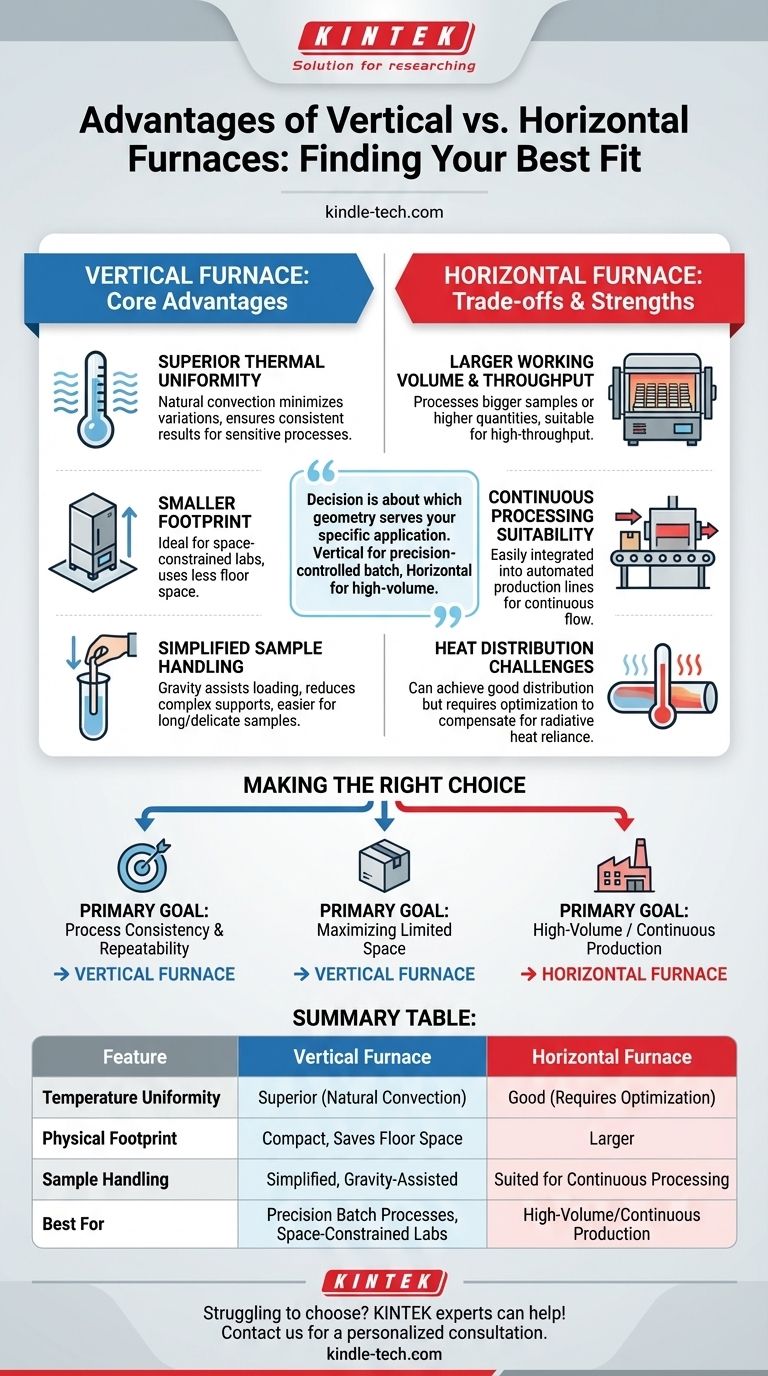
At its core, a vertical furnace offers three primary advantages over a horizontal furnace: superior temperature uniformity, a more compact physical footprint, and often simpler sample handling. These benefits stem directly from its vertical orientation, which leverages gravity and natural convection to create a more stable and efficient processing environment.
The decision between a vertical and horizontal furnace is not about which is universally superior, but about which geometry best serves your specific application. Vertical furnaces excel in precision-controlled batch processes and space-constrained environments, while horizontal furnaces are often better suited for high-volume or continuous production.

The Core Advantage: Superior Thermal Uniformity
The most significant technical advantage of a vertical furnace is its ability to achieve highly consistent temperature distribution along the length of the sample.
The Role of Natural Convection
In a vertical furnace, the heating elements surround the process tube. This orientation allows natural convection to work in harmony with radiative heat transfer, creating a stable thermal environment that minimizes temperature variations.
Impact on Process Consistency
This excellent temperature uniformity ensures that the entire sample is exposed to the same thermal conditions. For sensitive materials processing or scientific research, this leads to more consistent, reliable, and repeatable results.
Practical Benefits in the Lab Environment
Beyond thermal performance, the physical design of a vertical furnace offers distinct practical advantages.
A Significantly Smaller Footprint
Vertical furnaces occupy less floor space than their horizontal counterparts. This makes them an ideal choice for laboratories or production facilities where space is at a premium. The area beneath the furnace can often be used for staging or storing loads.
Simplified Sample Handling
Loading and unloading samples, particularly long or delicate ones, can be much simpler in a vertical design. Gravity helps center the sample within the tube, reducing the need for complex internal supports and making batch processing more convenient.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose Horizontal
While vertical furnaces offer clear benefits, they are not the best choice for every application. Understanding the strengths of horizontal furnaces is key to making an informed decision.
Larger Working Volume and Throughput
Horizontal furnaces can often be designed with a larger working volume. This allows them to process bigger individual samples or a higher quantity of smaller samples simultaneously, making them suitable for high-throughput applications.
Suitability for Continuous Processing
The horizontal layout is often better suited for continuous production lines. Samples can be more easily fed into one end and extracted from the other, integrating smoothly into an automated manufacturing process.
Heat Distribution in Horizontal Furnaces
While vertical furnaces have an inherent advantage, a well-designed horizontal furnace can still achieve excellent heat distribution. However, this may require more careful optimization of temperature profiles to compensate for potential variations caused by a primary reliance on radiative heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace configuration requires aligning the equipment's strengths with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: The superior thermal uniformity of a vertical furnace is the decisive factor.
- If your primary focus is maximizing limited lab or factory space: The compact footprint of a vertical furnace provides a clear advantage.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput or continuous production: A horizontal furnace's larger capacity and ease of integration into a production line is likely the better choice.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about selecting the optimal tool to achieve your specific scientific or production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vertical Furnace | Horizontal Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | Superior (Natural Convection) | Good (Requires Optimization) |
| Physical Footprint | Compact, Saves Floor Space | Larger |
| Sample Handling | Simplified, Gravity-Assisted | Suited for Continuous Processing |
| Best For | Precision Batch Processes, Space-Constrained Labs | High-Volume/Continuous Production |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's specific needs? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including both vertical and horizontal furnaces, to match your application requirements for precision, throughput, and space. Let us help you achieve more consistent and reliable results.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs



















