In short, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is generally considered a high-cost manufacturing process, particularly regarding the initial capital investment for equipment. The total cost is highly variable and depends heavily on the specific materials, required film quality, and production scale, but it is not a low-cost entry-level technology.
While the upfront and operational costs of CVD are significant, it is often chosen because its unique capabilities—like creating ultra-pure, uniform, and conformal thin films—provide a level of performance that less expensive methods cannot achieve. The decision is less about absolute cost and more about the value of the outcome.
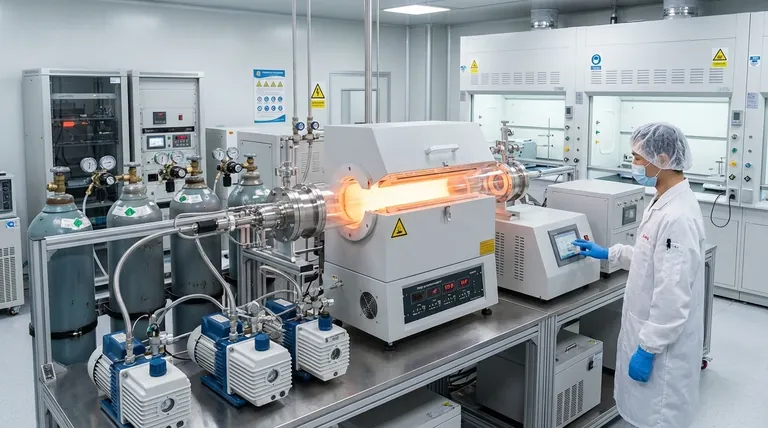

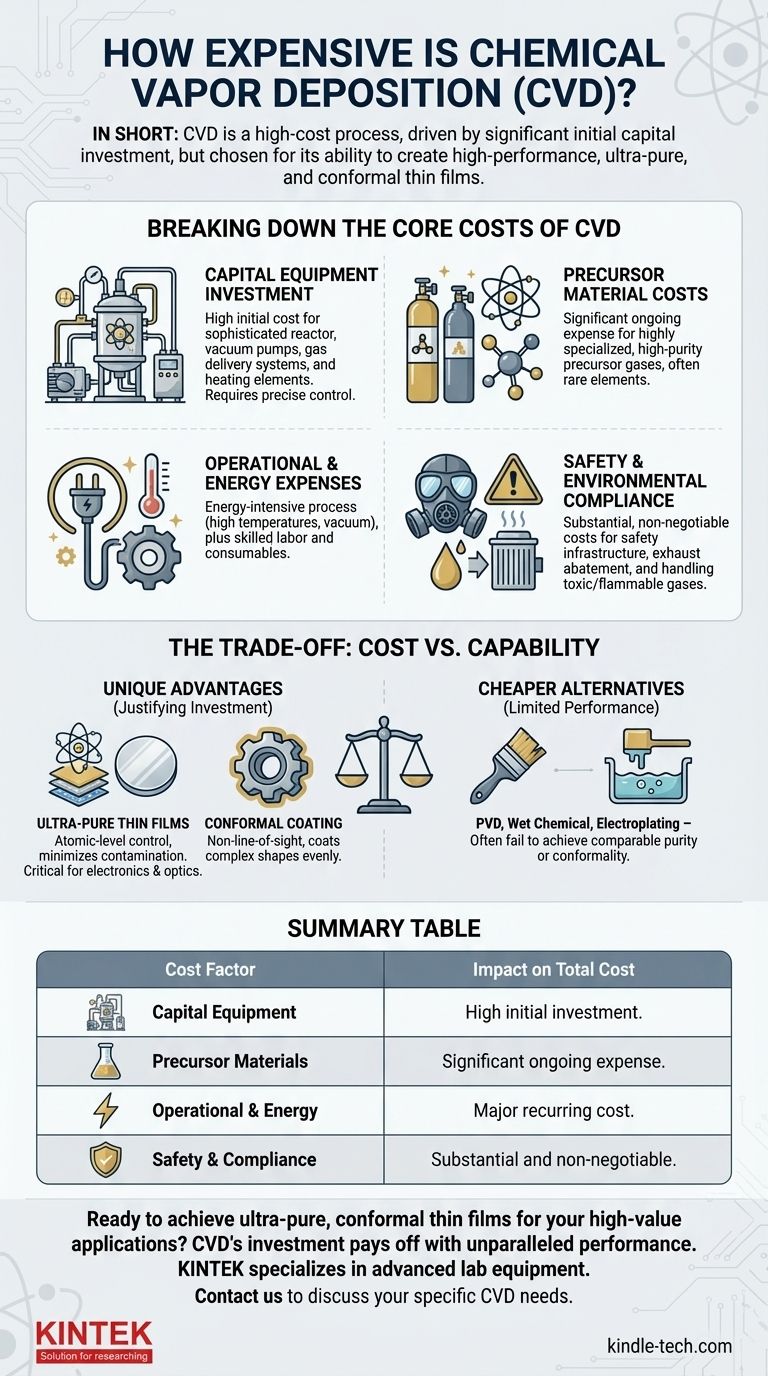
Breaking Down the Core Costs of CVD
The high cost of CVD is not a single line item but an accumulation of several demanding process requirements. Understanding these components is key to evaluating its feasibility for your project.
