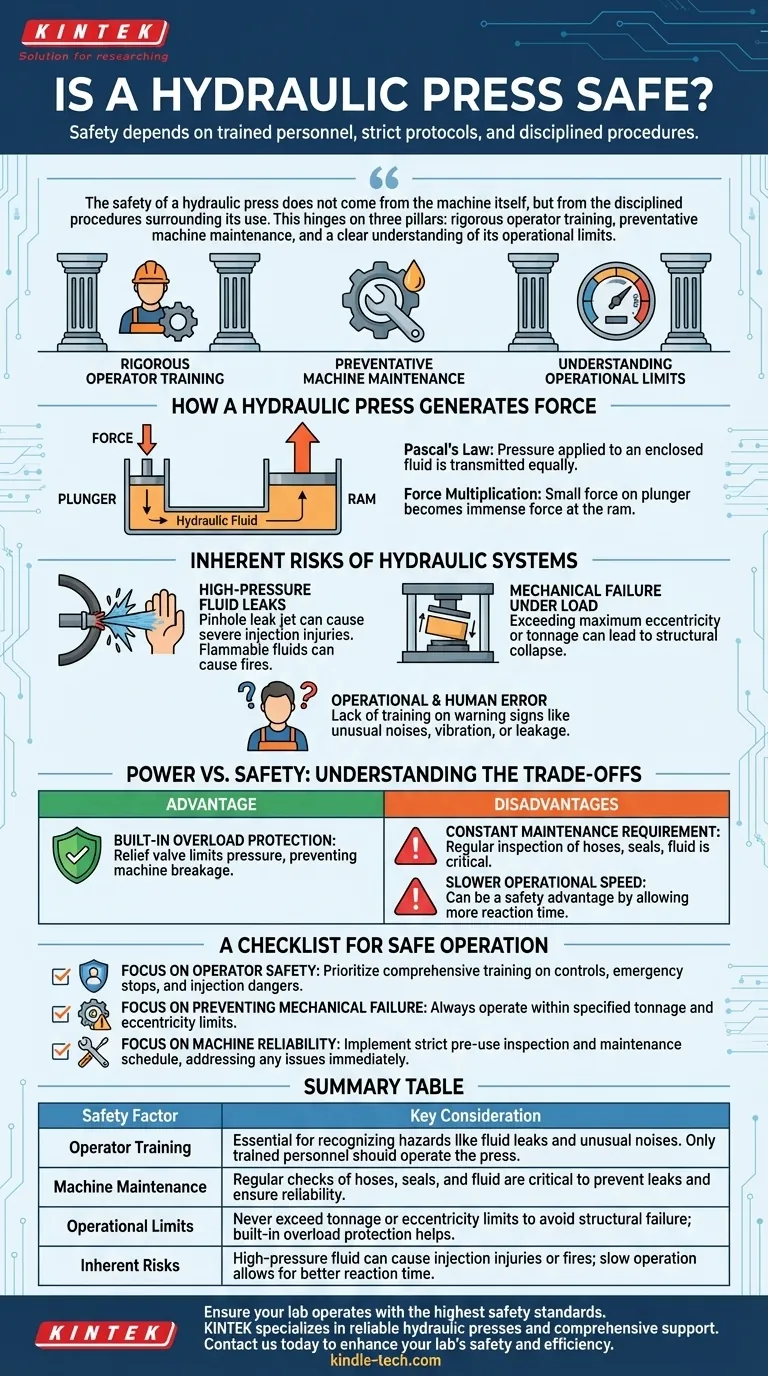
A hydraulic press is safe only when operated by trained personnel who strictly adhere to established safety and maintenance protocols. While these machines are designed with features like built-in overload protection, the immense force they generate through high-pressure fluid systems introduces significant risks that must be actively managed.
The safety of a hydraulic press does not come from the machine itself, but from the disciplined procedures surrounding its use. This hinges on three pillars: rigorous operator training, preventative machine maintenance, and a clear understanding of its operational limits.

How a Hydraulic Press Generates Force
A hydraulic press operates on a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics known as Pascal's Law. This law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
The Core Components
A press consists of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes, a plunger (smaller cylinder) and a ram (larger cylinder), filled with hydraulic fluid. A pump applies force to the fluid via the plunger.
