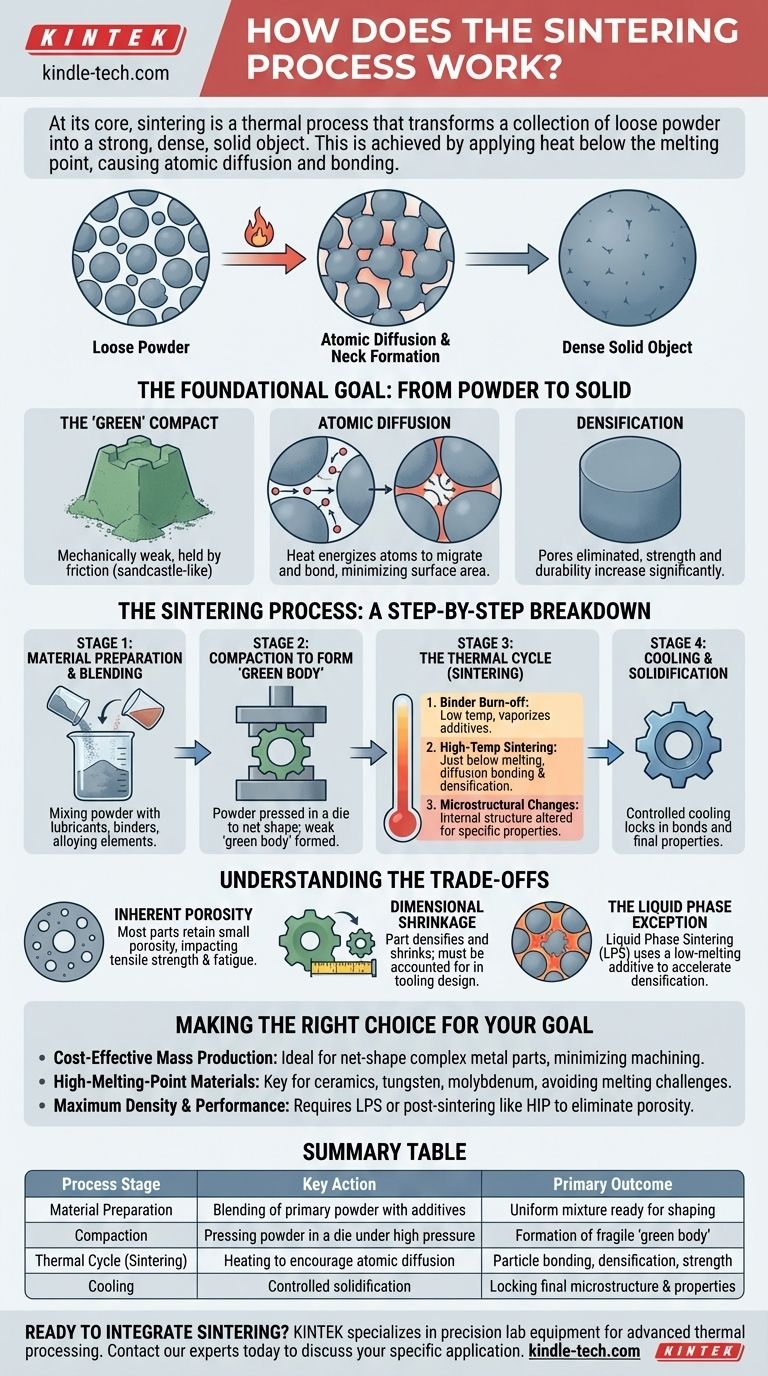
At its core, sintering is a thermal process that transforms a collection of loose powder into a strong, dense, solid object. This is achieved by applying heat at a temperature below the material's melting point, which causes the individual powder particles to bond together through atomic diffusion, dramatically reducing the empty space between them.
The fundamental misunderstanding of sintering is that it involves melting. It does not. The process works by encouraging atoms from individual particles to migrate and form strong bonds with neighboring particles, effectively fusing the powder into a single, cohesive mass.

The Foundational Goal: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramic manufacturing. Its primary purpose is to convert a fragile, pre-shaped powder form into a robust component with specific mechanical properties.
