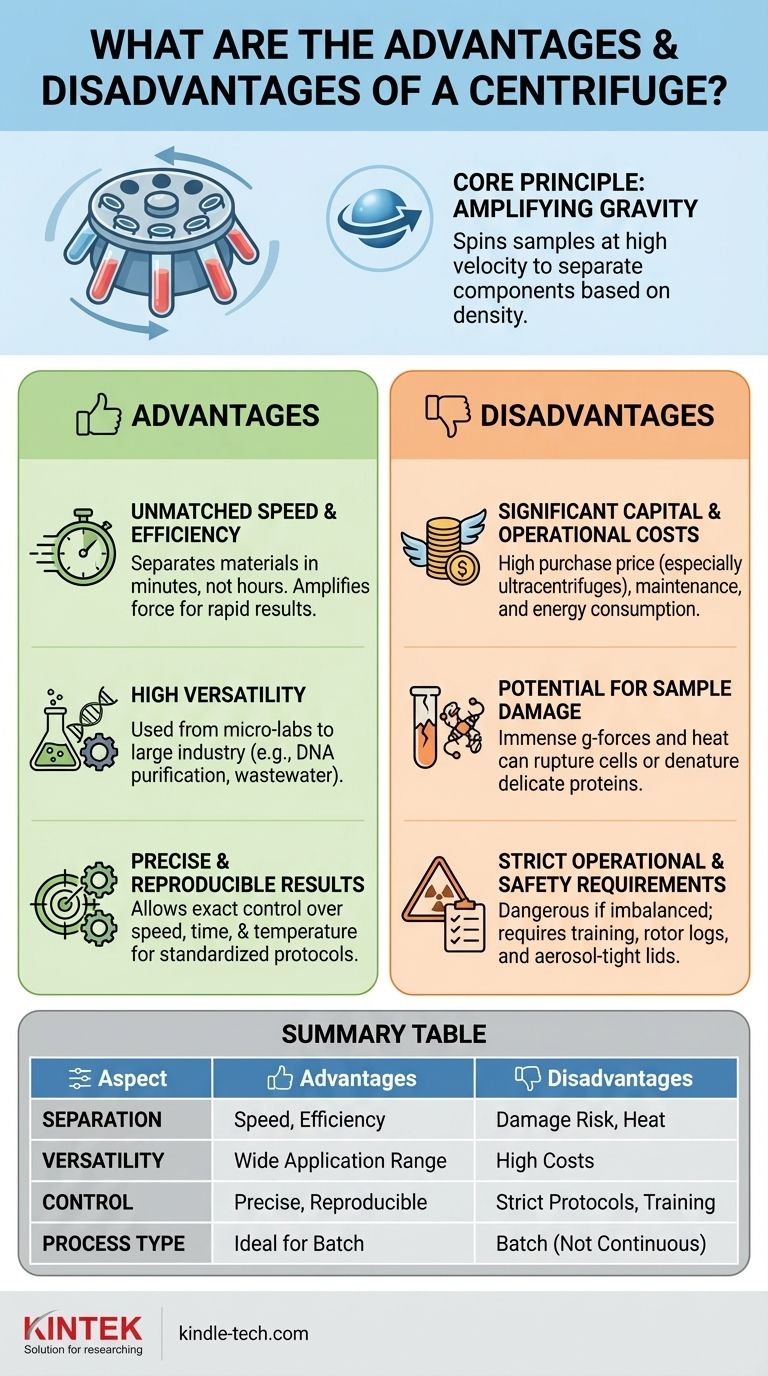
The primary advantage of a centrifuge is its ability to separate materials with incredible speed and efficiency by amplifying the force of gravity. However, this power comes with significant disadvantages, including high equipment cost, operational complexity, and the risk of damaging delicate samples due to the immense forces generated.
A centrifuge offers unparalleled power to separate components from a mixture, making it an indispensable tool in science and industry. The central trade-off is accepting its high cost, strict safety protocols, and the physical stress it places on samples in exchange for this remarkable speed and efficiency.

The Core Principle: Amplifying Gravity
A centrifuge works by spinning samples at high velocity around a fixed axis. This rotation creates a powerful centrifugal force, which is often expressed as a multiple of Earth's gravitational force (g-force or RCF - Relative Centrifugal Force).
This force drives denser particles to move outwards, away from the center of rotation, much faster than they would under normal gravity. Lighter particles or the liquid they are suspended in (the supernatant) remain closer to the top.
