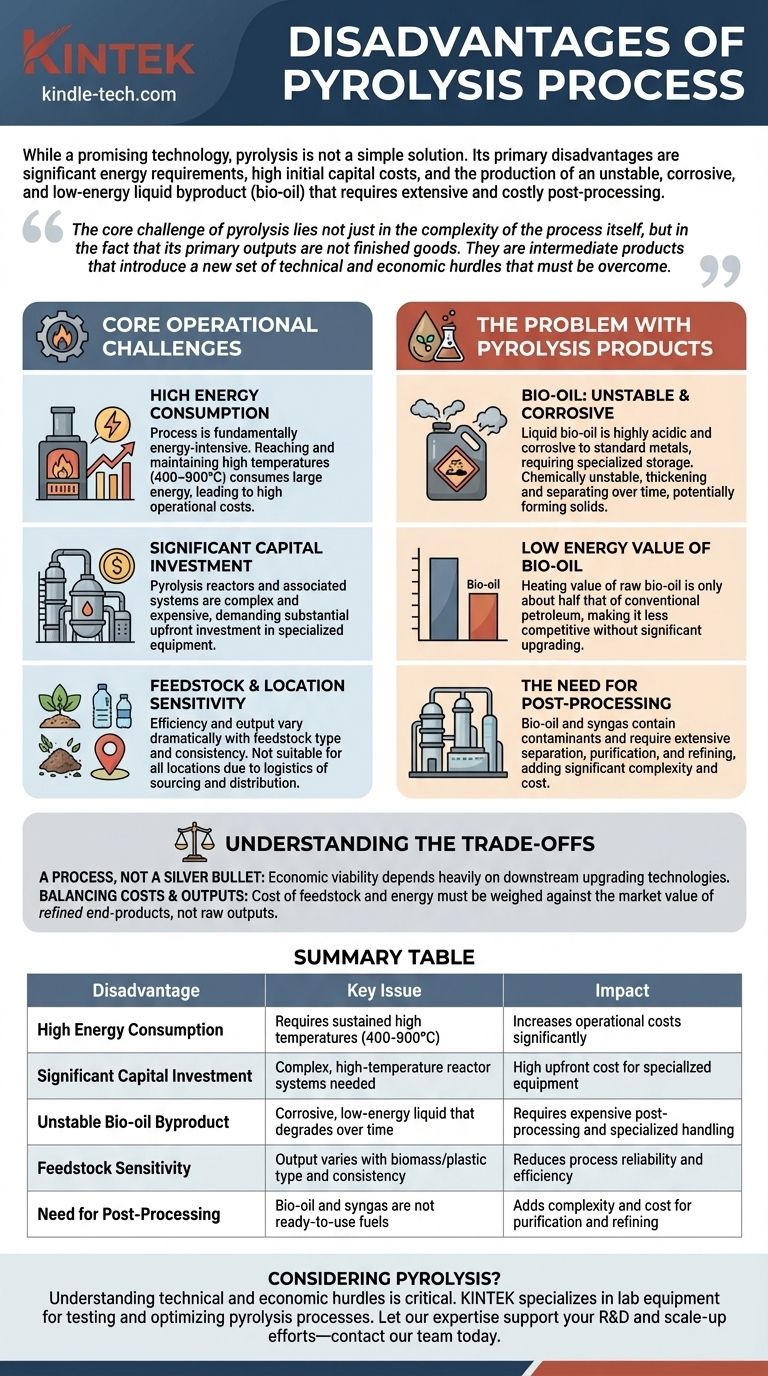
While a promising technology, pyrolysis is not a simple solution. Its primary disadvantages are significant energy requirements, high initial capital costs, and the production of an unstable, corrosive, and low-energy liquid byproduct (bio-oil) that requires extensive and costly post-processing before it can be used.
The core challenge of pyrolysis lies not just in the complexity of the process itself, but in the fact that its primary outputs are not finished goods. They are intermediate products that introduce a new set of technical and economic hurdles that must be overcome.