The Principle of Force Multiplication
Because the pressure is distributed equally, the force exerted by the ram is proportional to its larger surface area. This allows a small force applied to the plunger to be multiplied into an immense force at the ram, capable of shaping, cutting, or crushing heavy materials.
The Inherent Risks of Hydraulic Systems
The very source of a hydraulic press's power—high-pressure fluid—is also the source of its primary hazards. Understanding these risks is the first step toward mitigating them.
High-Pressure Fluid Leaks
Hydraulic fluid is held under extreme pressure. A pinhole leak can release a fine jet of fluid at a velocity high enough to penetrate skin, causing severe injection injuries.
Furthermore, some hydraulic fluids are flammable, meaning a leak near an ignition source can result in a fire.
Mechanical Failure Under Load
Exceeding the machine's designed limits is a direct path to catastrophic failure. The references specifically warn against using the press if it exceeds the maximum limit of eccentricity, meaning the load is not centered properly.
An off-center load places immense and uneven stress on the frame and components, which can lead to structural collapse.
Operational and Human Error
The most significant variable in press safety is the operator. Without proper training, an operator may not recognize warning signs like unusual noises, excessive vibration, or serious oil leakage.
These are critical indicators that the machine must be stopped immediately to prevent a larger failure. Only trained and authorized personnel should ever operate the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Power vs. Safety
The design of a hydraulic press presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages that directly impact its safety profile.
Advantage: Built-in Overload Protection
A key safety benefit is its natural overload protection. The maximum pressure is controlled by a relief valve. Once this pressure is reached, the system will not build any more, preventing the operator from applying a force that would break the machine.
Disadvantage: Constant Maintenance Requirement
Unlike simpler mechanical machines, hydraulic systems require regular maintenance. Hoses, seals, and the fluid itself must be inspected and replaced on a schedule to prevent leaks and ensure reliable operation.
Disadvantage: Slower Operational Speed
Hydraulic presses are generally slower than their mechanical counterparts. While this can be a drawback for high-volume production, the slower, more controlled movement can be a safety advantage, giving the operator more time to react.
A Checklist for Safe Operation
To ensure safety, you must move from understanding the risks to implementing concrete procedures.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize comprehensive training on specific machine controls, emergency stop procedures, and the dangers of high-pressure fluid injection.
- If your primary focus is preventing mechanical failure: Always operate within the machine's specified limits for tonnage and eccentricity, and never attempt to bypass the built-in overload protection.
- If your primary focus is machine reliability: Implement a strict pre-use inspection and maintenance schedule, immediately addressing any fluid leaks, unusual noises, or vibrations.
By respecting the machine's power and adhering to disciplined safety protocols, you can harness its capabilities safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Safety Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Operator Training | Essential for recognizing hazards like fluid leaks and unusual noises. Only trained personnel should operate the press. |
| Machine Maintenance | Regular checks of hoses, seals, and fluid are critical to prevent leaks and ensure reliability. |
| Operational Limits | Never exceed tonnage or eccentricity limits to avoid structural failure; built-in overload protection helps. |
| Inherent Risks | High-pressure fluid can cause injection injuries or fires; slow operation allows for better reaction time. |
Ensure your lab operates with the highest safety standards. A hydraulic press is a powerful tool, but its safety depends on proper use and maintenance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable hydraulic presses and comprehensive support. Our experts can help you choose the right press and provide guidance on safety protocols and maintenance schedules. Contact us today to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency—Reach out now for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press essential for LATP solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure High-Density Ion Conductivity
- How many pounds of force does a hydraulic press have? Find Your Ideal Tonnage for Any Application
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used for stainless steel surface modification? Prevent Organic Acid Corrosion
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses improve the molding quality of wood pellet fuel? Enhance Density and Durability
- What are the samples used in XRF? Unlock Accurate Results with Proper Sample Preparation
- Why is 10 MPa pressure necessary for all-solid-state lithium coin cells? Enhance Interfacial Contact and Performance
- What is the purpose of using mechanical pressure in DSSC assembly? Optimize Photoanode and Counter Electrode Stability
- What is the construction of a hydraulic press based on? Unlocking the Power of Pascal's Law



















