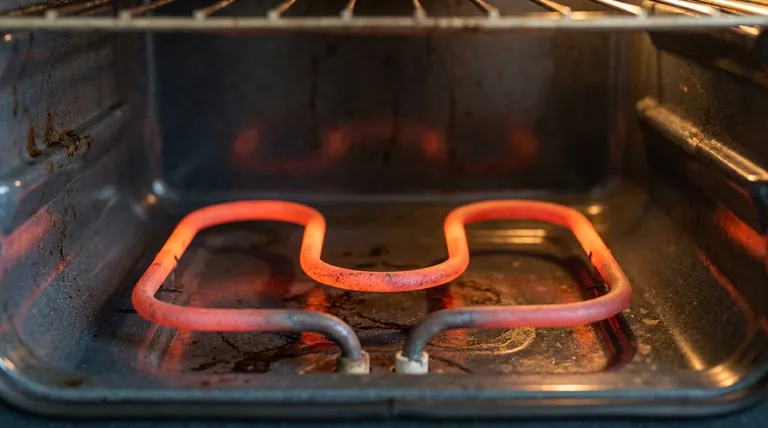
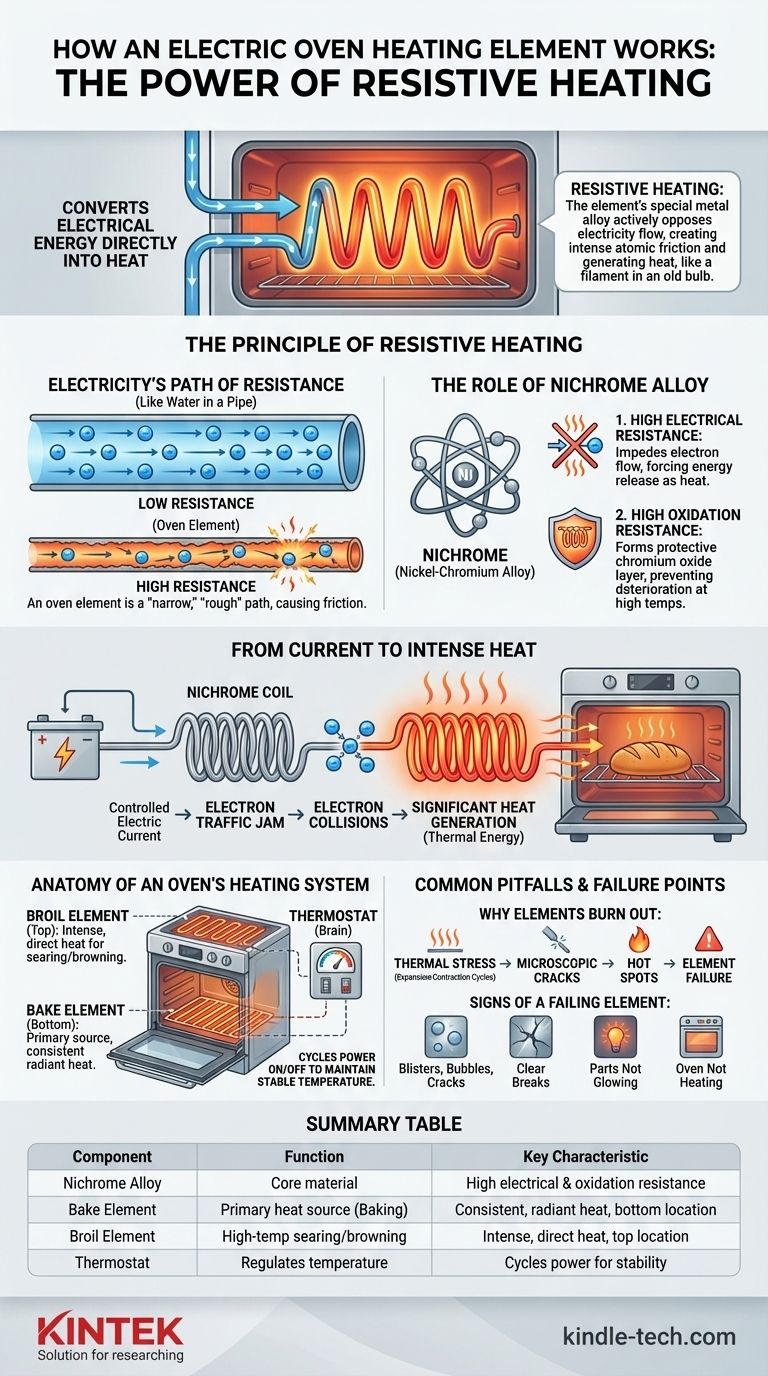
At its core, an electric oven heating element works by converting electrical energy directly into heat through a process known as resistive heating. When an electric current is passed through the element, the special metal alloy inside actively resists the flow of electricity. This opposition, or resistance, generates intense friction at an atomic level, causing the element to heat up and glow red-hot, much like the filament in an old incandescent light bulb.
