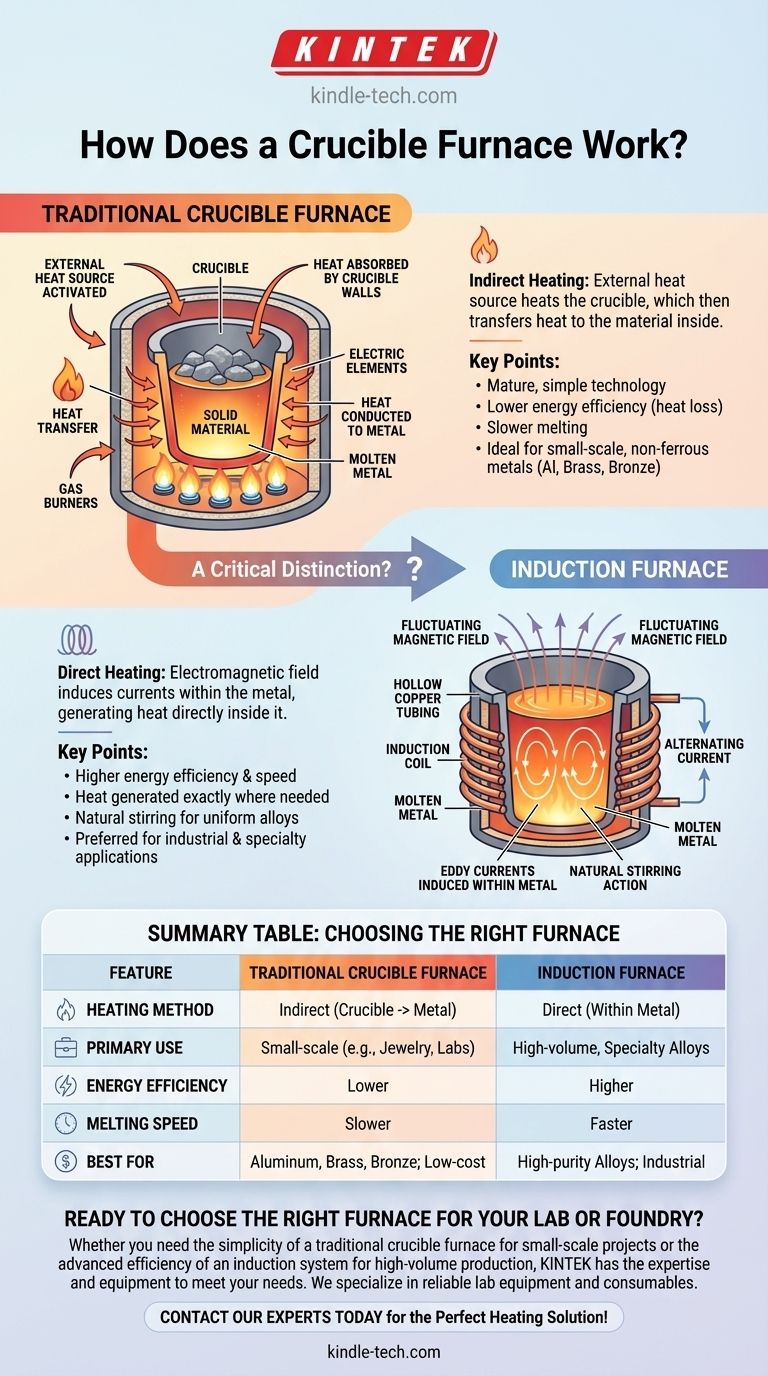
At its core, a crucible furnace works by indirect heating. It uses an external heat source, like a gas burner or electric element, to heat a durable container called a crucible. This heat is then transferred through the crucible's walls to the material inside, raising its temperature until it reaches its melting point and becomes molten.
The most critical concept to grasp is the difference in how heat is generated. A traditional crucible furnace heats the container from the outside, while a modern induction furnace uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself.

The Fundamental Principle: External Heat Transfer
The traditional crucible furnace is one of the oldest and most straightforward methods for melting materials. Its operation relies on the simple principle of transferring heat from an external source to the material via a container.
