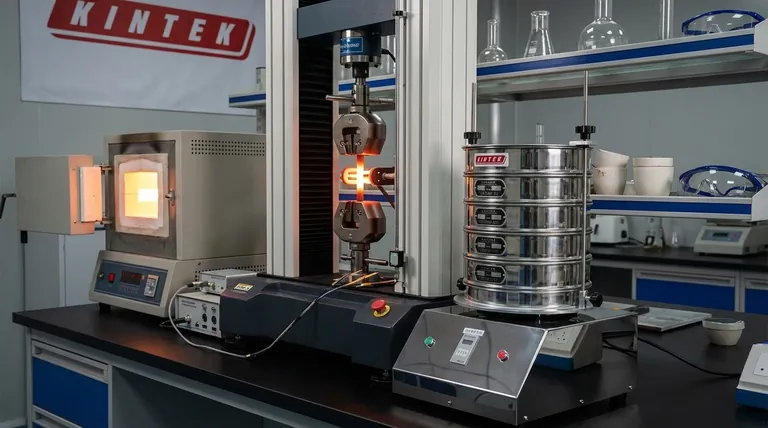
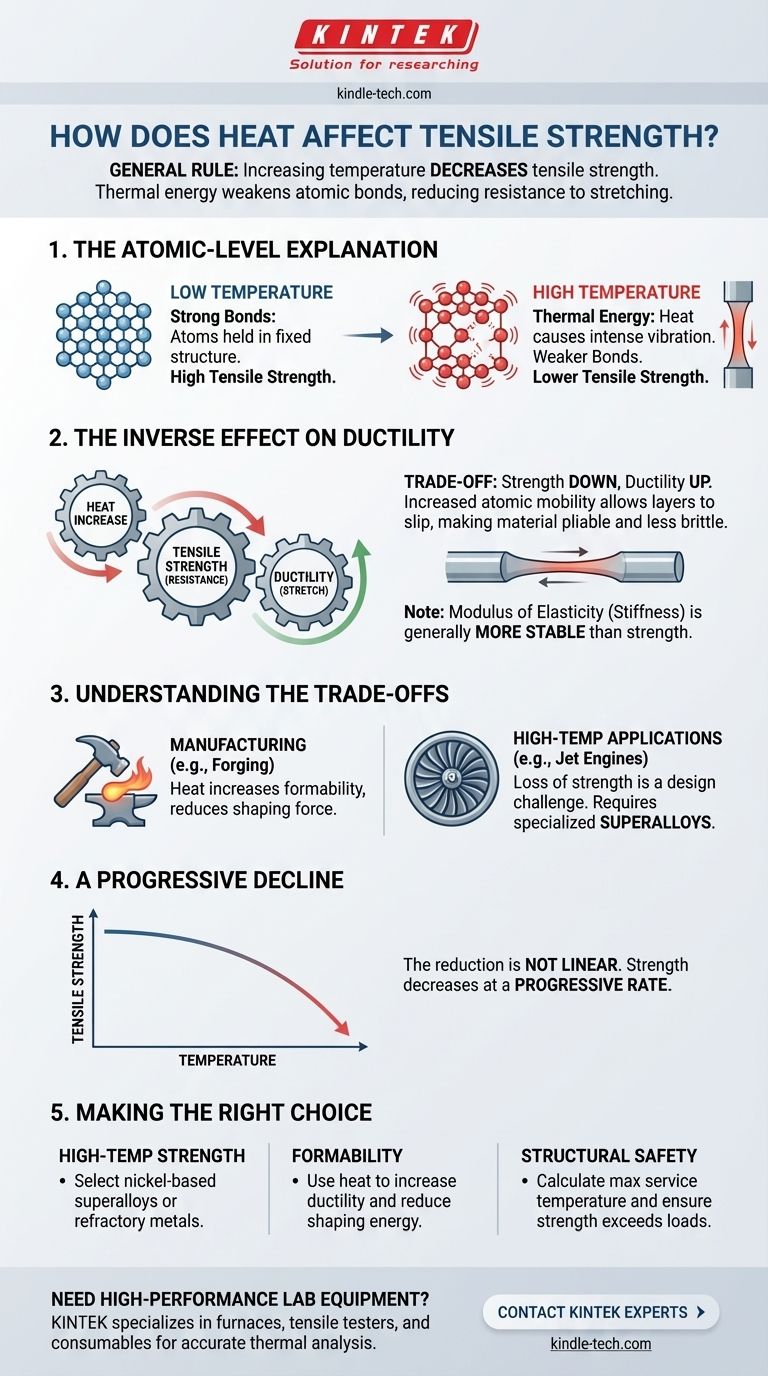
As a general rule, increasing a material's temperature decreases its tensile strength. This happens because thermal energy makes the atomic bonds within the material weaker and easier to pull apart, reducing its ability to resist being stretched.
