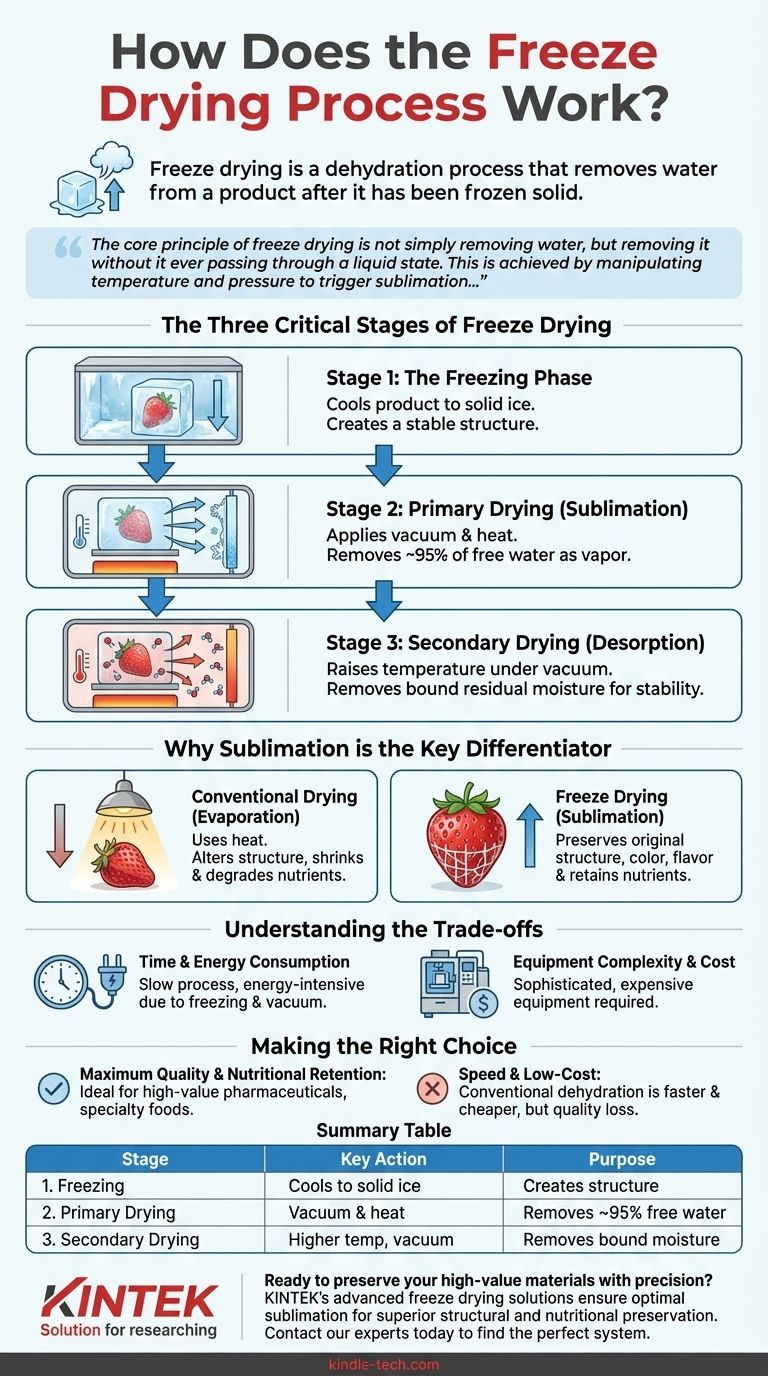
Freeze drying is a dehydration process that removes water from a product after it has been frozen solid. It works by lowering the air pressure and adding just enough heat to allow the frozen water to transform directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (vapor), a process known as sublimation, which preserves the material's structure, color, and nutritional value.
The core principle of freeze drying is not simply removing water, but removing it without it ever passing through a liquid state. This is achieved by manipulating temperature and pressure to trigger sublimation, which is the key to preserving a product's original characteristics with remarkable fidelity.

The Three Critical Stages of Freeze Drying
The entire process, also known as lyophilization, is a carefully controlled and sequential operation. Each stage has a distinct purpose in achieving complete and gentle dehydration.
Stage 1: The Freezing Phase
This initial step is foundational to the entire process. The material is cooled well below its freezing point until all the water within it becomes ice.
The goal is to completely solidify the product. The speed of freezing can influence the size of the ice crystals formed, which in turn affects the final structure of the dried product.
Stage 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
This is the longest and most critical stage, where the magic of freeze drying happens. Here, the frozen water is removed from the product.
A powerful vacuum is applied to the chamber, significantly lowering the pressure. A small, controlled amount of heat is then introduced, providing just enough energy for the ice to sublimate directly into water vapor.
This water vapor is then drawn away and collected on an extremely cold condenser plate, turning back into ice. This phase removes approximately 95% of the water content.
Stage 3: Secondary Drying (Desorption)
While primary drying removes the "free" ice, some water molecules remain bound to the material itself. The secondary drying phase is designed to remove this residual moisture.
The temperature is gradually raised, and the vacuum is maintained or even increased. This breaks the bonds between the remaining water molecules and the material, a process called desorption, ensuring the final product is thoroughly dry and shelf-stable.
Why Sublimation is the Key Differentiator
Conventional drying uses heat to evaporate liquid water, a process that fundamentally alters the food or material being dried. Freeze drying's reliance on sublimation is what makes it a superior preservation technique.
Preserving Structural Integrity
In conventional drying, the migration of liquid water to the surface causes the product's structure to shrink and collapse, altering its texture.
With freeze drying, the ice crystals act as a rigid scaffold. When they sublimate, they leave behind tiny pores, perfectly preserving the original size, shape, and texture of the material.
Retaining Nutritional and Sensory Value
High heat degrades sensitive vitamins, enzymes, and proteins, and it can also change a product's color and flavor.
Because freeze drying operates at low temperatures, it avoids this thermal damage. This results in a final product that retains nearly all of its original nutritional content, aroma, and taste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While freeze drying offers unparalleled quality, it is important to understand its limitations. It is a highly specialized process with specific requirements.
Time and Energy Consumption
The process, particularly the primary drying phase, is very slow and can take a significant amount of time to complete. This deliberate pace, combined with the need for freezing and vacuum systems, makes it an energy-intensive method.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Freeze dryers are sophisticated machines that must create and maintain extremely low temperatures and high vacuums. This specialized equipment is complex and represents a significant financial investment compared to conventional dehydrators.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use freeze drying depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum quality and nutritional retention: Freeze drying is the definitive choice for high-value products like pharmaceuticals, specialty ingredients, or premium survival foods.
- If your primary focus is speed and low-cost bulk processing: Conventional heat-based dehydration is a more practical and economical solution where some loss in quality is acceptable.
Ultimately, freeze drying is a preservation method engineered to maintain the essence of the original material.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Name | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Freezing | Cools product to solid ice | Creates a stable structure for drying |
| 2 | Primary Drying | Applies vacuum and heat for sublimation | Removes ~95% of free water as vapor |
| 3 | Secondary Drying | Raises temperature under vacuum | Removes bound residual moisture for stability |
Ready to preserve your high-value materials with precision?
KINTEK's advanced freeze drying solutions are engineered for laboratories and production facilities that demand maximum quality retention for pharmaceuticals, specialty foods, and sensitive biological samples. Our equipment ensures optimal sublimation for superior structural and nutritional preservation.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze drying system for your specific application and ensure your products maintain their essential qualities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- How is an autoclave utilized in antimicrobial experiments? Ensure Precise Nanoparticle Research Integrity
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization



