Key Components: The Crucible and the Heat Source
A basic crucible furnace has two primary parts. The first is the crucible, a pot-like container made from a refractory material like graphite, clay, or silicon carbide that can withstand extreme temperatures.
The second is the heat source. In gas-fired models, this is a powerful burner that envelops the crucible in flame. In electric versions, high-resistance heating elements surround the crucible, glowing hot to radiate heat inward.
The Step-by-Step Melting Process
The process is methodical. First, the solid material, such as scrap aluminum or bronze, is placed inside the crucible.
Next, the external heat source is activated. The heat energy saturates the furnace chamber and is absorbed by the crucible walls.
Finally, the crucible conducts this heat to the metal inside. The temperature of the metal steadily rises until it liquefies, at which point it can be poured into a mold.
A Critical Distinction: The Induction Furnace
While a traditional furnace heats the crucible, an induction furnace heats the metal directly, often using a crucible simply as a container. This represents a significant technological leap.
How Induction Changes the Game
An induction furnace uses a coil of hollow copper tubing with an alternating electric current flowing through it. This creates a powerful and rapidly fluctuating magnetic field around the crucible.
This magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal inside the crucible and induces strong electrical currents (known as eddy currents) within the metal itself.
The metal's natural resistance to these internal currents generates intense heat very quickly, causing the material to melt from the inside out. The furnace walls and crucible stay much cooler because the heat originates within the charge material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a traditional crucible furnace and an induction system depends entirely on the application's scale, budget, and performance requirements.
The Simplicity of Traditional Furnaces
Traditional crucible furnaces are mechanically simple and represent a mature technology. They are often the most cost-effective solution for small foundries, laboratories, jewelry makers, and hobbyists.
They excel at melting non-ferrous metals with lower melting points, such as aluminum, brass, and bronze.
The Inefficiencies of External Heat
The primary drawback of this method is its energy inefficiency. A significant amount of energy is wasted heating the furnace body, the surrounding air, and the crucible itself before the actual melting begins.
This indirect heating process is also slower and offers less precise temperature control compared to more modern methods.
The Advantages of Induction Heating
Induction furnaces are far more energy-efficient and faster because they don't waste energy heating intermediate components. The heat is generated exactly where it's needed.
The electromagnetic field also creates a natural stirring action in the molten metal, which is highly beneficial for creating uniform and consistent alloys. This makes induction the preferred method for industrial applications and specialty metals.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the core heating method is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, small-scale casting of non-ferrous metals: A traditional gas or electric resistance crucible furnace is a reliable and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production, speed, and energy efficiency: An induction furnace is the superior technology, offering precise control and faster melting times.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity or specialty alloys: The direct heating and inherent stirring action of an induction furnace provide unmatched quality and consistency.
Ultimately, knowing whether you need to heat the pot or heat the metal directly will guide you to the most effective solution.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Crucible Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirectly heats the crucible | Directly heats the metal via electromagnetic induction |
| Primary Use | Small-scale casting (e.g., jewelry, labs) | High-volume production, specialty alloys |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (heat lost to crucible/furnace) | Higher (heat generated within the metal) |
| Melting Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Best For | Aluminum, brass, bronze; low-cost projects | High-purity alloys, industrial applications |
Ready to choose the right furnace for your lab or foundry?
Whether you need the simplicity of a traditional crucible furnace for small-scale projects or the advanced efficiency of an induction system for high-volume production, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs. We specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific melting and casting applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect heating solution for your materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an alumina crucible in Li2.07Ni0.62N synthesis? Ensure High Purity & Thermal Stability
- Can you melt copper in a graphite crucible? Yes, Here's the Proven Method
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- How do you prevent the crucible from cracking during heating? Master Thermal Shock Prevention
- What are the types of crucible furnace? Choose the Right Heat Source for Your Melting Needs
- What is the function of ceramic crucibles during the industrial chemical analysis of charcoal? Enhance Data Accuracy
- Which crucible container can withstand high temperature and is used for metal and glass? Find the Right Material for Your Process
- Can a crucible withstand heat? Yes, with the right material and thermal properties.



















