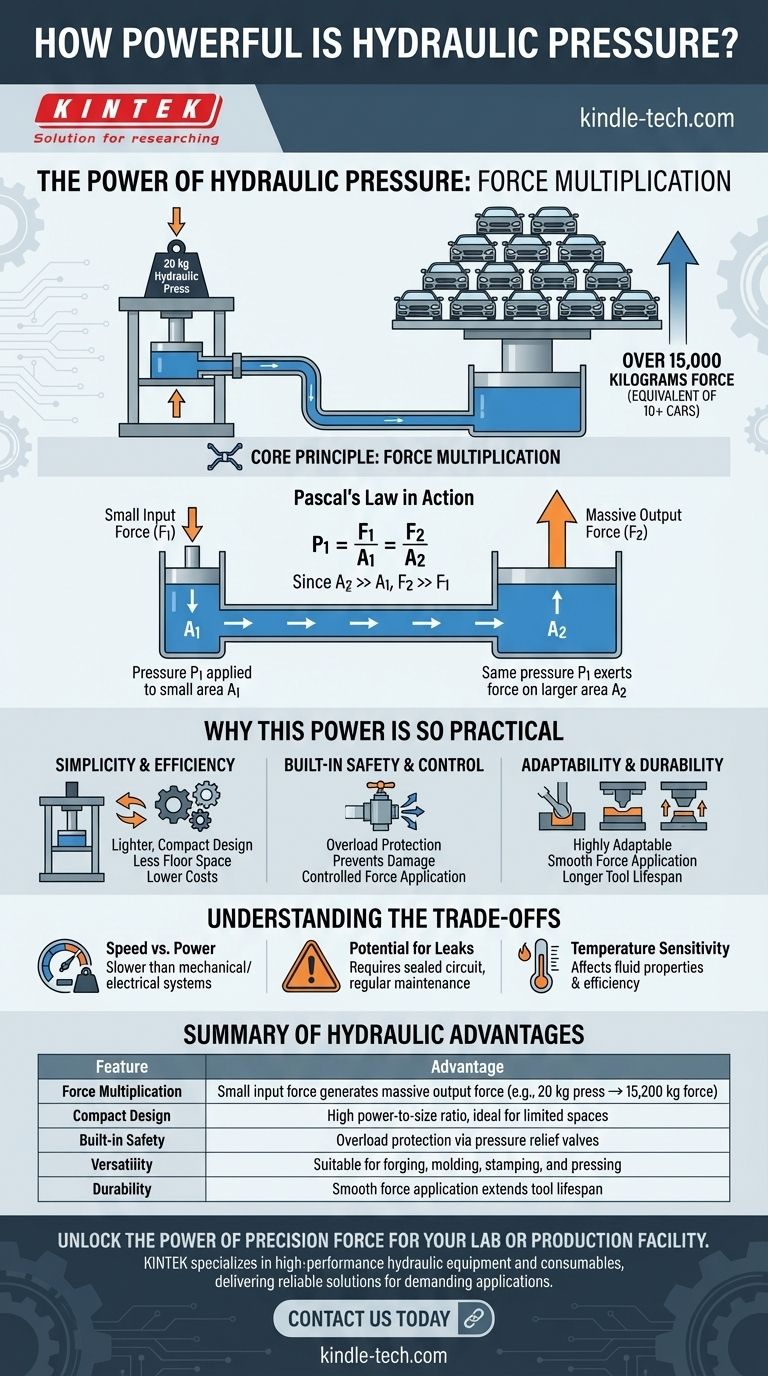
Hydraulic pressure is exceptionally powerful, capable of generating immense force from a compact system. A small, 20 kg hydraulic press, for example, can produce a maximum force of over 15,000 kilograms—the equivalent of stacking more than ten cars onto a single point. This power is scalable and can be engineered to lift buildings, shape solid steel, and power heavy construction equipment.
The core principle behind this immense power is force multiplication. Hydraulics use an incompressible fluid to convert a small force applied over a small area into a massive force exerted over a larger area, making it one of the most effective ways to generate high tonnage in a controlled manner.

