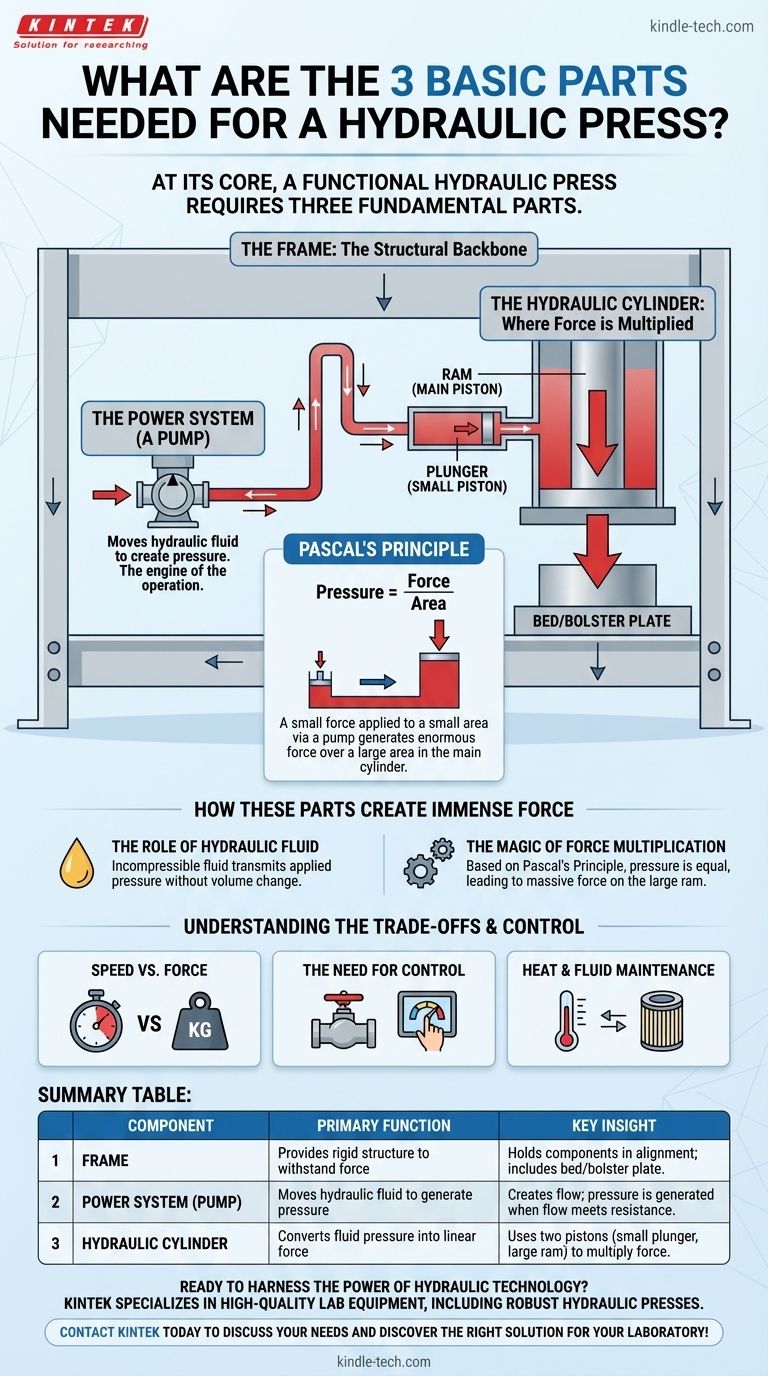
At its core, a functional hydraulic press requires three fundamental parts. These are the Frame which provides the structure, the Power System (a pump) to create fluid pressure, and the Hydraulic Cylinder assembly where that pressure is converted into immense force. These components work in unison, leveraging a simple physical principle to perform work.
The true insight isn't just knowing the parts, but understanding how they embody Pascal's Principle: a small force applied to a small area via a pump generates enormous force over a large area in the main cylinder.

Deconstructing the Core Components
To grasp how a hydraulic press functions, we must first understand the distinct role of each of its three essential parts.
The Frame: The Structural Backbone
The frame is the rigid structure that contains and withstands the massive forces generated by the press. It holds all other components in precise alignment.
This includes the bed or bolster plate, which is the flat surface that supports the material being worked on. Without a strong, unyielding frame, the press would simply deform or break itself apart under its own power.
The Power System: The Source of Pressure
The power system is almost always a pump. Its job is not to create pressure directly, but to move the hydraulic fluid.
Pressure is generated when this flow of incompressible fluid meets resistance, primarily from the load in the main cylinder. The pump is the engine that drives the entire operation.
The Cylinder & Piston: Where Force is Multiplied
This is the heart of the machine. It typically consists of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes: a small plunger (or small piston) and a much larger ram (the main piston).
The pump forces fluid into the small plunger cylinder, which in turn pushes that fluid into the large ram cylinder. This is where the physics of force multiplication occurs.
How These Parts Create Immense Force
The simple arrangement of a pump and two cylinders seems basic, yet it generates incredible power. This is achieved through the properties of the hydraulic fluid and a fundamental law of physics.
The Role of Hydraulic Fluid
Hydraulic presses use a specialized oil because it is effectively incompressible. When you push on it, it doesn't shrink in volume; instead, it transmits the pressure you've applied.
This property ensures that the force exerted by the pump is faithfully transferred through the system to the main ram without loss.
The Magic of Force Multiplication
The entire system operates on Pascal's Principle, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
Because pressure (Force ÷ Area) is the same in both the small plunger and the large ram, a tiny force applied over the small plunger's area results in a massive force over the ram's much larger area.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the concept is powerful, it is governed by physical laws that introduce critical trade-offs and practical considerations.
Speed vs. Force
The primary trade-off is speed for force. To achieve immense force multiplication, the large ram must move much more slowly and over a shorter distance than the small plunger. You cannot get more work out of the system than you put into it.
The Need for Control
A simple system of a pump and cylinders is a brute-force tool. To make it a precise instrument, a control system is necessary.
Components like directional control valves are what allow an operator to manage the speed, direction, and pressure of the ram, making the press a versatile and safe industrial machine.
Heat and Fluid Maintenance
Moving fluid under immense pressure generates significant heat. The system must be designed to manage this heat, and the hydraulic fluid must be kept clean and at proper levels to prevent damage and ensure consistent performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
How you think about these components depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is basic understanding: Think of it as a pump pushing fluid into a powerful cylinder, all held together by a strong frame.
- If your primary focus is the physics: Focus on how two connected pistons of different sizes use an incompressible fluid to multiply force according to Pascal's Principle.
- If your primary focus is practical application: Recognize that control systems, like valves and sensors, are what transform this simple concept into a precise industrial tool.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a masterclass in turning a simple physical law into a machine of immense practical power.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | Provides rigid structure to withstand force | Holds all components in alignment; includes the bed/bolster plate. |
| Power System (Pump) | Moves hydraulic fluid to generate pressure | Creates flow; pressure is generated when flow meets resistance. |
| Hydraulic Cylinder | Converts fluid pressure into linear force | Uses two pistons (small plunger, large ram) to multiply force. |
Ready to harness the power of hydraulic technology in your lab or workshop? The principles of force multiplication are key to efficient material processing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including robust hydraulic presses and consumables designed for precision and durability. Let our experts help you select the perfect press for your specific application, ensuring safety, control, and maximum performance.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your hydraulic press needs and discover the right solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- Why is a laboratory precision hot press necessary for processing high-performance composite solid-state electrolyte membranes?
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification



















