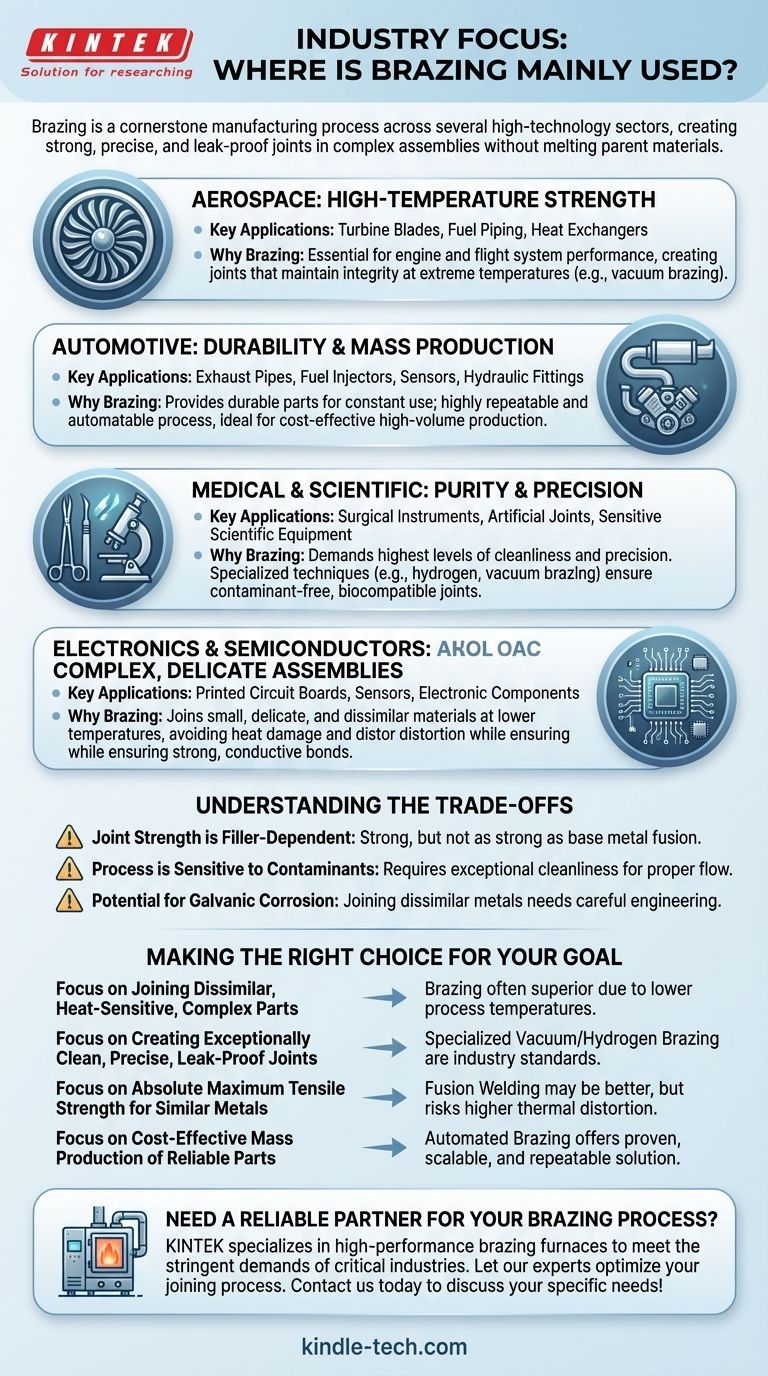
Brazing is not confined to a single industry but is a cornerstone manufacturing process across several high-technology sectors. The most prominent industries that rely on brazing are aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical, where the need for strong, precise, and reliable joints between metal components is paramount.
Brazing's value comes from its unique ability to create exceptionally strong, clean, and leak-proof joints in complex assemblies—often between dissimilar metals—without melting and distorting the parent materials. This makes it indispensable for applications where performance and reliability cannot be compromised.

Why High-Stakes Industries Rely on Brazing
Brazing is more than just a joining method; it's an enabling technology. Different industries leverage its specific advantages to meet their unique and demanding requirements.
