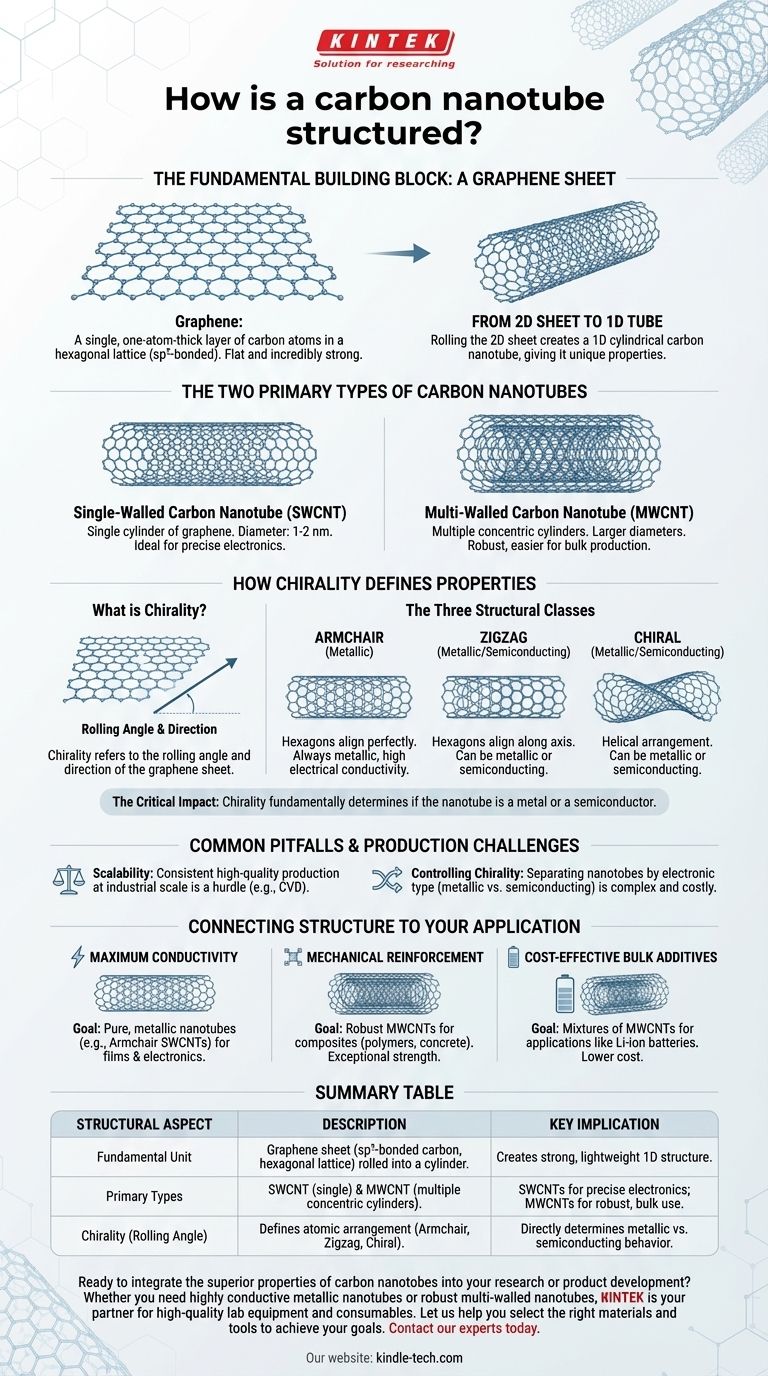
At its most fundamental level, a carbon nanotube is a sheet of graphene rolled into a seamless, hollow cylinder. Graphene itself is a single, one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice. This unique, one-dimensional cylindrical structure is what gives carbon nanotubes their extraordinary and highly sought-after properties.
The specific way a carbon nanotube is "rolled" from a flat graphene sheet—its diameter and twist angle, known as chirality—fundamentally determines its properties, dictating whether it behaves as a metal or a semiconductor.
