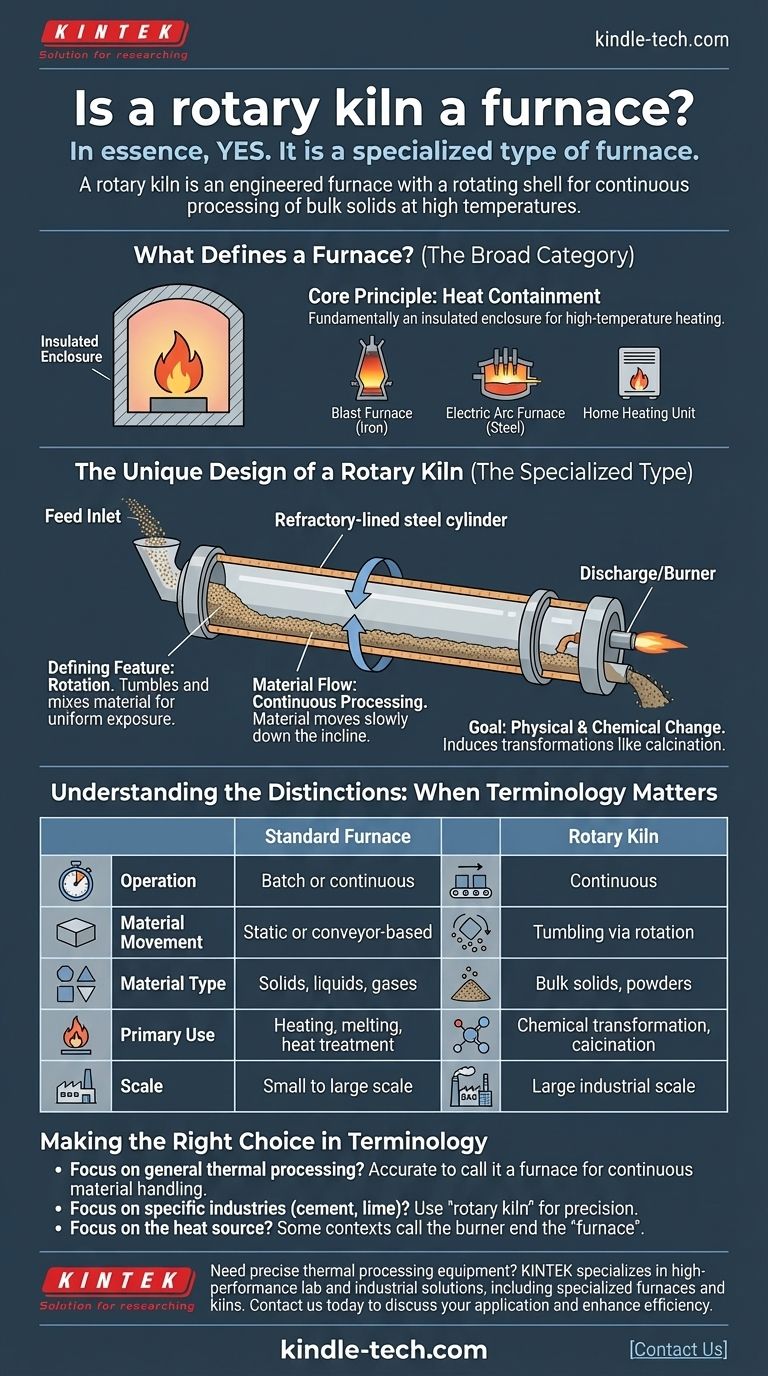
In essence, yes, a rotary kiln is a specialized type of furnace. While all kilns can be considered furnaces, not all furnaces are kilns. A rotary kiln is a furnace specifically engineered with a rotating cylindrical shell to continuously process bulk solid materials at high temperatures.
The critical distinction lies in function and mechanics. A furnace is a broad term for any enclosed structure that generates and contains high heat. A rotary kiln is a specific type of furnace defined by its rotation, which actively tumbles and mixes materials as they are heated and transported.
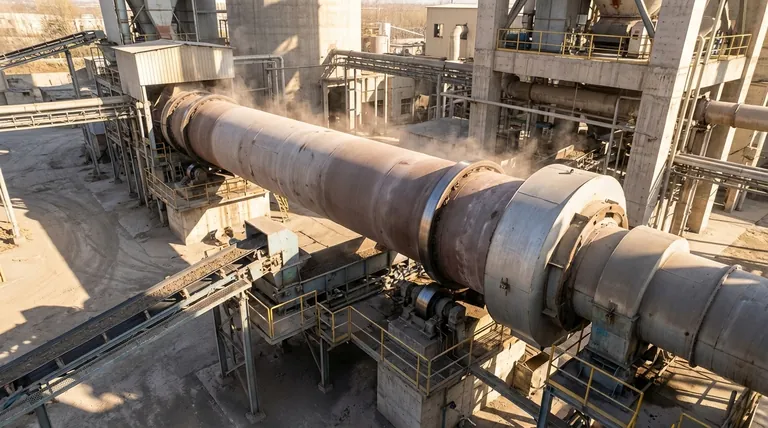

What Defines a Furnace?