How It Enables Separation
By controlling the speed (g-force) and duration of the spin, you can precisely separate components based on their size, shape, and density. A short, low-speed spin might pellet large cells, while a long, ultra-high-speed spin is required to pellet tiny viruses or protein complexes.
Key Advantages of Centrifugation
The ability to generate high g-forces is the source of all of a centrifuge's primary benefits.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
For many applications, centrifugation is the fastest method available for separating a solid from a liquid or separating immiscible liquids. A process that might take hours or days under normal gravity (sedimentation) can be completed in minutes.
High Versatility Across Applications
Centrifuges are used in nearly every scientific and industrial field. Benchtop microcentrifuges are used for DNA purification, large-floor models for harvesting cell cultures, and massive industrial decanter centrifuges for wastewater treatment or food processing.
This versatility extends to the types of samples it can handle, from blood and biological cells to polymers, nanoparticles, and isotopes.
Precise and Reproducible Results
Modern centrifuges allow for precise control over rotational speed, time, and temperature. This makes centrifugation a highly reproducible scientific method, which is critical for standardizing protocols in research and clinical diagnostics.
Understanding the Disadvantages and Risks
The same forces that make a centrifuge so powerful also introduce its most significant drawbacks and dangers.
Significant Capital and Operational Costs
Centrifuges are precision-engineered machines that must withstand enormous forces. This makes them expensive to purchase, with high-speed ultracentrifuges costing hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Costs extend beyond the initial purchase. Rotors, which hold the samples, have a limited lifespan and are also expensive. Furthermore, high-speed operation consumes a significant amount of electricity.
Potential for Sample Damage
The immense g-forces can damage or destroy delicate samples. Shear forces can rupture cells you are trying to study, and the act of forming a hard, dense pellet can denature proteins, rendering them inactive.
Additionally, air friction on a rapidly spinning rotor generates substantial heat, which can damage heat-sensitive samples if the centrifuge does not have a robust refrigeration system.
Strict Operational and Safety Requirements
Improperly operated centrifuges are extremely dangerous. The most critical safety requirement is balancing the rotor. An imbalanced load at high speed can cause the rotor to fail catastrophically, sending metal fragments through the machine's casing.
Proper maintenance, rotor logging to track usage, and aerosol-tight lids (for biohazards) are non-negotiable safety protocols. This requires diligent training and operator discipline.
Primarily a Batch Process
Most laboratory centrifuges are batch-based, meaning you can only process a fixed volume at one time. This can be a bottleneck compared to continuous-flow methods like filtration, especially in large-scale industrial processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing to use a centrifuge, and which type to use, depends entirely on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid separation of small-volume biological samples: A standard benchtop centrifuge is the ideal and indispensable tool for tasks like pelleting cells or precipitating DNA.
- If your primary focus is isolating very small particles like viruses or proteins: An expensive ultracentrifuge is necessary, and you must accept the high cost and potential for sample denaturation.
- If your primary focus is clarifying large, continuous industrial flows: A continuous-flow centrifuge is a powerful option, but you should compare its cost and complexity to alternatives like tangential flow filtration.
- If your primary focus is preserving the integrity of extremely delicate structures: You must weigh the speed of centrifugation against gentler, albeit slower, methods like gravity-based sedimentation or specific types of filtration.
Ultimately, the centrifuge is a powerful tool whose benefits must be carefully weighed against its costs and inherent risks.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Separation | Unmatched speed and efficiency | Can damage delicate samples (shear forces, heat) |
| Versatility | Wide range of applications (labs to industry) | High capital and operational costs |
| Control | Precise, reproducible results | Strict safety protocols and operator training needed |
| Process Type | Ideal for batch processing | Not suitable for continuous flow without specialized models |
Need a Centrifuge That Balances Performance with Safety?
Choosing the right centrifuge is critical for your lab's efficiency and sample integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including centrifuges tailored to your specific application—whether for cell culture, DNA purification, or industrial processing.
Let our experts help you select a centrifuge that maximizes separation speed while minimizing risks and costs. We offer solutions that ensure precise control, durability, and compliance with safety standards.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your centrifugation needs and discover how our equipment can enhance your laboratory workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the most common machine used to sterilize medical supplies? The Definitive Guide to Autoclaves
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam



