The Core Operational Challenges
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that heats material like biomass or plastic to high temperatures (typically 400-900°C) in an oxygen-free environment. While effective, the operational realities present significant barriers.
High Energy Consumption
The process is fundamentally energy-intensive. Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for decomposition consumes a large amount of energy, which translates directly into high operational costs.
Significant Capital Investment
Pyrolysis reactors and their associated systems are complex and expensive. They must be engineered to handle extreme temperatures and precisely control the atmosphere, demanding a substantial upfront investment in specialized equipment.
Feedstock and Location Sensitivity
The efficiency and output of pyrolysis can vary dramatically depending on the type and consistency of the feedstock. Furthermore, the process may not be suitable for all locations, especially if the logistics of sourcing feedstock or distributing the end products are unfavorable.
The Problem with Pyrolysis Products
A common misconception is that pyrolysis directly produces ready-to-use fuels. In reality, the raw outputs—bio-oil, syngas, and bio-char—each come with their own set of limitations.
Bio-oil: Unstable and Corrosive
The liquid bio-oil is perhaps the most challenging product. It is highly acidic and corrosive to standard metals, requiring specialized storage and handling equipment.
Worse, it is chemically unstable. Over time, bio-oil tends to thicken, increase in viscosity, and can even separate into different phases due to slow, ongoing chemical reactions. Heating it can accelerate these reactions, potentially forming solids.
Low Energy Value of Bio-oil
The heating value of raw bio-oil is only about half that of conventional petroleum-based heating oil. This makes it less competitive as a direct drop-in fuel replacement without significant upgrading.
The Need for Post-Processing
Neither the bio-oil nor the syngas are pure enough for most high-value applications. They contain contaminants and require extensive separation, purification, and refining before they can be used as transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks. This multi-step upgrading process adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is crucial to view pyrolysis not as a single, complete solution but as the first step in a longer and more complex value chain.
A Process, Not a Silver Bullet
The economic viability of a pyrolysis plant often depends less on the pyrolysis step itself and more on the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the downstream upgrading technologies. Without a clear and economical path to refine the outputs, the entire project can fail.
Balancing Costs and Outputs
Success requires a careful calculation. The cost of acquiring feedstock and the high energy cost of the operation must be weighed against the market value of the refined end-products, not the raw outputs.
Making an Informed Decision on Pyrolysis
To determine if pyrolysis is the right approach, you must first clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is highly effective, but you must have a clear, budgeted plan for managing and processing the unstable bio-oil and other byproducts it creates.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value fuels: Be prepared for significant downstream investment in hydrotreating or other upgrading technologies to stabilize the bio-oil, remove corrosive elements, and increase its energy density.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: The stability and market value of the resulting bio-char are your most critical metrics, and the process's overall energy balance must be carefully audited.
Understanding these inherent disadvantages is the first step toward developing a technically sound and economically viable pyrolysis project.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Energy Consumption | Requires sustained high temperatures (400-900°C) | Increases operational costs significantly |
| Significant Capital Investment | Complex, high-temperature reactor systems needed | High upfront cost for specialized equipment |
| Unstable Bio-oil Byproduct | Corrosive, low-energy liquid that degrades over time | Requires expensive post-processing and specialized handling |
| Feedstock Sensitivity | Output varies with biomass/plastic type and consistency | Reduces process reliability and efficiency |
| Need for Post-Processing | Bio-oil and syngas are not ready-to-use fuels | Adds complexity and cost for purification and refining |
Considering pyrolysis for your waste or energy project? Understanding the technical and economic hurdles is critical to success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for testing and optimizing pyrolysis processes, helping you accurately assess feedstock viability, analyze bio-oil quality, and plan for downstream upgrading. Let our expertise support your R&D and scale-up efforts—contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What material are furnace tubes? Choosing the Right Material for High-Temperature Success
- What is a tube furnace used for? Achieve Precise, Controlled Thermal Processing
- What is the high temperature of a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Model for Your Application
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control



