To understand the relationship, we must first establish a clear definition for the broader category of equipment.
The Core Principle: Heat Containment
A furnace is fundamentally an insulated enclosure designed to heat materials to very high temperatures. Its primary job is to contain thermal energy efficiently and safely to facilitate a specific process.
A Broad Family of Equipment
The term "furnace" covers a vast range of industrial and domestic equipment. This includes blast furnaces for iron production, electric arc furnaces for steelmaking, and even the simple heating unit in a home's central air system.
The Unique Design of a Rotary Kiln
A rotary kiln is a highly specialized furnace with distinct mechanical features that enable unique processes.
The Defining Feature: Rotation
The kiln is a long, refractory-lined steel cylinder mounted at a slight angle. Its slow rotation (typically 1-3 revolutions per minute) is its most important characteristic.
This rotation lifts and tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the hot gases flowing through the cylinder.
Material Flow: Continuous Processing
Unlike a "batch" furnace that heats a single, static load, a rotary kiln is built for continuous operation. Material is constantly fed into the upper end and slowly travels down the length of the kiln due to the incline and rotation, eventually exiting the lower end as a finished product.
The Goal: Physical and Chemical Change
The combination of heat and mechanical mixing in a kiln is designed to induce specific physical and chemical transformations. This is its primary purpose in industries like cement manufacturing (calcination), mineral processing, and waste incineration.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When the Distinction Matters
While technically a type of furnace, calling a rotary kiln just a "furnace" misses the critical details of its operation. The distinction is crucial for understanding its capabilities and limitations.
Process Control and Uniformity
The tumbling action inside a rotary kiln provides a level of mixing and heat transfer uniformity that is impossible to achieve in a static furnace. This is essential for processes where every particle must reach a specific temperature for a precise duration.
Material Suitability
Rotary kilns are exclusively designed for granular, powdered, or lumpy bulk solids. A static furnace, by contrast, might be used for melting metals (which become liquid) or firing large, solid objects like ceramics or bricks.
Industrial Scale and Efficiency
The continuous, flow-through design of a rotary kiln makes it exceptionally well-suited for massive-scale industrial production, processing hundreds or thousands of tons per day. Its design is optimized for the energy efficiency required at that scale.
Making the Right Choice in Terminology
Using the correct term demonstrates a clear understanding of the process and equipment involved.
- If your primary focus is general thermal processing: It is accurate to describe a rotary kiln as a furnace designed for continuous material handling.
- If your primary focus is a specific industry (cement, lime, alumina): You must use the term "rotary kiln" for precision, as it describes the central piece of equipment with functions no generic furnace can perform.
- If your primary focus is the heat source itself: In some contexts, engineers may refer to the burner and combustion chamber at the discharge end of the kiln as the "furnace," distinguishing it from the kiln shell where material processing occurs.
Understanding this relationship moves you from a general concept to a specific, operational reality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Furnace | Rotary Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Batch or continuous | Continuous |
| Material Movement | Static or conveyor-based | Tumbling via rotation |
| Material Type | Solids, liquids, gases | Bulk solids, powders |
| Primary Use | Heating, melting, heat treatment | Chemical transformation, calcination |
| Scale | Small to large scale | Large industrial scale |
Need precise thermal processing equipment for your lab or production facility? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and industrial solutions, including specialized furnaces and kilns for continuous processing. Our experts can help you select the right system for uniform heating, chemical transformations, and efficient bulk material handling. Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a carbon regeneration kiln? Reuse Spent Carbon to Cut Costs & Waste
- How does a rotary calciner work? Achieve Uniform Thermal Processing for Bulk Solids
- What is the process of carbon regeneration? Restore Spent Carbon for Cost-Effective, Sustainable Use
- What happens in a rotary kiln? A Guide to Continuous High-Temperature Processing
- What is the sintering process in kilns? Transform Powder into Dense, High-Strength Components
- Do electric kilns use a lot of electricity? Understanding Kiln Power Consumption and Costs
- What are the factors affecting calcination? Master Temperature, Time, Atmosphere & Material Properties
- What is the residence time of microwave pyrolysis? Achieve Fast, Efficient Biomass Conversion



















