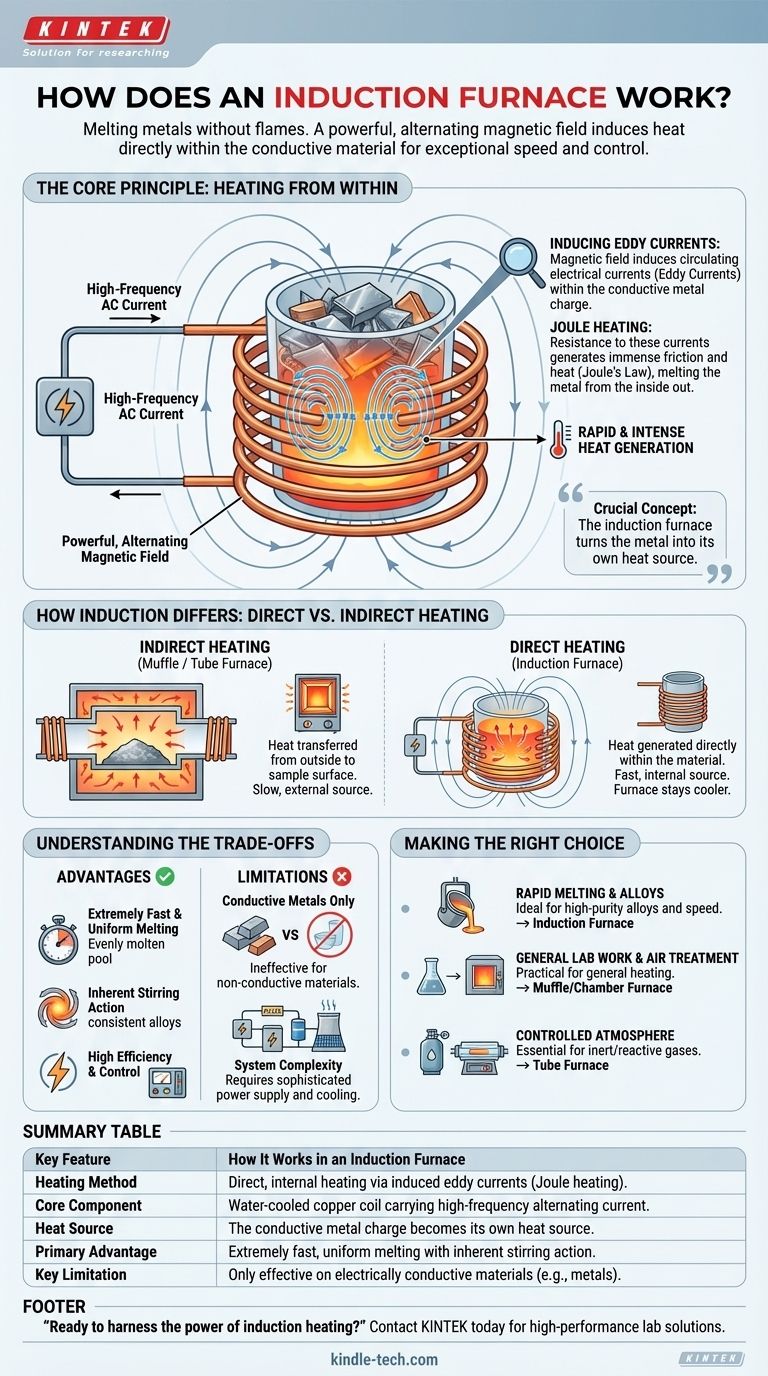
At its core, an induction furnace works without flames or external heating elements. It uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the conductive metal you want to melt. This process, called electromagnetic induction, induces strong electrical currents (eddy currents) inside the metal itself, and the resistance to this current flow rapidly produces extremely high temperatures.
The crucial concept to understand is that an induction furnace turns the metal into its own heat source. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat a chamber to transfer heat to the material, induction heating generates the heat from within the material, resulting in exceptional speed, efficiency, and control.
