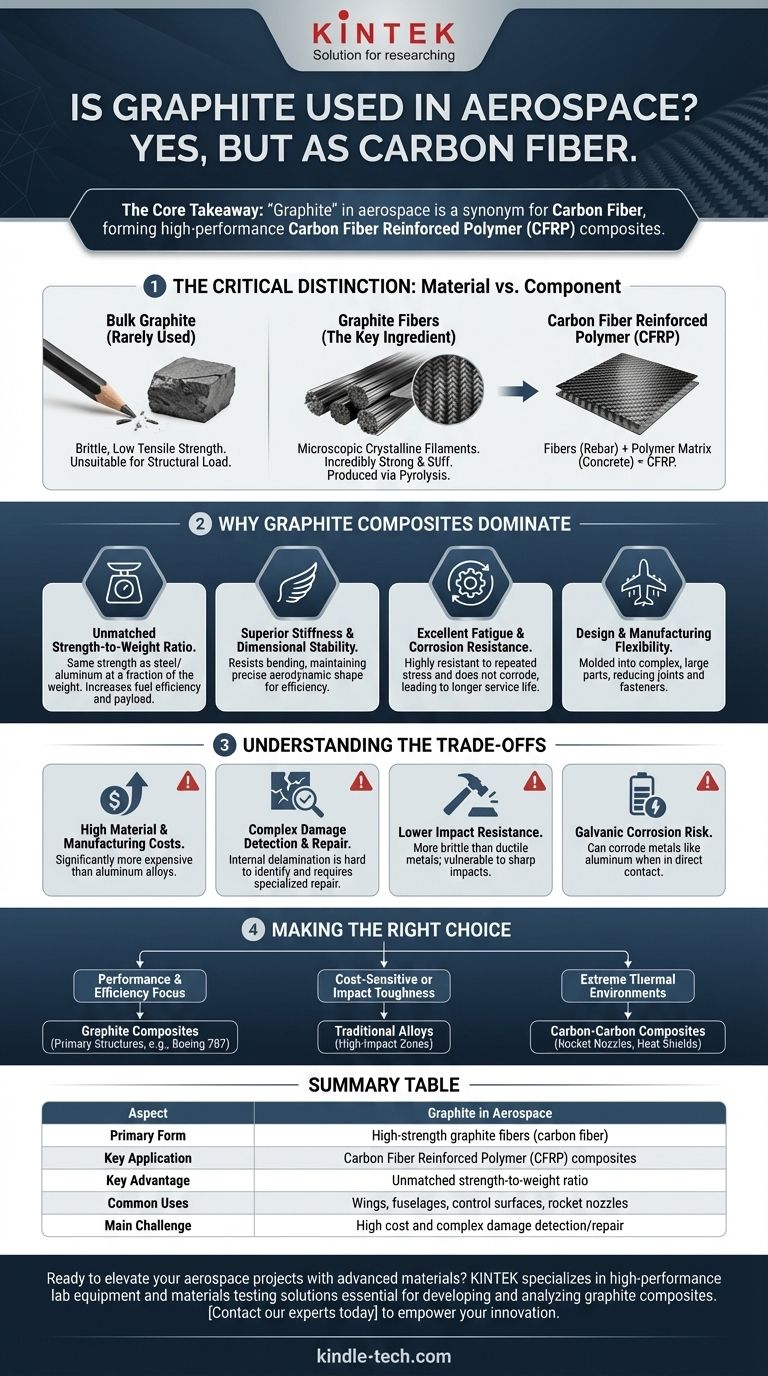
Yes, but it's crucial to understand what "graphite" means in this context. When aerospace engineers refer to graphite, they are almost never talking about the soft, brittle material found in pencils. Instead, they are referring to high-strength, high-stiffness graphite fibers that serve as the reinforcement in advanced composite materials, which are essential to modern aircraft and spacecraft.
The core takeaway is that "graphite" in aerospace is a synonym for carbon fiber. This material, when combined with a polymer resin, creates composites that offer an unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio, forming the backbone of modern high-performance aerospace structures.
The Critical Distinction: Material vs. Component
To understand its role, you must distinguish between the raw material and the final engineered part. The two are fundamentally different.
Bulk Graphite is Rarely Used
The form of graphite used in pencils or as a solid lubricant has very limited structural application in aerospace. Its brittleness and low tensile strength make it unsuitable for carrying flight loads.