The Principle of Force Multiplication
The magic of hydraulics isn't in the fluid itself, but in how the system leverages pressure. This is governed by a fundamental concept known as Pascal's Law.
Pascal's Law in Action
Pascal's Law states that when pressure is applied to a confined, incompressible fluid (like hydraulic oil), that pressure is transmitted equally throughout the entire fluid.
Think of it like squeezing a sealed water bottle. The pressure you apply with your hand is felt equally on all interior surfaces of the bottle.
The Role of Piston Size
A hydraulic system uses this principle with two pistons of different sizes: a small input piston and a large output piston.
You apply a modest force to the small piston. This creates pressure in the fluid. Because that pressure is transmitted equally everywhere, the same pressure pushes up on the much larger output piston.
Since the output piston has a much larger surface area, the same pressure results in a significantly multiplied output force. This is the secret to its power.
From Theory to Reality
The specifications you provided illustrate this perfectly. A machine that weighs only 20 kg can be engineered to exert a recommended force of 9,500 kg and a maximum force of 15,200 kg.
This incredible power-to-weight ratio is why hydraulics are a cornerstone of modern industry and heavy machinery.
Why This Power is So Practical
The ability to generate immense force is only useful if it's controllable, safe, and efficient. Hydraulic systems excel in these areas, making them highly practical.
Simplicity and Efficiency
Compared to complex mechanical gear systems, a hydraulic press has a very simple design with fewer moving parts.
This leads to a lighter, more compact machine that requires less floor space while still delivering enormous power. The reduction in parts also lowers initial and ongoing production costs.
Built-in Safety and Control
Hydraulic systems have built-in overload protection. A simple pressure relief valve can release excess pressure, preventing damage to the machine or the workpiece.
This makes it possible to safely manage and apply forces that would be catastrophic if they went out of control in a purely mechanical system.
Adaptability and Durability
The design of a hydraulic press is highly adaptable, allowing it to be used for a wide range of applications from forging and molding to stamping and pressing.
Furthermore, the smooth application of force and overload protection contribute to a longer lifespan for the tools and dies used in the press.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, hydraulic systems are not the solution for every problem. Understanding their limitations is key to appreciating their strengths.
Speed vs. Power
The trade-off for immense, controllable force is often speed. Moving fluid to generate pressure takes time, making hydraulic systems generally slower than their high-speed mechanical or electric counterparts.
Potential for Leaks
Hydraulic systems depend on a perfectly sealed circuit. Any leak of hydraulic fluid can reduce system power, create a mess, and potentially pose an environmental or safety hazard. This necessitates regular maintenance.
Temperature Sensitivity
The performance of a hydraulic system can be affected by temperature. Extreme cold can make the fluid thick and sluggish, while extreme heat can cause it to thin out and lose its lubricating properties, affecting efficiency and component lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Hydraulic power offers a unique combination of strength, control, and efficiency. The decision to use it depends entirely on the specific demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is immense, controllable force: Hydraulic systems are the unparalleled choice for heavy lifting, pressing, or shaping hard materials.
- If your primary focus is a high power-to-size ratio: The compact nature of hydraulic components makes them ideal for mobile machinery and applications with limited space.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive action: A purely mechanical or electrical system may be a more suitable and efficient choice for tasks like rapid stamping.
Ultimately, the power of hydraulics comes from its elegant ability to turn a small, manageable input into an enormous, and precisely controlled, output.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Force Multiplication | Small input force generates massive output force (e.g., 20 kg press → 15,200 kg force) |
| Compact Design | High power-to-size ratio, ideal for limited spaces |
| Built-in Safety | Overload protection via pressure relief valves |
| Versatility | Suitable for forging, molding, stamping, and pressing |
| Durability | Smooth force application extends tool lifespan |
Unlock the power of precision force for your lab or production facility. KINTEK specializes in high-performance hydraulic equipment and consumables, delivering reliable solutions for demanding applications. Whether you need robust pressing, molding, or material testing capabilities, our expertise ensures efficiency and safety. Contact us today to explore how our hydraulic systems can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard



















