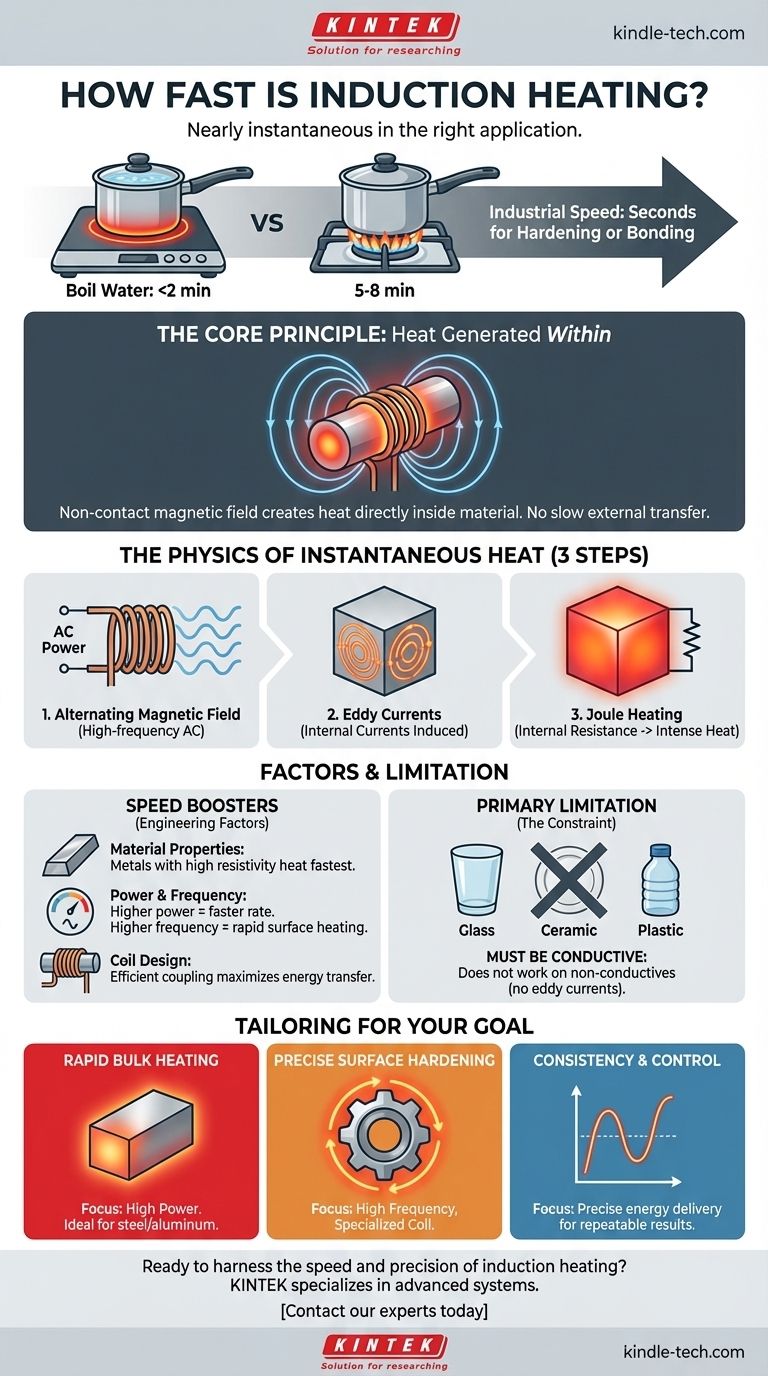
In the right application, induction heating is nearly instantaneous. For a familiar comparison, a new induction cooktop can boil water in under two minutes, whereas traditional gas or electric methods often take five to eight minutes. In industrial settings, this speed allows for processes like metal hardening or bonding to be completed in a matter of seconds.
The remarkable speed of induction heating comes from its core principle: it generates heat directly within the material itself through a non-contact magnetic field, eliminating the slow process of transferring heat from an external source.