Capital Equipment Investment
The largest financial barrier is the CVD reactor and its support systems. This is a sophisticated piece of machinery that must maintain precise control over multiple variables.
Key equipment costs include the reaction chamber itself, high-performance vacuum pumps to create the necessary environment, and a complex gas delivery system to manage the flow of precursor chemicals. The need for high-temperature heating elements and sophisticated sensors adds further to the expense.
Precursor Material Costs
CVD works by reacting volatile precursor gases to deposit a solid film. The chemicals used for this process are often highly specialized and expensive to synthesize and purify.
For high-purity applications, such as in semiconductor manufacturing, the cost of these precursor materials can be a significant portion of the ongoing operational budget. The price is dictated by the rarity of the elements and the complexity of creating a stable, volatile compound.
Operational and Energy Expenses
Running a CVD process is energy-intensive. The system requires significant power to maintain high temperatures (often several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius) and operate the vacuum systems continuously.
Beyond energy, operational costs include the labor of skilled technicians required to run and maintain the equipment, as well as consumables like cleaning agents and replacement parts for the high-wear environment inside the reactor.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Many precursor gases used in CVD are toxic, flammable, or pyrophoric (ignite spontaneously in air). This necessitates extensive safety infrastructure, including gas detection systems, emergency shut-offs, and specialized ventilation and abatement systems to treat exhaust gases.
The cost of ensuring operator safety and complying with environmental regulations is a substantial and non-negotiable part of a CVD facility's budget.
The Trade-off: Cost vs. Capability
While CVD is expensive, it is often indispensable. Cheaper alternatives typically cannot match its unique advantages, which justifies the investment for high-value applications.
The Value of Purity and Control
As the references note, CVD excels at creating ultra-pure thin films. The vacuum environment and high-purity precursors minimize contamination, which is critical for electronics and optical components.
The process also allows for atomic-level control over film thickness, enabling the production of layers that are just a few atoms thick. This precision is simply not possible with methods like painting or electroplating.
The Advantage of Conformal Coating
CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. The precursor gas flows around the component, ensuring that even highly complex, three-dimensional shapes receive a perfectly uniform coating.
This "conformality" is a key advantage over line-of-sight processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), where surfaces not directly facing the source receive little or no coating. For coating internal surfaces or intricate parts, CVD is often the only viable option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating the cost of CVD requires aligning its expense with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and purity: The high cost of CVD is a necessary investment to achieve material properties unattainable with other methods.
- If your primary focus is coating complex shapes uniformly: CVD's conformal nature justifies its cost, as cheaper alternatives will fail to coat all surfaces evenly.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for a simple application: You should explore lower-cost alternatives like wet chemical coating, electroplating, or PVD first, as CVD is likely overkill.
Ultimately, the cost of Chemical Vapor Deposition is best understood as a premium paid for unparalleled control and quality.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Equipment | CVD reactor, vacuum pumps, gas delivery system | High initial investment |
| Precursor Materials | Specialized, high-purity gases and chemicals | Significant ongoing expense |
| Operational & Energy | High-temperature heating, vacuum maintenance, skilled labor | Major recurring cost |
| Safety & Compliance | Gas handling, ventilation, exhaust abatement systems | Substantial and non-negotiable |
Ready to achieve ultra-pure, conformal thin films for your high-value applications? The significant investment in CVD technology pays off with unparalleled performance for semiconductors, optics, and complex components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Our experts can help you determine if CVD is the right solution for your project and guide you through the selection process. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques



