Graphite Fibers are the Key Ingredient
The "graphite" that revolutionizes aerospace consists of microscopic crystalline filaments of carbon. These fibers, often thinner than a human hair, are incredibly strong and stiff along their length. They are produced through a highly controlled heating process called pyrolysis.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) is the End Product
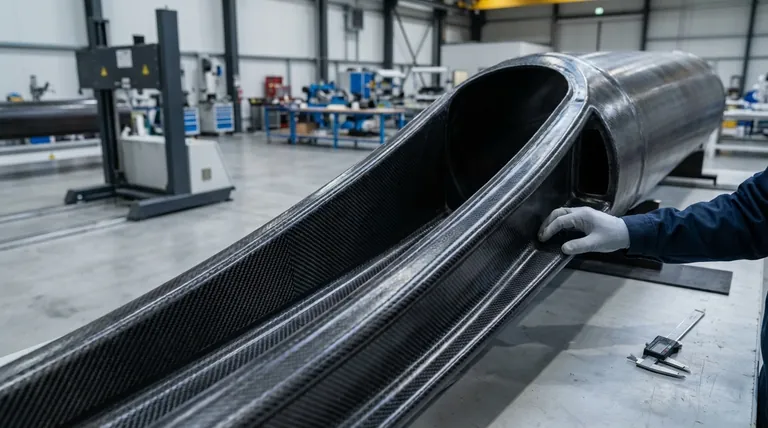
These individual graphite fibers are woven into fabrics or aligned in sheets and then impregnated with a polymer matrix, typically an epoxy resin. After being cured under heat and pressure, this forms a solid, rigid material known as Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) or, more simply, a "graphite composite." Think of the graphite fibers as rebar and the polymer matrix as the concrete holding it all together.
Why Graphite Composites Dominate Aerospace Design
Metals like aluminum and titanium were the standard for decades, but the unique properties of CFRPs provide a decisive advantage in many applications.
Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
This is the single most important property. A CFRP component can have the same strength as a steel or aluminum part but at a fraction of the weight. This directly translates to increased fuel efficiency, greater payload capacity, and higher performance.
Superior Stiffness and Dimensional Stability
Graphite composites are extremely stiff, meaning they resist bending and flexing under load. This is critical for maintaining the precise aerodynamic shape of wings and control surfaces, ensuring maximum efficiency and predictable handling.
Excellent Fatigue and Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, which can develop micro-cracks and fail after repeated stress cycles (fatigue), CFRP is highly resistant to it. It also does not corrode like aluminum, leading to longer service life and significantly reduced maintenance costs for an aircraft's airframe.
Design and Manufacturing Flexibility
Composites can be molded into complex, aerodynamic shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create from metal. This allows for the creation of single, large parts—like an entire fuselage section—reducing the number of joints and fasteners, which are common points of failure and add weight.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite its advantages, graphite composite is not a perfect material. Engineers must contend with significant challenges.
High Material and Manufacturing Costs
The raw materials and the energy-intensive manufacturing process make CFRP significantly more expensive than aluminum alloys. This cost is a major consideration in any design decision.
Complex Damage Detection and Repair
Damage to a composite structure can be difficult to identify. While a metal part will dent, a composite can suffer from internal delamination (separation of the layers) with little visible surface damage. Repairing these structures is also a specialized, time-consuming process.
Lower Impact Resistance
CFRP can be more brittle than ductile metals. A sharp impact from a dropped tool or runway debris can cause significant subsurface damage that compromises the material's strength, whereas an aluminum skin might only dent.
Galvanic Corrosion Risk
When graphite composites are in direct contact with certain metals, particularly aluminum, they can create an electrical circuit in the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture). This causes the metal to corrode rapidly, a phenomenon known as galvanic corrosion, which requires careful design and isolation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use graphite composites versus traditional metals is a complex engineering trade-off based on the specific mission requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and fuel efficiency: Graphite composites are the superior choice for primary structures like wings, fuselages, and control surfaces, as seen in the Boeing 787 and Airbus A350.
- If your design is cost-sensitive or requires high impact toughness: Traditional alloys like aluminum and titanium remain essential, especially for components in high-impact zones or where cost is the main driver.
- If you are designing for extreme thermal environments: Specialized forms like Carbon-Carbon composites (where both fiber and matrix are carbon) are necessary for parts like rocket nozzles and vehicle heat shields that must withstand thousands of degrees.
Understanding the precise properties and limitations of graphite-based materials is fundamental to advancing the field of aerospace engineering.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Graphite in Aerospace |
|---|---|
| Primary Form | High-strength graphite fibers (carbon fiber) |
| Key Application | Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched strength-to-weight ratio |
| Common Uses | Wings, fuselages, control surfaces, rocket nozzles |
| Main Challenge | High cost and complex damage detection/repair |
Ready to elevate your aerospace or laboratory projects with advanced materials? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including materials testing solutions essential for developing and analyzing graphite composites. Our expertise supports the precise research and quality control needed in aerospace engineering. Contact our experts today to discover how KINTEK can empower your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 types of biomass? A Guide to Woody, Agricultural, and Waste Sources
- Is a carbon brush a good conductor of electricity? The Surprising Engineering Choice
- Under what conditions should a carbon fiber brush be replaced? Identify Critical Failure to Ensure Performance
- How should a carbon fiber brush be stored after cleaning? Preserve Performance and Longevity
- Why is it important to prevent mechanical damage to a carbon fiber brush? Ensure Peak Performance & Longevity



















