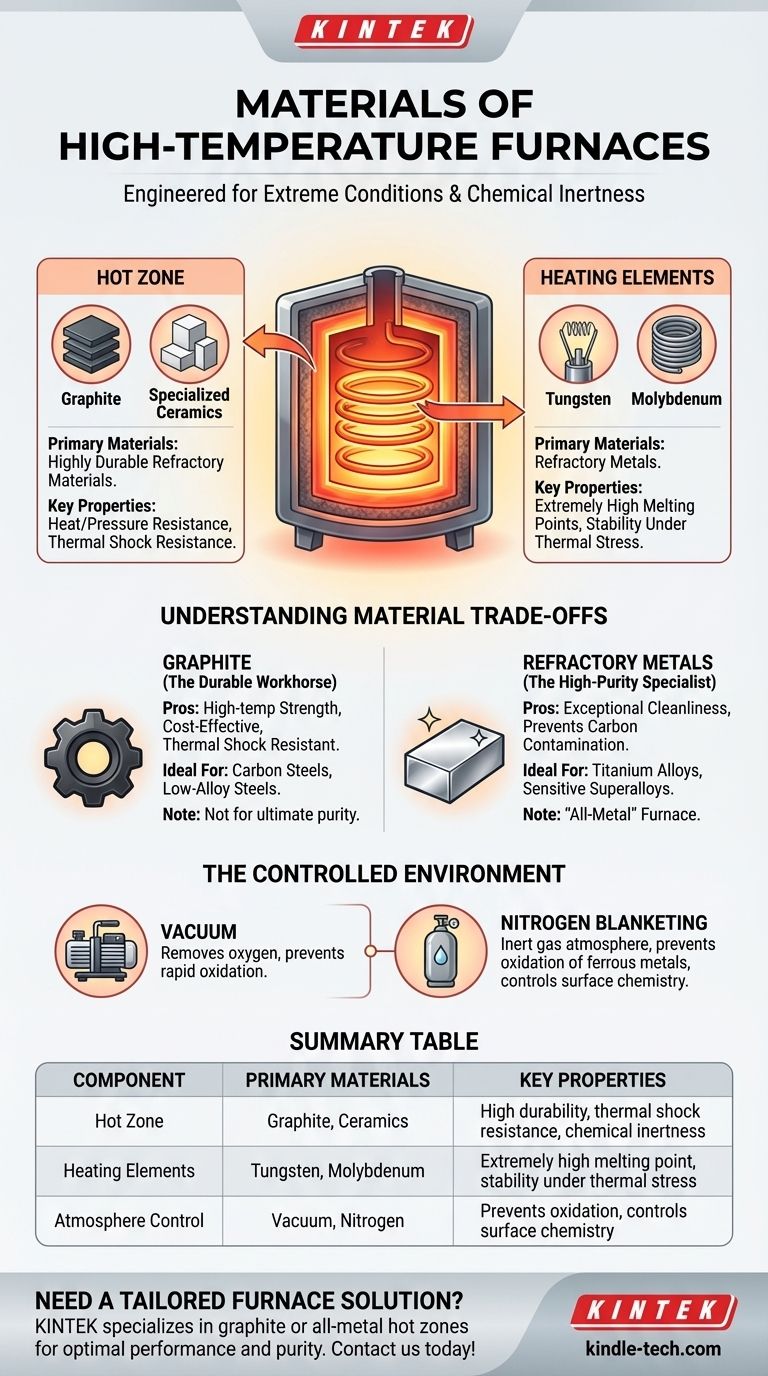
At their core, high-temperature furnaces are constructed from a select group of materials engineered to endure extreme conditions. The main body, or "hot zone," is typically made from highly durable refractory materials like graphite or specialized ceramics. The components that generate the intense heat, the heating elements, are almost always made of refractory metals such as tungsten or molybdenum.
The central principle behind a high-temperature furnace is not just heat resistance, but also chemical inertness. The materials are chosen to create a stable, controlled environment that can heat a workpiece to extreme temperatures without contaminating it or reacting with it.
