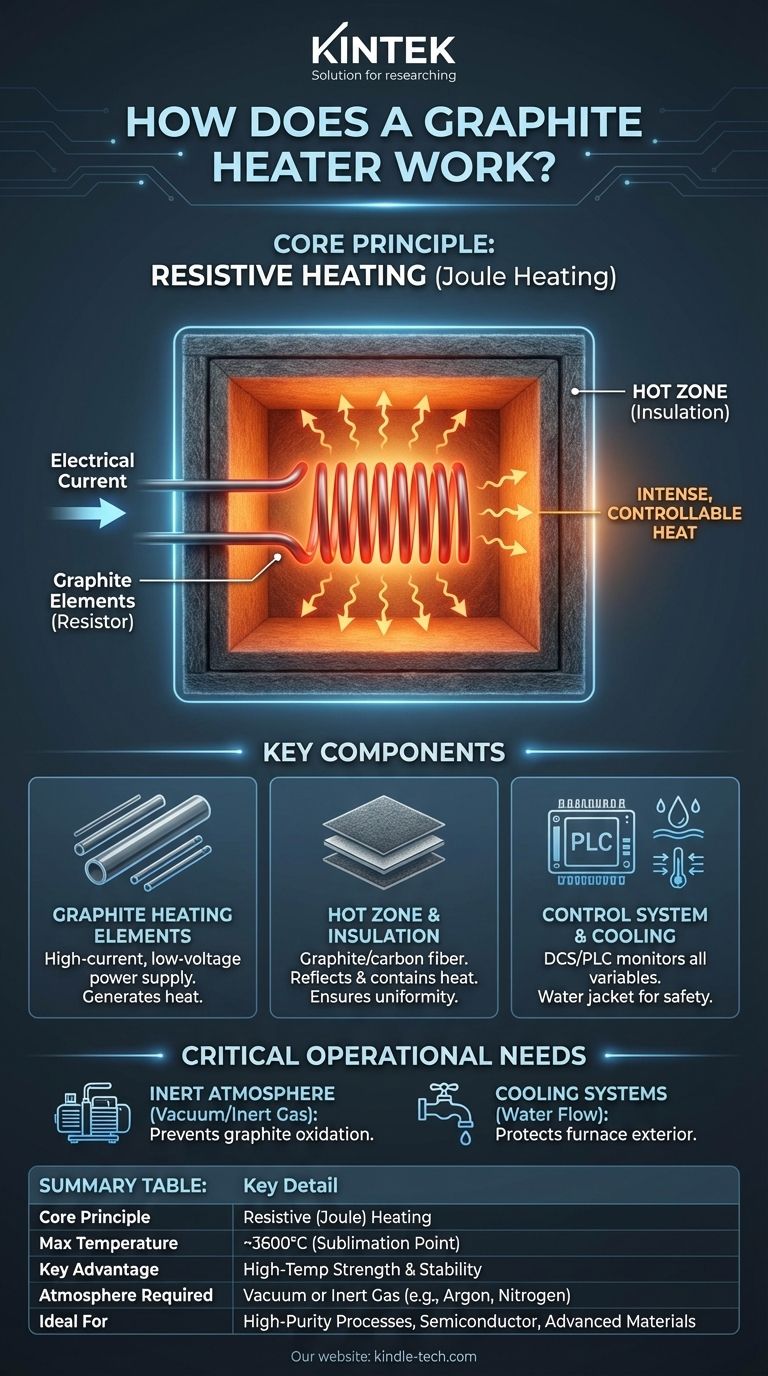
At its core, a graphite heater functions by the principle of resistive heating. A large electrical current is passed through specially designed graphite elements, which resist the flow of electricity. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into intense, controllable heat within an insulated chamber, allowing for extremely high and stable operating temperatures.
A graphite heater is not just a component; it's a complete system. It leverages the unique electrical resistance and unparalleled high-temperature tolerance of graphite to generate heat, while an insulated "hot zone" and a sophisticated control system work together to contain and regulate that heat with high precision.