The function of an oven's heating element is not merely to conduct electricity, but to actively resist its flow. This intentional opposition is what generates the intense, controlled heat required for cooking, turning electrical energy directly into thermal energy.

The Principle of Resistive Heating
To understand how your oven works, you must first grasp the fundamental relationship between electricity and resistance. This simple principle is the foundation of all electric heating.
Electricity's Path of Resistance
Think of electricity flowing through a wire like water flowing through a pipe. A wide, smooth pipe allows water to flow easily with little friction. Similarly, a good conductor like a copper wire allows electricity to flow with very low resistance.
An oven heating element, however, is designed to be a very "narrow" and "rough" pipe for electricity.
The Role of Nichrome Alloy
Heating elements are typically made from nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium. This material is chosen for two critical properties:
- High Electrical Resistance: It naturally impedes the flow of electrons, forcing them to work harder and release energy as heat.
- High Oxidation Resistance: It forms a protective outer layer of chromium oxide when heated, which prevents it from deteriorating or burning out quickly at extreme temperatures.
From Current to Intense Heat
When you turn on your oven, a controlled electric current is sent to the nichrome coil inside the element. The alloy's high resistance causes a "traffic jam" for the flowing electrons.
These electron collisions generate significant heat. The energy that is lost by the electrons pushing through the resistive material is converted directly into thermal energy, causing the element to glow and radiate heat into the oven cavity.
Anatomy of an Oven's Heating System
The heating element doesn't work in isolation. It's a key component in a system designed to create and maintain specific cooking temperatures.
The Bake Element
Located at the bottom of the oven, the bake element is the primary source of heat for most baking functions. It provides consistent, radiant heat that rises and circulates throughout the oven.
The Broil Element
The broil element is at the top of the oven. It is designed for high-temperature, top-down cooking, providing intense, direct heat to sear or brown the surface of food quickly.
The Thermostat's Critical Role
The elements do not stay on continuously. A thermostat inside the oven acts as the system's brain, constantly monitoring the internal temperature.
When the oven reaches your set temperature, the thermostat cuts power to the element. As the temperature begins to drop, the thermostat sends power again. This constant cycling is what maintains a stable cooking environment.
Common Pitfalls and Failure Points
Heating elements are simple, but they are subject to intense stress and are often the first component in an electric oven to fail.
Why Elements Burn Out
The most common cause of failure is simple wear and tear. The constant cycle of extreme heating and cooling (thermal stress) causes the internal metal coil to expand and contract.
Over thousands of cycles, this can create a weak spot or a microscopic crack. At this weak point, resistance increases dramatically, creating a "hot spot" that can melt the metal and break the electrical circuit, rendering the element useless.
Signs of a Failing Element
You can often diagnose a bad element with a simple visual inspection. Key signs include:
- Visible blisters, bubbles, or cracks on the element's surface.
- A clear break or gap in the element.
- Parts of the element not glowing when the oven is on.
- The oven failing to heat up to the proper temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this process empowers you to diagnose issues and use your appliance more effectively.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an oven that won't heat: First, visually inspect the bake and broil elements for any breaks, blisters, or spots that fail to glow red when turned on.
- If your primary focus is longevity: Avoid placing foil directly on the oven floor, as this can trap heat and cause the bake element to overheat and fail prematurely.
- If your primary focus is understanding the process: Remember that the element's entire purpose is to create friction for electricity, converting that energy into the controlled heat that cooks your food.
By grasping this simple principle of resistance, you can demystify your oven's operation and better appreciate the engineering at work.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Nichrome Alloy | The core material of the heating element | High electrical resistance and oxidation resistance |
| Bake Element | Primary heat source for baking | Located at the bottom, provides consistent, radiant heat |
| Broil Element | For high-temperature searing/browning | Located at the top, provides intense, direct heat |
| Thermostat | Regulates oven temperature | Cycles power to the element to maintain a stable temperature |
Need precise, reliable heating for your laboratory processes? The principle of resistive heating is fundamental to many lab ovens and furnaces. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment designed for accuracy and durability. Whether you need a standard drying oven or a high-temperature muffle furnace, our solutions are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory. Contact us today to find the perfect heating solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Copper Foam
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.



