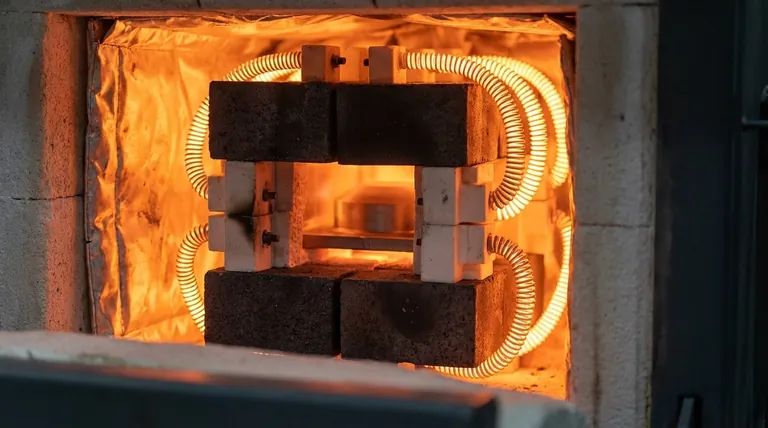
The Core Components of a Furnace
A high-temperature furnace is a system of specialized parts, each made from materials chosen for a specific function. The two most critical areas are the structural hot zone and the heating elements themselves.
The "Hot Zone": The Heart of the Furnace
The hot zone is the insulated chamber that contains the workpiece and withstands the highest temperatures. Its construction is fundamental to the furnace's performance.
The most common materials are refractory materials, which are defined by their exceptional resistance to heat and pressure. Graphite is the most widely used due to its excellent durability, structural integrity at high temperatures, and relatively low cost.
For other applications, specialized ceramics may be used for their unique insulating properties and chemical stability.
Heating Elements: The Source of Extreme Heat
The components responsible for generating the heat must have extremely high melting points and remain stable under immense thermal stress.
This is why refractory metals are the standard choice. Tungsten and molybdenum are frequently used because they can operate at the extreme temperatures required for processing advanced alloys and materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Refractory Metals
The choice of material for the hot zone is one of the most significant design decisions, creating a fundamental trade-off between cost, durability, and operational purity.
Graphite: The Durable Workhorse
Graphite is the most common material for furnace hot zones. Its combination of high-temperature strength, thermal shock resistance, and cost-effectiveness makes it the ideal choice for a wide range of applications.
It is particularly well-suited for processing carbon steels, low-alloy steels, and many iron-based alloys where ultimate purity is not the primary concern.
Refractory Metals: The High-Purity Specialist
When the process demands an exceptionally clean environment, a hot zone made entirely of refractory metals is required. This is often called an "all-metal" furnace.
These furnaces are essential for processing highly reactive or sensitive materials like titanium alloys or certain medical-grade superalloys. The metal interior prevents potential carbon contamination that could occur in a graphite-lined furnace.
The Controlled Environment: More Than Just Heat
The physical structure of the furnace is only half the story. The atmosphere inside the furnace is just as critical and is carefully controlled to protect the workpiece.
The Role of a Vacuum
Most high-temperature furnaces are also vacuum furnaces. Pulling a vacuum removes oxygen and other atmospheric gases that would cause rapid oxidation and damage to the material being heated.
Why Nitrogen is Used
In many processes, an inert gas like nitrogen is intentionally introduced into the chamber after the vacuum is established. This process, known as nitrogen blanketing, creates a positive pressure of non-reactive gas.
This nitrogen atmosphere serves to prevent oxidation of ferrous metals and can help control the surface chemistry of steel products, a process known as decarburization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The materials used to construct a furnace directly dictate its capabilities and ideal applications. Understanding this link is key to achieving the desired metallurgical results.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment of steels and alloys: A furnace with a graphite-based hot zone offers the best balance of performance, durability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or high-purity materials like titanium: An all-metal furnace with a refractory metal hot zone is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure material integrity.
Ultimately, the construction of a high-temperature furnace is a deliberate exercise in materials science, designed to create a perfectly controlled world of extreme heat.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Zone | Graphite, Ceramics | High durability, thermal shock resistance, chemical inertness |
| Heating Elements | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Extremely high melting point, stability under thermal stress |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum, Nitrogen | Prevents oxidation, controls surface chemistry |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your specific material processing goals? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing furnaces with graphite or all-metal hot zones to ensure optimal performance and purity for your laboratory needs. Whether you're heat-treating steels or processing sensitive alloys like titanium, our expertise ensures you get the right solution. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab



