The core principle is a fundamental trade-off in materials science: as you add heat, you typically sacrifice strength (the ability to resist a load) in exchange for increased ductility (the ability to deform without breaking).

The Atomic-Level Explanation
How Atoms Provide Strength
Atoms in a solid material are held in a relatively fixed structure, like a lattice, by strong electromagnetic bonds. Tensile strength is a measure of how much force is needed to overcome these bonds and pull the atoms apart.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Heat is simply a form of energy. When you heat a material, you are transferring thermal energy to its atoms, causing them to vibrate more rapidly and intensely.
Weakening the Bonds
This increased vibration forces the atoms further apart, weakening the bonds holding them together. With weaker bonds, less external force is required to pull the material apart, resulting in lower tensile strength.
The Inverse Effect on Ductility
Strength Goes Down, Ductility Goes Up
While strength decreases with heat, a related property—ductility—increases. Ductility is the material's ability to stretch or deform without fracturing.
Why Materials Become More Pliable
The same atomic vibrations that weaken the bonds also allow atomic layers to slip past one another more easily. This increased atomic mobility makes the material more pliable and less brittle, allowing it to stretch further before it breaks.
The Stability of Stiffness
It is important to note that the modulus of elasticity, or the material's stiffness, is generally more stable than its strength. This means that while its ultimate breaking point drops with heat, its initial resistance to bending or stretching changes less dramatically.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Strength vs. Formability Compromise
This relationship is the basis for many manufacturing processes. Forging, for example, intentionally heats metal to make it less strong and more ductile, allowing it to be hammered into a new shape with less force.
The Challenge of High-Temperature Applications
Conversely, for components that must operate under high heat, such as jet engine turbine blades or engine pistons, this loss of strength is a critical design challenge. Engineers must use specialized superalloys designed to retain their atomic bond strength at extreme temperatures.
A Progressive Decline
The reduction in tensile strength is not linear. As temperatures rise, the strength decreases at a progressive rate. This means the material weakens more and more rapidly as it gets hotter, a crucial factor for safety calculations in structural engineering, especially in fire-risk scenarios.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this principle is essential for correct material selection and safe design.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength: You must select materials specifically alloyed to counteract this effect, such as nickel-based superalloys or refractory metals.
- If your primary focus is formability and manufacturing: Applying heat is a fundamental tool to increase ductility and reduce the energy required to shape a material.
- If your primary focus is structural safety: You must calculate the maximum service temperature and ensure the material's tensile strength at that temperature remains safely above any anticipated loads.
Mastering the relationship between heat, strength, and ductility is fundamental to engineering reliable and effective systems.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Tensile Strength | Ductility |
|---|---|---|
| Increases | Decreases | Increases |
| Decreases | Increases | Decreases |
Need high-performance lab equipment to test material properties under heat? KINTEK specializes in furnaces, tensile testers, and consumables that help you accurately analyze how temperature impacts your materials. Whether you're developing high-temperature alloys or optimizing manufacturing processes, our reliable equipment ensures precise, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's thermal analysis needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution



















