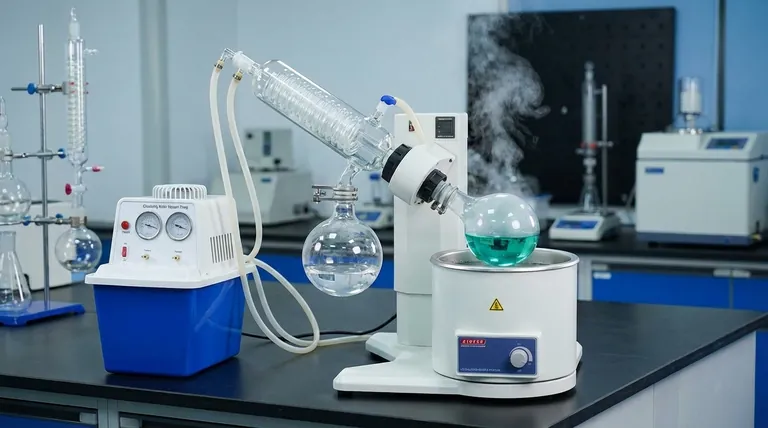
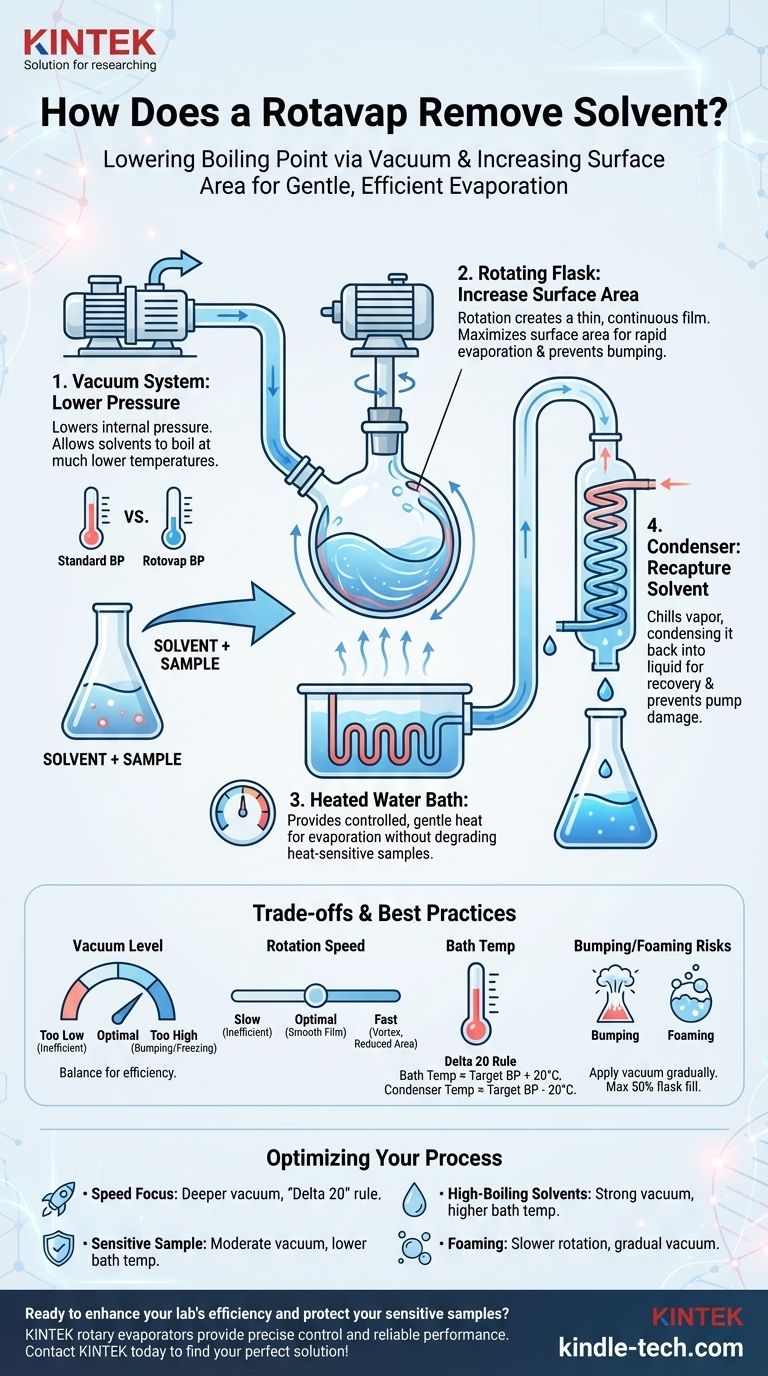
At its core, a rotary evaporator, or rotovap, removes a solvent by lowering its boiling point. It achieves this by reducing the pressure inside the system with a vacuum pump. This allows the solvent to boil at a much lower, gentler temperature, protecting the target compound from heat damage while rotation increases the surface area for rapid evaporation.
The true function of a rotovap is not just to heat a solvent, but to manipulate the physics of boiling. By simultaneously reducing pressure and increasing surface area, it allows for fast, controlled evaporation at temperatures far below the solvent's normal boiling point.