The Fundamental Building Block: A Graphene Sheet
The Hexagonal Lattice
The foundation of a carbon nanotube is the sp²-hybridized bonds between carbon atoms. These strong covalent bonds form a repeating hexagonal pattern, exactly like chicken wire, creating a flat and incredibly strong sheet called graphene.
From 2D Sheet to 1D Tube
Imagine taking this flat graphene sheet and rolling it up to connect one edge to the other seamlessly. The result is a carbon nanotube—a cylindrical fullerene. This transformation from a two-dimensional sheet to a one-dimensional tube is the source of its unique characteristics.
The Two Primary Types of Carbon Nanotubes
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
A single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) consists of a single cylinder of graphene. Their diameters are typically in the range of 1-2 nanometers, making them ideal for applications in electronics where precise properties are required.
Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
A multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) is composed of multiple concentric cylinders of graphene nested inside one another, much like Russian nesting dolls. MWCNTs have larger outer diameters and are generally more robust and easier to produce in bulk than SWCNTs.
How Chirality Defines a Nanotube's Properties
What is Chirality?
Chirality refers to the angle and direction in which the graphene sheet is rolled to form the tube. It is described by a vector that defines how to "cut" the strip from the graphene lattice before rolling it up.
The Three Structural Classes
Based on this vector, nanotubes are classified into three types:
- Armchair: The hexagonal pattern aligns perfectly along the circumference of the tube.
- Zigzag: The hexagonal pattern aligns along the axis of the tube.
- Chiral: All other nanotubes, which have a helical or twisted arrangement of hexagons around the tube.
The Critical Impact: Metallic vs. Semiconducting
This structural difference has a profound impact on a nanotube's electrical behavior.
Armchair nanotubes are always metallic and exhibit extremely high electrical conductivity. In contrast, zigzag and chiral nanotubes can be either metallic or semiconducting, depending on their specific atomic arrangement.
Common Pitfalls and Production Challenges
The Challenge of Scalability
A prime challenge in realizing the full potential of carbon nanotubes is scaling up production. While methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are dominant, producing high-quality nanotubes consistently at an industrial scale remains a significant hurdle.
Controlling Chirality
For advanced electronics, separating nanotubes by their electronic type (metallic vs. semiconducting) is critical. Most synthesis methods produce a mixture of all chiralities, and separating them is a complex and costly process that limits their widespread use in applications like transistors.
Connecting Structure to Your Application
The specific structure of a carbon nanotube directly relates to its suitability for a given task.
- If your primary focus is maximum electrical conductivity: The goal is to use pure, metallic nanotubes, with armchair SWCNTs being the theoretical ideal for applications in films and electronics.
- If your primary focus is mechanical reinforcement: MWCNTs are often preferred for composites, such as in advanced polymers or concrete, as their structure provides exceptional strength and they are more cost-effective to produce in bulk.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk additives: For applications like improving conductivity in lithium-ion batteries, mixtures of MWCNTs are the standard choice due to their lower production cost and sufficient performance.
Understanding this link between atomic structure and real-world function is the key to unlocking the potential of these materials.
Summary Table:
| Structural Aspect | Description | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Unit | A single sheet of graphene (sp²-bonded carbon in a hexagonal lattice) rolled into a cylinder. | Creates an incredibly strong and lightweight one-dimensional structure. |
| Primary Types | SWCNT: Single graphene cylinder. MWCNT: Multiple concentric graphene cylinders. | SWCNTs for precise electronics; MWCNTs for robust, bulk applications. |
| Chirality (Rolling Angle) | Defines the atomic arrangement (Armchair, Zigzag, Chiral). | Directly determines if the nanotube is a metal or a semiconductor. |
Ready to integrate the superior properties of carbon nanotubes into your research or product development?
The precise structure of CNTs is the key to their performance. Whether you need highly conductive metallic nanotubes for electronics or robust multi-walled nanotubes for composite materials, KINTEK is your partner. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for nanotechnology research and development.
Let us help you select the right materials and tools to achieve your goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation



