The Physics of Instantaneous Heat
To understand why induction is so fast, we must look at how it works. It is not a conventional heating method; it is a process of electromagnetic energy transfer.
Step 1: The Alternating Magnetic Field
An induction system begins with a coil, typically made of copper. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space around and within the coil.
Step 2: Generating Internal Currents (Eddy Currents)
When an electrically conductive material, like a piece of steel, is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents inside the material.
These circulating currents are known as eddy currents. They are generated instantly and without any physical contact.
Step 3: Heat from Internal Resistance (Joule Heating)
The induced eddy currents flow against the material's own electrical resistivity. This friction at an atomic level generates intense, localized heat.
This phenomenon is known as Joule heating. Because this happens deep inside the material, the object effectively heats itself from the inside out, resulting in exceptionally rapid temperature increases.
Key Factors That Determine Induction Speed
While induction is inherently fast, its precise speed and effectiveness are governed by several key engineering factors.
Material Properties
The material being heated is the most important factor. The process relies on a material's ability to conduct electricity and its inherent electrical resistance. Metals and semiconductors are ideal candidates.
Power and Frequency of the System
A higher power supply will deliver more energy, leading to a faster rate of heating.
Additionally, the frequency of the alternating current (often between 100 to 500 kHz) can be adjusted. Higher frequencies tend to generate heat closer to the surface, which is ideal for rapid surface hardening.
The Induction Coil Design
The shape and proximity of the induction coil to the workpiece are critical. A well-designed coil couples tightly with the part, ensuring the maximum amount of magnetic energy is transferred efficiently, which translates directly to heating speed.
The Primary Limitation to Consider
Induction heating is a powerful tool, but its primary limitation is fundamental to how it works.
The Material Must Be Conductive
The entire process relies on inducing electrical currents within the target material. Therefore, induction heating does not work on non-conductive materials like most ceramics, glass, or plastics.
This is its single greatest constraint. If the target material cannot support the flow of eddy currents, no heat will be generated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of induction allows you to apply it effectively based on your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid bulk heating: Prioritize a high-power system and ensure the material (like steel or aluminum) has properties well-suited for induction.
- If your primary focus is precise surface hardening: Focus on using a higher frequency and a carefully designed coil that concentrates the magnetic field only on the desired area.
- If your primary focus is consistency and control: Leverage induction's ability to be precisely controlled by power and time, delivering the exact same amount of energy for every cycle, ensuring repeatable results that are difficult to achieve with flame or oven heating.
Ultimately, the speed of induction heating is not just a feature but a direct result of its precise, non-contact, and fundamentally efficient method of energy transfer.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Speed |
|---|---|
| Material Properties | Metals with high electrical resistivity heat fastest. |
| System Power | Higher power input results in a faster heating rate. |
| Current Frequency | Higher frequencies enable rapid, localized surface heating. |
| Coil Design | An efficient coil design maximizes energy transfer for speed. |
Ready to harness the speed and precision of induction heating in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including induction heating systems. Our solutions deliver the rapid, controlled heating you need for applications like metal hardening, brazing, and materials testing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction heating technology can accelerate your processes and improve your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can copper be melting in induction furnace? Unlock Superior Melting Precision & Quality
- How does heating occur in induction heating? Unlock the Power of Internal, Non-Contact Heat
- What metals can be melted in an induction furnace? A Guide to Efficient Melting for Any Conductive Metal
- How does a vim furnace work? Achieve Ultimate Purity in High-Performance Metal Melting
- How accurate is vacuum casting? Achieve High-Fidelity Prototypes and Low-Volume Production
- How to control the heat of an induction heater? Master Power, Frequency & Duty Cycle
- Is an induction furnace AC or DC? Discover the Core Principle of Induction Heating
- What is the process of vacuum arc degassing? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Steel



















