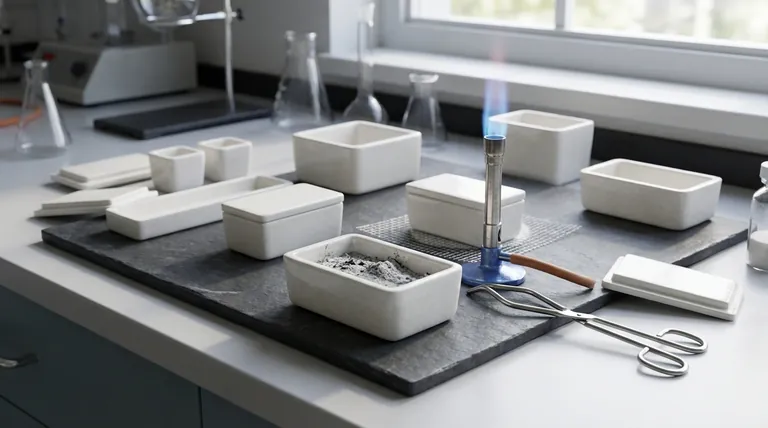
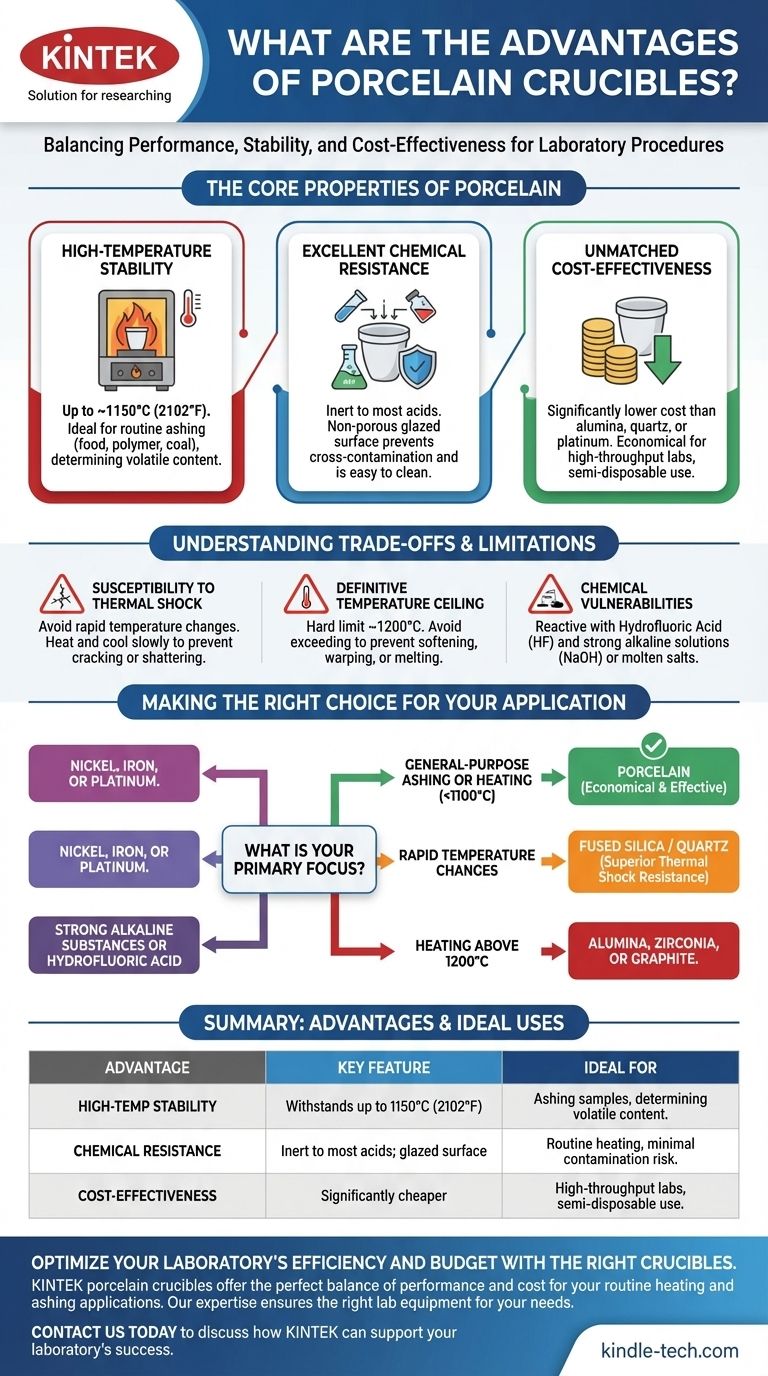
The primary advantages of porcelain crucibles are their excellent chemical resistance, stability at high temperatures up to around 1150°C (2102°F), and exceptionally low cost. This combination makes them the standard, economical choice for many routine laboratory heating procedures, such as determining volatile content or ashing samples.
