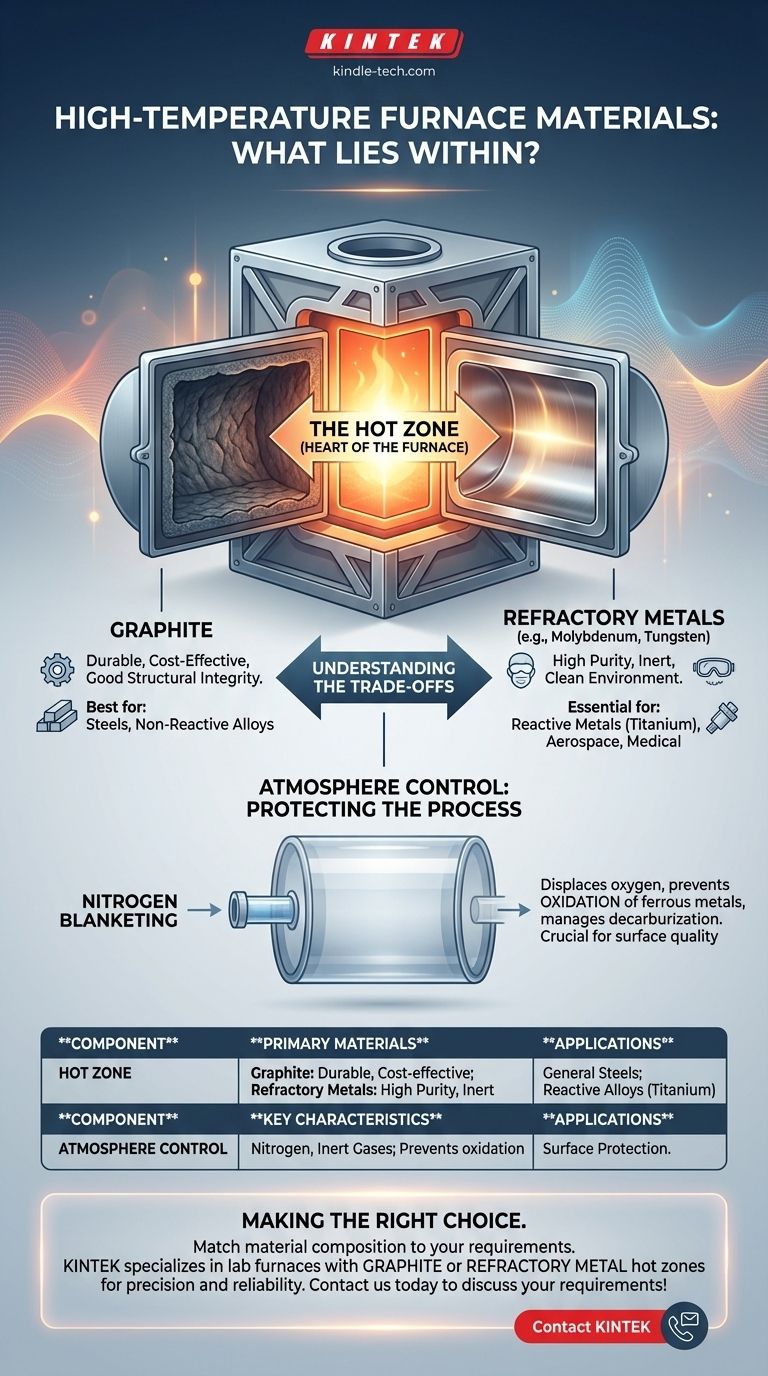
At their core, high-temperature furnaces are constructed from a system of specialized materials designed to contain extreme heat, with the internal "hot zone" typically made of either graphite or refractory metals. The outer body provides structural support, while internal systems manage the atmosphere to protect the materials being processed.
The choice of material for a high-temperature furnace is not merely about withstanding heat. It is a critical decision that dictates the furnace's cleanliness, operational cost, and suitability for processing specific materials like reactive alloys or common steels.

Deconstructing the High-Temperature Furnace
A furnace is more than just a hot box; it's an engineered system. The materials for each component are chosen to fulfill a specific function, from structural integrity to chemical inertness at temperatures up to 1800°C.
The Internal Chamber (The "Hot Zone")
This is the heart of the furnace where the heat is generated and the work is done. The material choice here is paramount.
The most common material for the hot zone is graphite. Its popularity stems from its excellent durability, structural integrity at high temperatures, and relatively low cost.
The alternative is a hot zone constructed from refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten. These are chosen for applications that demand an exceptionally clean environment, free from the carbon particles present in a graphite system.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
Simply reaching a high temperature is not enough; the chemical environment within the furnace is just as important. Uncontrolled atmospheres can lead to oxidation and ruin the materials being heat-treated.
This is why many furnaces use a nitrogen blanketing process. Nitrogen, an inert gas, is pumped into the chamber through inlets and flowmeters to displace oxygen.
This controlled atmosphere prevents the oxidation of ferrous metals and can help manage the carbon content on the surface of steel products, a process known as decarburization.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Refractory Metals
The decision between a graphite or refractory metal hot zone is a fundamental engineering trade-off. There is no single "best" material; there is only the right material for the application.
The Cost and Durability Factor
For a wide range of applications involving carbon steels and other common alloys, graphite is the go-to choice. It offers the best balance of performance, long service life, and cost-effectiveness.
The Cleanliness and Reactivity Factor
When processing materials that can react with carbon, a graphite hot zone becomes a liability. For example, titanium and its alloys require an extremely clean environment.
In these cases, a refractory metal hot zone is essential. It provides the necessary inertness to prevent contamination and ensure the metallurgical purity of the final product. Other sensitive applications, such as in the medical or aerospace fields, also drive the need for refractory metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The material composition of a furnace directly defines its capabilities. To select the correct type, you must first define the requirements of the materials you intend to process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating of steels and other non-reactive alloys: A furnace with a graphite hot zone provides the most cost-effective and durable solution.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals like titanium or applications demanding the highest purity: A furnace with a refractory metal hot zone is non-negotiable to prevent contamination.
Ultimately, understanding these material distinctions is the key to matching the furnace's capability to your specific engineering requirement.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Materials | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Zone | Graphite or Refractory Metals (Molybdenum, Tungsten) | Graphite: Cost-effective, durable. Refractory Metals: High purity, inert. |
| Atmosphere Control | Nitrogen, Inert Gases | Prevents oxidation, controls surface chemistry. |
| Applications | Steels, Reactive Alloys (e.g., Titanium) | Graphite for general use; Refractory Metals for high-purity needs. |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's specific materials? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces with graphite or refractory metal hot zones designed for precision and reliability. Whether you're processing common steels or reactive alloys, our experts will help you select the right solution to enhance your lab's efficiency and ensure contamination-free results. Contact us today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens when a material is annealed? A Guide to Softer, More Workable Materials
- What is the purpose of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What are the disadvantages of quenching? Managing the Risks of Distortion and Cracking
- Why is vacuum drying equipment required for carbide production? Preserve Powder Purity & Prevent Cobalt Oxidation
- What role does a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace play for AISI 316? Ensure Pure Microstructural Standardization
- What is the critical function of high vacuum in Pr3+:CaF2 ceramic preparation? Achieving Optical-Grade Transparency
- Why is a high-temperature annealing furnace used for 316L steel pre-treatment? Ensure High-Energy Pulse Accuracy
- How does a laboratory vacuum oven facilitate the gel content testing of UV-cured silicone rubber films?



