The Core Principle: Resistive Heating
The entire operation of a graphite heater is based on a fundamental law of physics. Understanding this principle is key to understanding its value in industrial applications.
How Resistance Creates Heat
When electricity flows through any material, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the current's flow causes energy to be released, primarily as heat. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating or resistive heating. Graphite heaters are engineered to maximize this effect in a controlled way.
Why Graphite is the Ideal Material
Graphite is not simply a convenient choice; its properties make it uniquely suited for high-temperature applications.
- High Electrical Resistance: Graphite has enough resistance to generate significant heat efficiently but is conductive enough to carry the required current without failing.
- Extreme Temperature Tolerance: Unlike most metals that melt, graphite sublimes (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature, around 3600°C (6500°F). This allows it to operate reliably in conditions where metallic heaters would be destroyed.
- Structural Integrity: Graphite actually becomes stronger as its temperature increases, maintaining its structural integrity within the furnace.
Key Components of a Graphite Heating System
A graphite furnace is more than just its heating elements. It's an integrated system where each part plays a critical role in performance and safety.
The Graphite Heating Elements
These are the heart of the system. They can be shaped as rods, tubes, or plates, depending on the furnace design. A high-current, low-voltage power supply sends electricity through these elements to generate the required heat.
The Hot Zone
The heating elements are enclosed within a chamber, often called the "hot zone." This zone is constructed from graphite-based insulation materials like graphite felt or carbon fiber composites. Its purpose is to reflect and contain the heat, ensuring temperature uniformity and conserving electrical energy.
The Control System
As the reference mentions, a complex process requires a sophisticated brain. A Distributed Control System (DCS) or a similar programmable logic controller (PLC) monitors and manages every critical variable. This includes electrical power input, temperature sensors, pressure levels, and the flow rates for both process gases and cooling water.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Needs
While powerful, graphite heaters have specific requirements that are essential for their proper function and longevity.
The Critical Need for an Inert Atmosphere
Graphite will rapidly oxidize and burn away in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. To prevent this, graphite furnaces must operate either in a vacuum or be filled with a non-reactive, inert gas such as argon or nitrogen. The control of "gas flows" is not optional; it's fundamental to the heater's survival.
The Role of Cooling Systems
The intense heat generated inside the furnace must be contained. The outer body of the furnace is typically a double-walled steel vessel. Water is continuously circulated between these walls to keep the exterior cool, protecting the equipment and ensuring operator safety. A failure in "water flows" would lead to a catastrophic system failure.
Material Brittleness
While strong at high temperatures, graphite is a brittle ceramic material at room temperature. The heating elements and insulation must be handled with care during installation and maintenance to avoid cracks or damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how these elements work together allows you to assess the technology for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures (above 2000°C): Graphite heaters are the industry standard due to graphite's unmatched sublimation point and structural stability.
- If your primary focus is process purity and control: The required inert atmosphere has the added benefit of preventing product contamination, making these heaters ideal for semiconductor, medical, and advanced materials manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: The quality and design of the graphite "hot zone" insulation are paramount for minimizing heat loss and reducing overall energy consumption.
By mastering these core principles, you can effectively leverage the power and precision of graphite heating for any demanding high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Resistive (Joule) Heating |
| Max Temperature | ~3600°C (Sublimation Point) |
| Key Advantage | High-Temperature Strength & Stability |
| Atmosphere Required | Vacuum or Inert Gas (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) |
| Ideal For | High-Purity Processes, Semiconductor, Advanced Materials |
Ready to leverage the power of graphite heating for your most demanding applications?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including robust graphite heating systems designed for precision and durability. Whether your goal is achieving extreme temperatures, ensuring process purity, or maximizing energy efficiency, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite heaters can enhance your high-temperature processes and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes



