Aerospace: For Strength at Extreme Temperatures
The aerospace industry operates under the most demanding conditions, requiring parts that are lightweight, incredibly strong, and capable of withstanding extreme temperature fluctuations and vibrations.
Brazing is used to manufacture critical components like turbine blades, fuel piping, and heat exchangers. The process, particularly vacuum brazing, creates joints that maintain their integrity at high temperatures, which is essential for engine and flight system performance.
Automotive: For Durability and Mass Production
In the automotive sector, reliability and cost-effectiveness are key. Components must endure constant use, vibration, and exposure to the elements for years.
Brazing is essential for producing durable parts like exhaust pipes, fuel injectors, sensors, and hydraulic fittings. The process is highly repeatable and can be automated, making it a cost-effective solution for the high-volume production demanded by the industry.
Medical and Scientific: For Purity and Precision
Medical devices demand the highest levels of cleanliness and precision. Joints must be perfectly formed, free of contaminants, and often biocompatible.
Specialized techniques like hydrogen and vacuum brazing are used to create assemblies with extreme cleanliness. This is critical for manufacturing surgical instruments, artificial joints, and sensitive scientific equipment where any imperfection or contamination could have serious consequences.
Electronics and Semiconductors: For Complex, Delicate Assemblies
The electronics industry requires joining very small, delicate, and often dissimilar materials (like metal to ceramic) without causing heat damage or distortion.
Because brazing occurs at a temperature below the melting point of the components, it is ideal for assembling printed circuit boards, sensors, and other electronic components. It allows for strong, conductive joints without damaging the sensitive materials involved.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is a specific tool with its own set of considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Joint Strength is Filler-Dependent
A brazed joint is only as strong as its filler metal. While very strong, it typically does not match the absolute strength of a properly welded joint where the base metals are fused together.
Process is Sensitive to Contaminants
Brazing requires an exceptionally clean surface for the filler metal to flow properly and create a strong bond. This means parts must be meticulously cleaned before the process, which adds time and cost to manufacturing.
Potential for Galvanic Corrosion
When joining dissimilar metals, the combination of the two parent metals and the filler metal can create a galvanic cell. If not engineered correctly for its service environment, this can lead to corrosion at the joint over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining process depends entirely on the specific demands of your component and its application.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar, heat-sensitive, or complex parts: Brazing is often the superior choice due to its lower process temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating exceptionally clean, precise, and leak-proof joints: Specialized processes like vacuum or hydrogen brazing are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is the absolute maximum tensile strength for similar metals: Fusion welding may be a more direct solution, but you must account for higher thermal distortion.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of reliable metal parts: Automated brazing offers a proven, scalable, and highly repeatable solution.
Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your application—from strength and material compatibility to cleanliness—is the key to leveraging the right manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Why Brazing is Used |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, heat exchangers | High-temperature strength, lightweight assemblies |
| Automotive | Fuel injectors, exhaust systems | Durability, cost-effective mass production |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants | Extreme cleanliness, precision, biocompatibility |
| Electronics | Sensors, circuit boards | Joins delicate materials without heat damage |
Need a reliable partner for your brazing process? The right equipment is crucial for achieving strong, clean, and precise joints in critical applications. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and production equipment, including brazing furnaces, to meet the stringent demands of industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Let our experts help you optimize your joining process—contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum oven in NRPE preparation? Enhance Purity and Battery Performance
- Why is 1177 °C precision critical for GH3535 furnace treatment? Ensure Microstructural Integrity
- Why is a high-temperature annealing furnace used for Zircaloy-2 before irradiation? Essential Sample Preparation Guide
- What type of brazing works at lower temperature? Silver Alloys for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven necessary for single-crystal cathode powders? Ensure Peak Material Stability
- Can you calibrate a vacuum gauge? Ensure Accurate Pressure Readings for Your Lab
- What do sintering temperatures range from? Unlock the Key to Perfect Material Densification
- What is the purpose of constant temperature heating equipment in in-situ curing? Optimize Quasi-Solid-State Electrolytes



















