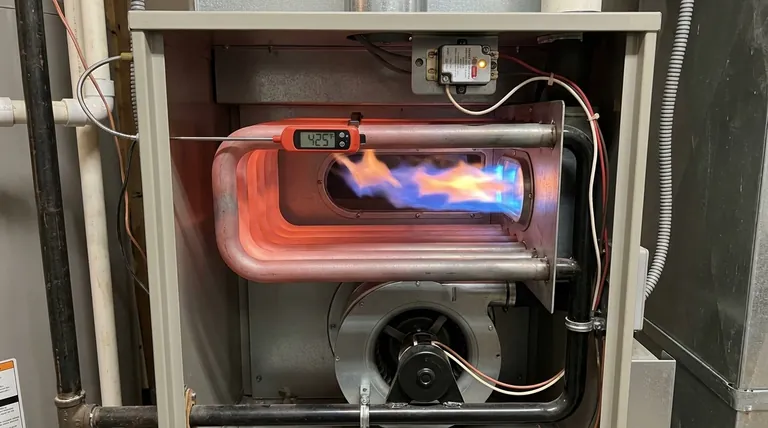
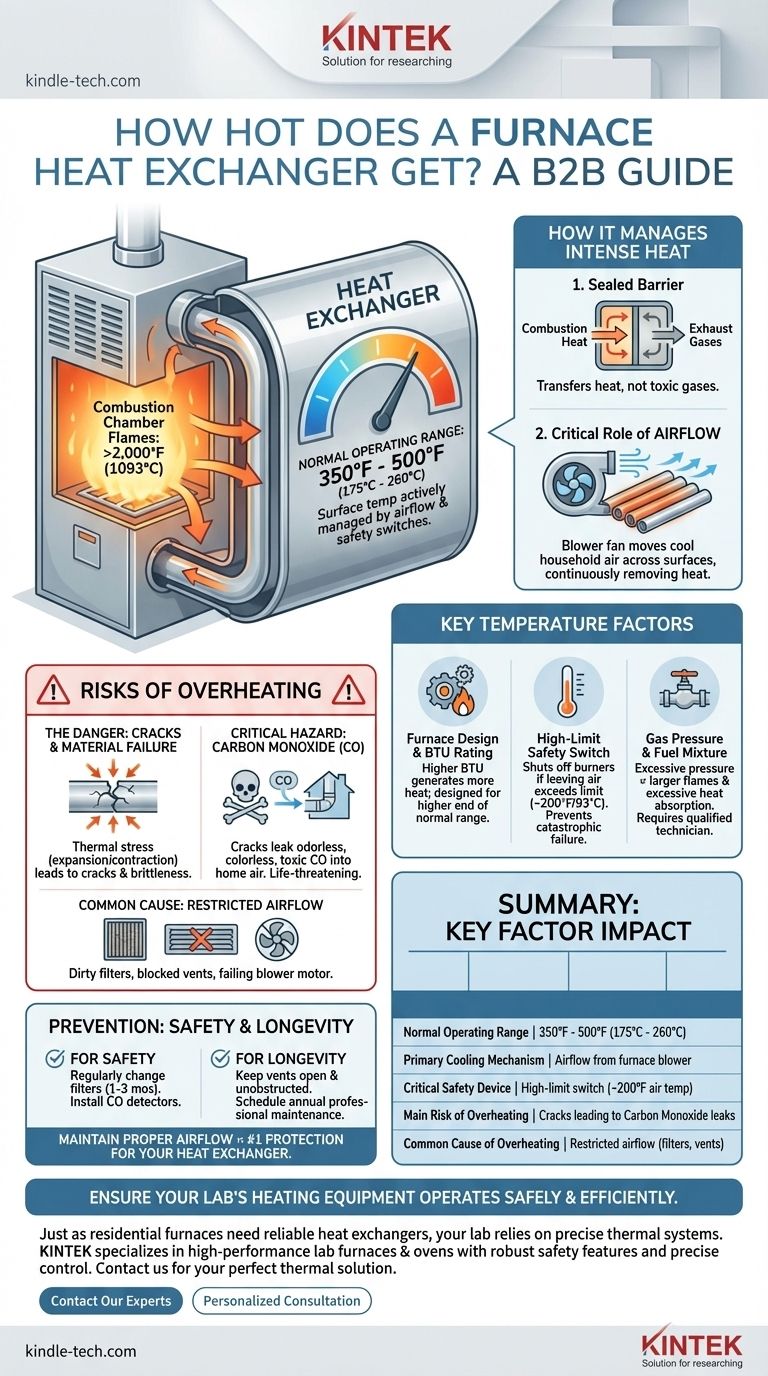
In a standard residential gas furnace, the surface of the heat exchanger typically operates between 350°F and 500°F (175°C to 260°C) during a normal heating cycle. While the burner flames inside can reach over 2,000°F (1093°C), the heat exchanger is specifically designed and cooled by circulating air to remain at these much lower, safer temperatures.