The Starting Point: The 'Green' Compact
The process begins with a "green compact" or "green body." This is the term for the powder that has been pressed and shaped, but not yet heated.
This green compact is mechanically weak and held together only by the friction between particles, much like a sandcastle.
The Driving Force: Atomic Diffusion
When heated, atoms in the material gain energy and become mobile. They begin to move across the boundaries where particles touch.
This atomic migration closes the gaps and pores between particles, creating solid "necks" that grow over time. The system naturally seeks a lower energy state, which is achieved by minimizing surface area—and a single dense solid has far less surface area than millions of tiny particles.
The Primary Outcome: Densification
The most important result of sintering is densification. As pores are eliminated and particles merge, the overall density of the material increases significantly.
This transformation is what gives the final part its strength, hardness, and durability. The initial fragile compact becomes a functional engineering component.
The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
While the details vary based on the material and desired outcome, the process follows a consistent, logical sequence.
Stage 1: Material Preparation and Blending
First, the primary material powder is prepared. This often involves mixing it with other substances.
These can include alloying elements to create a specific metal alloy, lubricants to aid in compaction, or binders that help the green compact hold its shape.
Stage 2: Compaction to Form the 'Green Body'
Next, the blended powder is loaded into a die and pressed under high pressure. This compaction process forms the powder into the desired net shape of the final part.
The resulting green body has the correct geometry but lacks any significant structural strength.
Stage 3: The Thermal Cycle (Sintering)
The green compact is then placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated. This stage has distinct phases:
- Binder Burn-off: At lower temperatures, any lubricants or organic binders are vaporized and removed.
- High-Temperature Sintering: The temperature is raised to just below the material's melting point. This is where diffusion bonding occurs, porosity is reduced, and the part gains its strength.
- Microstructural Changes: At these high temperatures, the material's internal crystalline structure can be intentionally altered to achieve specific properties, such as hardness or ductility.
Stage 4: Cooling and Solidification
Finally, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. This locks the newly formed bonds and microstructure into place, resulting in a solid, unified mass with its final mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful process, but it is governed by physical trade-offs that are critical to understand for successful application.
Inherent Porosity
Unless combined with secondary processes, most sintered parts retain a small amount of residual porosity. This can impact properties like ultimate tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to a fully dense, wrought, or cast equivalent.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the part densifies, it shrinks. This shrinkage must be accurately predicted and accounted for during the design of the compaction tooling to ensure the final part meets dimensional tolerances. The shrinkage is generally uniform if the green density is consistent.
The Liquid Phase Exception
A common variation called Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) introduces a small amount of a secondary material with a lower melting point. This additive melts during the thermal cycle, and the resulting liquid flows into the pores via capillary action.
This liquid phase significantly accelerates densification and can help achieve near-full density, but it requires careful control of material chemistry and temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of sintering allows you to leverage it effectively for specific manufacturing challenges.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex metal parts: Sintering is ideal, as it creates net-shape components with good tolerances, minimizing the need for costly secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-melting-point materials: Sintering is a key enabling technology for materials like ceramics, tungsten, and molybdenum, as it bypasses the extreme challenges of melting and casting them.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and performance: You will likely need to employ techniques like Liquid Phase Sintering or plan for post-sintering steps like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to eliminate residual porosity.
By controlling heat and pressure to manipulate materials at an atomic level, sintering provides a unique and powerful pathway from simple powder to a high-performance finished component.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Material Preparation | Blending of primary powder with additives (lubricants, binders) | Uniform mixture ready for shaping |
| Compaction | Pressing powder in a die under high pressure | Formation of a fragile 'green body' in the desired shape |
| Thermal Cycle (Sintering) | Heating in a controlled furnace to encourage atomic diffusion | Particle bonding, densification, and strength development |
| Cooling | Controlled solidification | Locking in final microstructure and mechanical properties |
Ready to integrate sintering into your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermal processing. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing manufacturing, our sintering furnaces and expertise help you achieve superior part density and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges



















