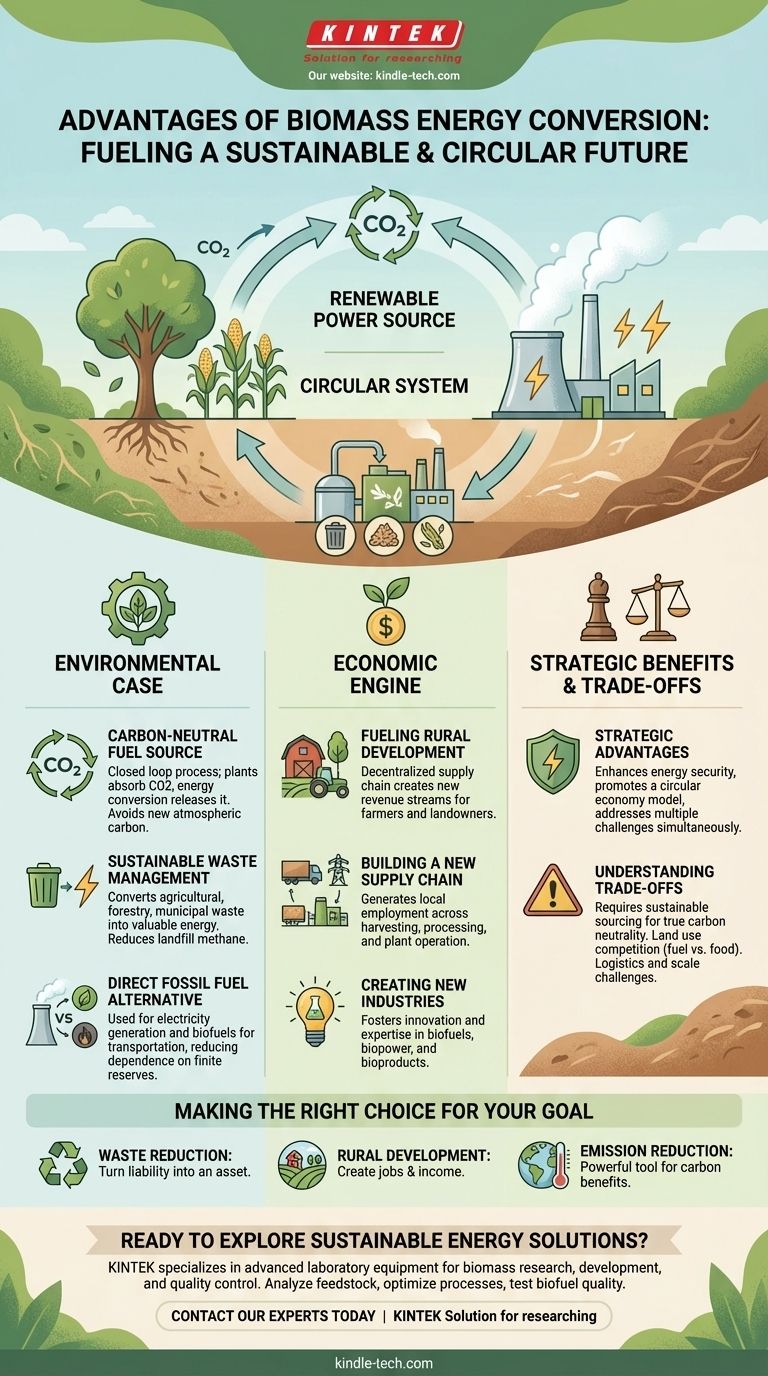
At its core, biomass energy conversion is a strategy for transforming organic materials into a reliable and renewable power source. The primary advantages are its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by offsetting fossil fuel use, create economic value from waste products, and stimulate development in rural economies.
The true advantage of biomass is not just that it is a renewable fuel source, but that it creates a circular system. It repurposes organic waste into a valuable energy asset, simultaneously addressing challenges in waste management, energy security, and economic development.

The Environmental Case for Biomass
The most frequently cited benefits of biomass conversion relate to its environmental impact. This stems from its unique position within the planet's natural carbon cycle and its ability to solve other environmental problems.
A Carbon-Neutral Fuel Source
Biomass is considered carbon-neutral in principle. As plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. When this biomass is converted to energy, it releases that same CO2 back, creating a closed loop. This process avoids adding new carbon to the atmosphere, unlike the burning of fossil fuels.
Sustainable Waste Management
A significant advantage is the ability to convert agricultural, forestry, and municipal organic waste into energy. This process turns a disposal problem—which can lead to methane emissions in landfills—into a valuable resource, effectively solving two problems at once.
A Direct Alternative to Fossil Fuels
Biomass can be used in power plants to generate electricity, sometimes by co-firing with coal to reduce overall emissions. It can also be processed into biofuels, providing a renewable alternative for the transportation sector and reducing dependence on finite fossil fuel reserves.
The Economic Engine of Biomass
Beyond the environmental benefits, biomass conversion offers compelling economic opportunities, particularly for local and rural communities.
Fueling Rural Development
The biomass supply chain is inherently decentralized. It relies on sourcing materials from agriculture and forestry, creating consistent demand and new revenue streams for farmers and landowners. This stimulates economic activity in rural areas that may have limited industrial opportunities.
Building a New Supply Chain
From cultivation and harvesting to transportation, processing, and plant operation, the entire biomass lifecycle generates local employment. It supports a diverse ecosystem of jobs that strengthen local economies.
Creating New Industries
The development of biomass conversion technologies fosters innovation and creates new industries. As the world transitions to cleaner energy, expertise in biofuels, biopower, and bioproducts becomes an increasingly valuable economic asset.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the advantages are significant, a balanced perspective requires acknowledging the challenges. True sustainability depends entirely on responsible implementation.
The Nuance of Carbon Neutrality
The "carbon-neutral" label assumes the biomass is sourced sustainably. If forests are not replanted, or if significant fossil fuel energy is used to harvest and transport the biomass, the net carbon benefit is reduced.
Land Use and Resource Competition
Using dedicated energy crops for biomass raises a critical debate about land use competition. Prioritizing land for fuel over food can have significant social and ethical implications that must be carefully managed.
The Challenge of Scale
Biomass has a lower energy density than fossil fuels, meaning more material is needed to produce the same amount of energy. This can make logistics, storage, and transportation complex and costly, often limiting biomass plants to a smaller, more decentralized scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating biomass requires aligning its specific strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Biomass is an exceptional choice for creating a circular economy, turning liability (organic waste) into an asset (energy).
- If your primary focus is rural economic development: Biomass projects offer one of the most direct ways to create jobs and stable income in agricultural and forestry communities.
- If your primary focus is reducing greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass is a powerful tool, provided it is sourced from sustainably managed resources or waste streams to ensure true carbon benefits.
Biomass energy represents a critical bridge, connecting the goals of sustainable waste management with the production of renewable energy.
Summary Table:
| Advantage Category | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Carbon-neutral energy, sustainable waste management, fossil fuel alternative |
| Economic | Rural development, new jobs and revenue streams, creation of new industries |
| Strategic | Energy security, circular economy model, addresses multiple challenges simultaneously |
Ready to explore sustainable energy solutions for your operations?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables needed for biomass research, development, and quality control. Whether you're analyzing feedstock, optimizing conversion processes, or testing biofuel quality, our reliable tools help you innovate with confidence.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your biomass energy projects and help you build a more sustainable future.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth



