A furnace heat exchanger is engineered to operate well below its material failure point. Its temperature is actively managed by airflow and protected by a high-limit safety switch, as overheating is the primary cause of cracks that can lead to dangerous carbon monoxide leaks.

How a Heat Exchanger Manages Intense Heat
To understand its operating temperature, you first need to understand the heat exchanger's core function. It acts as a sealed barrier, allowing heat from combustion to be transferred to your home's air without allowing the toxic exhaust gases to mix.
The Combustion Chamber vs. The Exchanger Surface
The flames produced by your furnace's burners are extremely hot, easily exceeding 2,000°F (1093°C). However, this intense heat is contained within the initial section of the heat exchanger.
The heat exchanger itself is a series of metal tubes or chambers designed to have a large surface area. Its job is not to get as hot as the flame, but to efficiently transfer that heat to the air being pushed past it by the furnace blower.
The Critical Role of Airflow
Airflow is the single most important factor in regulating the heat exchanger's temperature. The furnace's blower fan constantly moves cooler household air across the exchanger's outer surfaces.
This process continuously removes heat from the metal, keeping it within its safe operating range. Think of it like running cool water over a hot pan—the water carries the heat away, preventing the pan from getting hotter.
Key Factors That Determine Temperature
The exact temperature of your heat exchanger is not a static number. It's a dynamic variable influenced by the furnace's design, its current operating state, and critical safety mechanisms.
Furnace Design and BTU Rating
A furnace with a higher BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating generates more heat. Its heat exchanger is built to handle this increased thermal load, but it will naturally operate at the higher end of the typical temperature range compared to a lower-BTU unit.
The High-Limit Switch: Your Furnace's Safety Net
Every furnace is equipped with a high-limit switch. This is a safety sensor that measures the temperature of the air leaving the furnace.
If this air temperature exceeds a preset limit, typically around 200°F (93°C), the switch will automatically shut off the burners. This is a direct response to the heat exchanger getting too hot, and it serves to prevent catastrophic failure.
Gas Pressure and Fuel Mixture
The gas valve regulates the flow and pressure of fuel to the burners. If this pressure is set too high, the flames will be larger and hotter than intended, forcing the heat exchanger to absorb an excessive amount of heat. This is why gas pressure should only be adjusted by a qualified technician.
Understanding the Risks of Overheating
A heat exchanger that operates above its designed temperature is a significant safety risk. The primary danger is not fire but the failure of the component itself.
The Danger: Cracks and Material Failure
When metal is repeatedly overheated and cooled, it expands and contracts. This thermal stress can cause the metal to become brittle and eventually develop cracks.
Even a microscopic crack compromises the integrity of the heat exchanger, creating a pathway for dangerous combustion byproducts to enter your home's air supply.
Why a Cracked Heat Exchanger is a Critical Hazard
The most dangerous byproduct of combustion is carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless, colorless, and highly toxic gas.
A cracked heat exchanger can leak CO directly into your ductwork, where it is then distributed throughout your entire home. This is a life-threatening situation that requires immediate attention.
Common Causes of Overheating
The most common cause of an overheating heat exchanger is restricted airflow. This is almost always due to one of three issues:
- A severely clogged air filter.
- Blocked or closed supply and return air vents.
- A failing or malfunctioning blower motor.
Making the Right Choice for Safety and Longevity
Your furnace's heat exchanger is designed to last for many years, but its lifespan is directly tied to proper operation and maintenance. Protecting it from overheating is the best way to ensure both safety and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is safety: Change your furnace filter regularly (every 1-3 months) and ensure you have working carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home.
- If your primary focus is longevity and efficiency: Keep all air vents open and unobstructed, and schedule annual professional maintenance to have a technician clean the system and verify safe operation.
Ultimately, maintaining proper airflow is the single most effective action you can take to protect your heat exchanger and ensure your furnace operates safely.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Heat Exchanger Temperature |
|---|---|
| Normal Operating Range | 350°F to 500°F (175°C to 260°C) |
| Primary Cooling Mechanism | Airflow from the furnace blower |
| Critical Safety Device | High-limit switch (shuts off burners at ~200°F air temp) |
| Main Risk of Overheating | Cracks leading to carbon monoxide leaks |
| Common Cause of Overheating | Restricted airflow (dirty filter, blocked vents) |
Ensure your lab's heating equipment operates safely and efficiently. Just as a residential furnace relies on a properly functioning heat exchanger, your laboratory processes depend on precise and reliable thermal systems. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and related equipment designed with robust safety features and precise temperature control. Our products are engineered for longevity and safety, helping you prevent equipment failure and maintain a secure lab environment. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your application. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- What is conduction in vacuum? Understanding Heat Transfer in the Absence of Matter
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance



