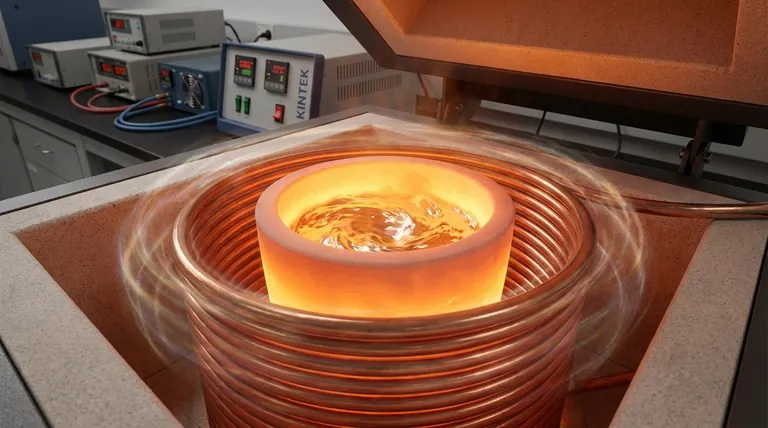

The Core Principle: Heating from Within
The magic of induction heating lies in its ability to transfer energy through a magnetic field without any physical contact. This fundamental principle is what sets it apart from nearly every other heating technology.
The Role of the Copper Coil
The process begins with a hollow copper coil. A specialized power supply unit drives a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through this coil.
This flow of AC electricity generates a powerful and rapidly changing electromagnetic field in the space surrounded by the coil.
Inducing the Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, such as scrap metal or a specific charge, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the metal.
These circulating currents are known as eddy currents. They are a direct result of Faraday's law of induction.
Why Eddy Currents Create Heat
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As the strong eddy currents are forced to flow through it, they overcome this resistance, and this friction generates immense heat.
This phenomenon is described by Joule's law. The heat produced is proportional to the material's resistance and the square of the current, allowing for incredibly fast and intense heating that melts the metal from the inside out.
How Induction Differs from Other Furnaces
Understanding the difference between direct and indirect heating is key to grasping the unique advantages of an induction furnace. It's not just a different type of oven; it's a fundamentally different way of generating heat.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace or chamber furnace operates like a high-powered oven. Electrical coils heat the chamber, and that heat is then transferred to the sample through convection (air movement) and radiation.
Similarly, a tube furnace heats the outside of a ceramic tube, which in turn slowly heats the sample inside. In all these cases, the heat source is external to the material being processed.
An induction furnace is a form of direct heating. The furnace itself stays relatively cool while the electromagnetic field passes through the refractory crucible and generates heat only within the conductive metal charge.
The Result: Speed and Uniformity
Because the heat is generated everywhere within the metal at once, melting is extremely rapid and uniform.
The electromagnetic field also creates a natural stirring action within the molten metal, which ensures a consistent temperature and a homogenous mixture when creating precise alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its unique mechanism comes with specific requirements and limitations.
Material Limitation: Conductive Metals Only
The primary requirement is that the material being heated must be electrically conductive.
Induction heating is ineffective for non-conductive materials like ceramics, glass, or certain polymers, as the magnetic field cannot induce the necessary eddy currents.
System Complexity
An induction furnace system is more than just a heating coil. It requires a sophisticated power supply with an inverter to create the high-frequency AC, a capacitor bank to balance the electrical load, and often a robust cooling system (typically water) to keep the copper coil from melting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting of metals or creating high-purity alloys: The speed, efficiency, and inherent stirring action of an induction furnace make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or heat-treating samples in air: A simpler and more versatile muffle or chamber furnace is often more practical and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is processing samples in a controlled atmosphere: A tube furnace provides the sealed environment necessary for working with inert or reactive gases.
Ultimately, the induction furnace provides unparalleled performance for applications where the metal itself must be the target of the heating process.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | How It Works in an Induction Furnace |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct, internal heating via induced eddy currents (Joule heating). |
| Core Component | Water-cooled copper coil carrying high-frequency alternating current. |
| Heat Source | The conductive metal charge becomes its own heat source. |
| Primary Advantage | Extremely fast, uniform melting with inherent stirring action. |
| Key Limitation | Only effective on electrically conductive materials (e.g., metals). |
Ready to harness the power of induction heating for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for rapid melting and precise alloying. Our solutions help you achieve superior results with unmatched efficiency and control.
Let's discuss your specific metal processing needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature does steel liquify? Understanding the Melting Range for Your Applications
- Why high frequency is used in induction furnace? For Precise, Rapid, and Efficient Metal Melting
- Can you melt gold in an induction furnace? A Guide to Clean, Efficient Gold Melting
- Is an induction furnace AC or DC? Discover the Core Principle of Induction Heating
- What are the advantages of induction equipment? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Precise Heating
- What are induction furnaces employed for? Precision Melting and Heat Treatment for Modern Metallurgy
- How does vacuum induction melting work? Achieve Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Alloys
- Is induction heating more efficient than resistance? Unlock up to 50% greater energy savings.



