The Science Behind Efficient Evaporation
To understand how a rotovap works, you must first understand why simply boiling away a solvent on a hot plate is often a poor choice for chemical purifications.
The Problem: Heat and Bumping
Directly heating a solution to its atmospheric boiling point can destroy heat-sensitive compounds. A high temperature provides enough energy to break chemical bonds, ruining the product you're trying to isolate.
Furthermore, aggressive heating can cause bumping, where the solution superheats and erupts violently. This leads to sample loss and contamination.
The Solution: The Pressure-Temperature Relationship
The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure. By lowering the surrounding pressure, you lower the temperature required for the liquid to boil.
This is the same reason water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes. A rotovap exploits this fundamental principle by creating a low-pressure environment with a vacuum pump.
The Four Key Components of a Rotary Evaporator
A rotovap is a system of four interconnected parts, each playing a critical role in controlling the evaporation process.
The Vacuum System: Lowering the Boiling Point
The vacuum pump is the heart of the operation. Its job is to remove air from the system, drastically lowering the internal pressure.
This pressure reduction is what allows solvents like ethyl acetate (normal boiling point: 77°C) to evaporate efficiently at a gentle bath temperature of 40°C or even lower.
The Rotating Flask: Increasing Surface Area and Preventing Bumping
The motor rotates the flask containing your solution. This rotation spreads the liquid into a thin, continuous film on the flask's inner wall.
This action dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process significantly faster than heating a static pool of liquid. The constant agitation also ensures even heating and prevents the bumping that plagues simple distillation.
The Water Bath: Providing Gentle, Controlled Heat
Evaporation is an endothermic process; it requires an input of energy (the latent heat of vaporization) to occur. The heated water bath provides this energy in a gentle, stable, and controlled manner.
Because the vacuum has already lowered the solvent's boiling point, the bath temperature can be kept low, providing just enough energy for evaporation without degrading the sample.
The Condenser: Recapturing the Solvent
As the solvent evaporates in the rotating flask, the vapor travels up into the condenser. This piece of glassware contains a cold coil, typically chilled with circulating water or coolant.
When the warm solvent vapor hits the cold surface, it condenses back into a liquid. This liquid then drains into a collection flask, preventing solvent vapors from entering the vacuum pump and allowing for proper waste disposal or recycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Effective rotovap use is a balancing act. Simply turning all the dials to maximum is inefficient and can be counterproductive.
Setting the Right Vacuum Level
A deeper vacuum allows for lower bath temperatures, but too much vacuum can be problematic. It can cause violent bumping or, for some solvents, lower the boiling point so much that the liquid freezes in the flask, stopping evaporation completely.
Controlling the Rotation Speed
The goal is to create a smooth, even film inside the flask. A rotation speed that is too slow is inefficient. A speed that is too fast can cause the liquid to climb the walls of theflask in a vortex, which actually reduces the effective surface area.
Managing Bath Temperature
A common guideline is the "Delta 20" rule. The bath temperature should be about 20°C warmer than the target boiling point of your solvent at your set vacuum. Likewise, the condenser coolant should be at least 20°C colder than that target temperature to ensure efficient condensation.
The Risk of Bumping and Foaming
Bumping occurs when the vacuum is applied too quickly. Foaming is common with certain samples or solvents. To prevent these, always apply the vacuum gradually and consider using a lower rotation speed if your sample begins to foam. Never fill the evaporating flask more than halfway.
Optimizing Your Rotovap Process
Your specific goal determines how you should balance the variables of vacuum, temperature, and rotation.
- If your primary focus is speed: Use a deeper vacuum to significantly lower the solvent's boiling point and a bath temperature that follows the "Delta 20" rule.
- If your primary focus is protecting a highly heat-sensitive compound: Use a moderate vacuum and a correspondingly low bath temperature, accepting that the process will take longer.
- If you are working with high-boiling point solvents (like water, DMF, or DMSO): You will require a stronger vacuum pump and a higher bath temperature to achieve efficient evaporation.
- If your solvent is foaming: Reduce the rotation speed, apply the vacuum more slowly, and ensure your flask is not more than half full.
Mastering these principles transforms the rotovap from a simple machine into a precision tool for chemical separation.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers pressure to reduce boiling point | Protects heat-sensitive compounds |
| Rotating Flask | Spreads liquid into a thin film | Increases surface area, prevents bumping |
| Heated Water Bath | Provides gentle, controlled heat | Enables efficient evaporation at low temperatures |
| Condenser | Cools and recaptures solvent vapor | Allows for solvent recovery and prevents pump damage |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your sensitive samples? A KINTEK rotary evaporator provides the precise control and reliable performance you need for gentle, rapid solvent removal. Our rotovaps are designed for laboratories that demand quality and reproducibility. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect rotary evaporator for your specific application and solvent systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- How do vacuum pumps enhance efficiency and performance? Boost Your System's Speed and Lower Costs
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments



















