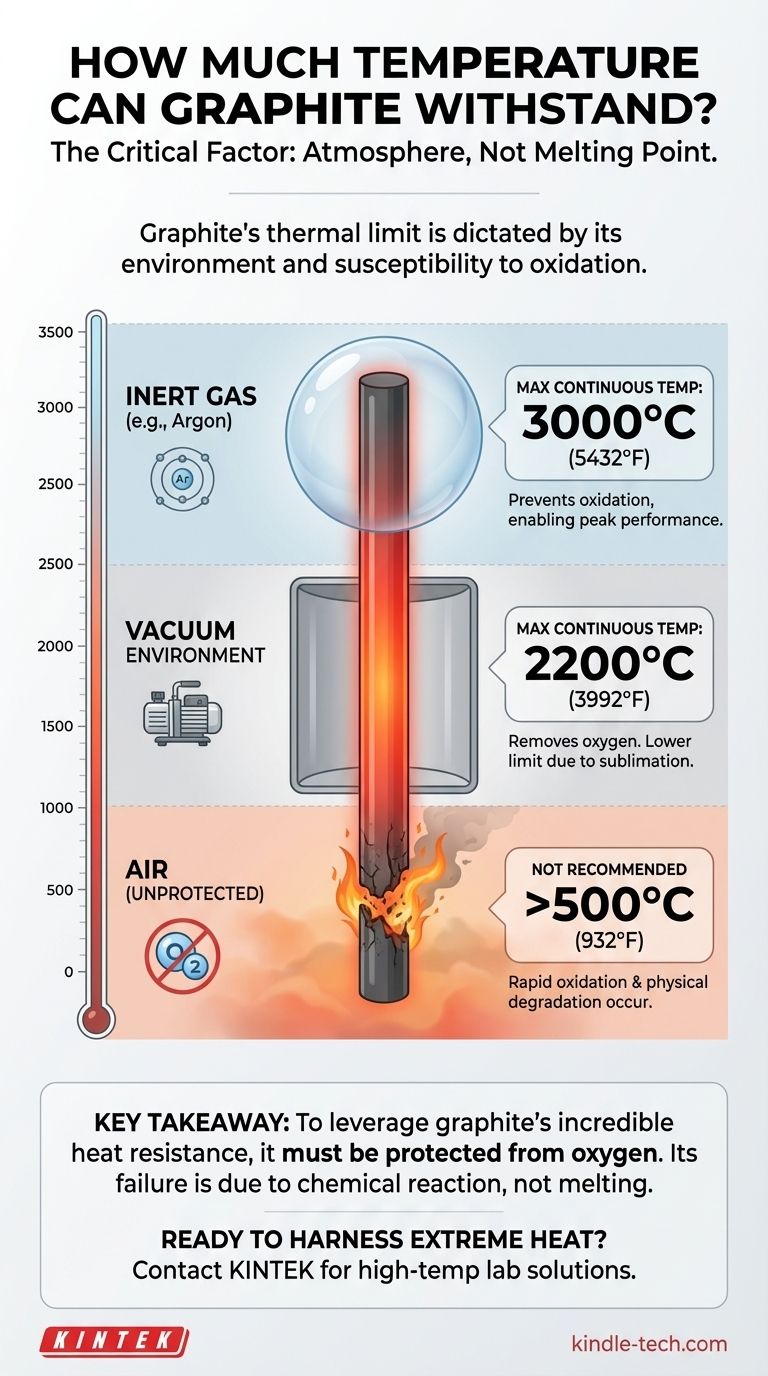
Under the right conditions, graphite can withstand exceptionally high temperatures, capable of operating continuously at 3000°C (5432°F) and even higher. This remarkable thermal stability, however, is not an absolute property. It is entirely dependent on the surrounding atmosphere, as graphite's primary point of failure at high temperatures is not melting, but reacting with oxygen.
The core issue is not graphite's melting point, but its susceptibility to oxidation. Its maximum operating temperature is dictated by its environment: it excels in an inert gas or vacuum but will rapidly degrade in the presence of air at high temperatures.

The Critical Factor: Atmosphere
Graphite does not have a traditional melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates (turns from a solid directly into a gas) at an extremely high temperature of around 3600°C. However, this is a theoretical limit that is rarely relevant in practical applications.
Why Oxidation is the True Limit
Graphite is a form of carbon. When heated in the presence of oxygen, it will begin to oxidize and physically degrade at temperatures far below its sublimation point. This process can start at temperatures as low as 500°C.
Therefore, to leverage its incredible heat resistance, graphite must be protected from oxygen.
Operating in an Inert Atmosphere
The most common method for protection is to use graphite components within an inert gas atmosphere, such as argon.
By displacing all oxygen, an inert environment allows graphite heating elements and furnace components to operate on a continuous basis at 3000°C.
The Vacuum Environment
Graphite also performs well in a vacuum, which removes the oxygen that would cause it to degrade.
However, the operational limit in a vacuum is typically lower than in an inert gas. A common continuous operating temperature for graphite furnaces under vacuum is 2200°C.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Understanding the environmental constraints is crucial to avoid premature failure of graphite components in high-heat applications.
The Problem with Operating in Air
Attempting to use unprotected graphite at high temperatures in a normal air environment will cause it to burn away, losing mass and structural integrity very quickly. It is fundamentally unsuitable for this type of use case.
Application Determines the Setup
The choice between an inert gas or a vacuum is a critical design decision. As seen in high-temperature furnaces, graphite can be used to create exceptionally uniform heating zones, but only when the correct atmospheric conditions are established and maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific environment and temperature requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute maximum temperature: An inert gas atmosphere is required, enabling continuous operation up to 3000°C.
- If your primary focus is operating within a vacuum: Plan for a lower continuous temperature limit, typically around 2200°C.
- If your application involves an oxygen-rich atmosphere: Standard graphite is not a viable material and you must consider alternatives or specialized protective coatings.
Understanding that graphite's thermal limit is defined by its environment is the key to successfully harnessing its remarkable capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Maximum Continuous Operating Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas (e.g., Argon) | 3000°C (5432°F) | Prevents oxidation, enabling peak performance. |
| Vacuum | 2200°C (3992°F) | Lower limit due to sublimation rates. |
| Air (Unprotected) | Not Recommended >500°C (932°F) | Rapid oxidation and degradation occur. |
Ready to harness the extreme heat resistance of graphite in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature solutions for laboratories. Whether you need a furnace with precise atmospheric control or expert advice on selecting the right components for your application, our team is here to ensure your success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve superior thermal processing results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres



