While specialized materials exist for extreme conditions, porcelain crucibles represent the ideal balance of performance and cost-effectiveness for a vast range of general-purpose laboratory applications. Understanding their limits is the key to using them successfully.

The Core Properties of Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating kaolin clay and other materials in a kiln. The resulting properties make it uniquely suited for the lab environment.
High-Temperature Stability
Porcelain crucibles can withstand continuous temperatures up to approximately 1150°C (2102°F). A glazed finish is typically applied, which can have a slightly lower maximum temperature.
This thermal stability makes them perfect for common high-heat procedures like ashing food, polymer, or coal samples, where organic material is burned off to determine the inorganic residue.
Excellent Chemical Resistance
A key advantage of porcelain is its inertness. It is highly resistant to the corrosive action of most acids and other chemical reagents.
The smooth, glazed interior surface is non-porous, preventing samples from soaking into the crucible wall and minimizing the risk of cross-contamination between experiments. It also makes them very easy to clean.
Unmatched Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to crucibles made from alumina, quartz, or platinum, porcelain is significantly less expensive.
This low cost allows laboratories to stock them in large quantities. They are often treated as semi-disposable, reducing concerns about breakage or contamination in high-throughput environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single material is perfect for every task. The value of porcelain is best understood by recognizing its specific limitations.
Susceptibility to Thermal Shock
The most significant drawback of porcelain is its poor resistance to thermal shock. Rapid changes in temperature will cause it to crack or shatter.
You must heat and cool porcelain crucibles slowly and evenly. Never place a hot porcelain crucible on a cold surface or introduce a cold one into a pre-heated furnace. This is the most common cause of failure.
A Definitive Temperature Ceiling
While stable at high heat, porcelain has a hard limit. Attempting to use it above ~1200°C will cause it to soften, warp, or melt.
For applications requiring higher temperatures, such as melting certain metals or glasses, materials like alumina (up to 1700°C) or zirconia (up to 2200°C) are required.
Chemical Vulnerabilities
While generally inert, porcelain will react with and be damaged by a few specific chemicals.
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) will dissolve the silica in porcelain. Likewise, hot, concentrated alkaline solutions (like sodium hydroxide) and molten alkaline salts (alkaline fusions) will attack the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct crucible is a matter of matching the material to the demands of the procedure.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose ashing or heating below 1100°C: Porcelain is the most economical and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is applications with rapid temperature changes: Choose a fused silica (quartz) crucible for its superior thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is heating materials above 1200°C: You must use an alumina, zirconia, or graphite crucible.
- If your primary focus is working with strong alkaline substances or hydrofluoric acid: Use crucibles made of nickel, iron, or platinum.
By understanding both its strengths and weaknesses, you can leverage porcelain as a reliable and cost-effective tool in the laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Stability | Withstands temperatures up to 1150°C (2102°F) | Ashing samples, determining volatile content |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most acids; non-porous, glazed surface | Routine heating with minimal contamination risk |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Significantly cheaper than alumina, quartz, or platinum | High-throughput labs, semi-disposable use |
Optimize your laboratory's efficiency and budget with the right crucibles.
Porcelain crucibles from KINTEK offer the perfect balance of performance and cost for your routine heating and ashing applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right lab equipment for your specific needs, maximizing value and results.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how KINTEK's porcelain crucibles and other lab consumables can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles necessary for liquid lead corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Data
- Why must aluminum alloys be heated in alumina crucibles? Ensure Pure Results in Molten Corrosion Experiments
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible required for LLTO calcination? Ensure Material Purity and Stoichiometry
- What is the function of an alumina crucible in NaSICON synthesis? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reactions
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety



















