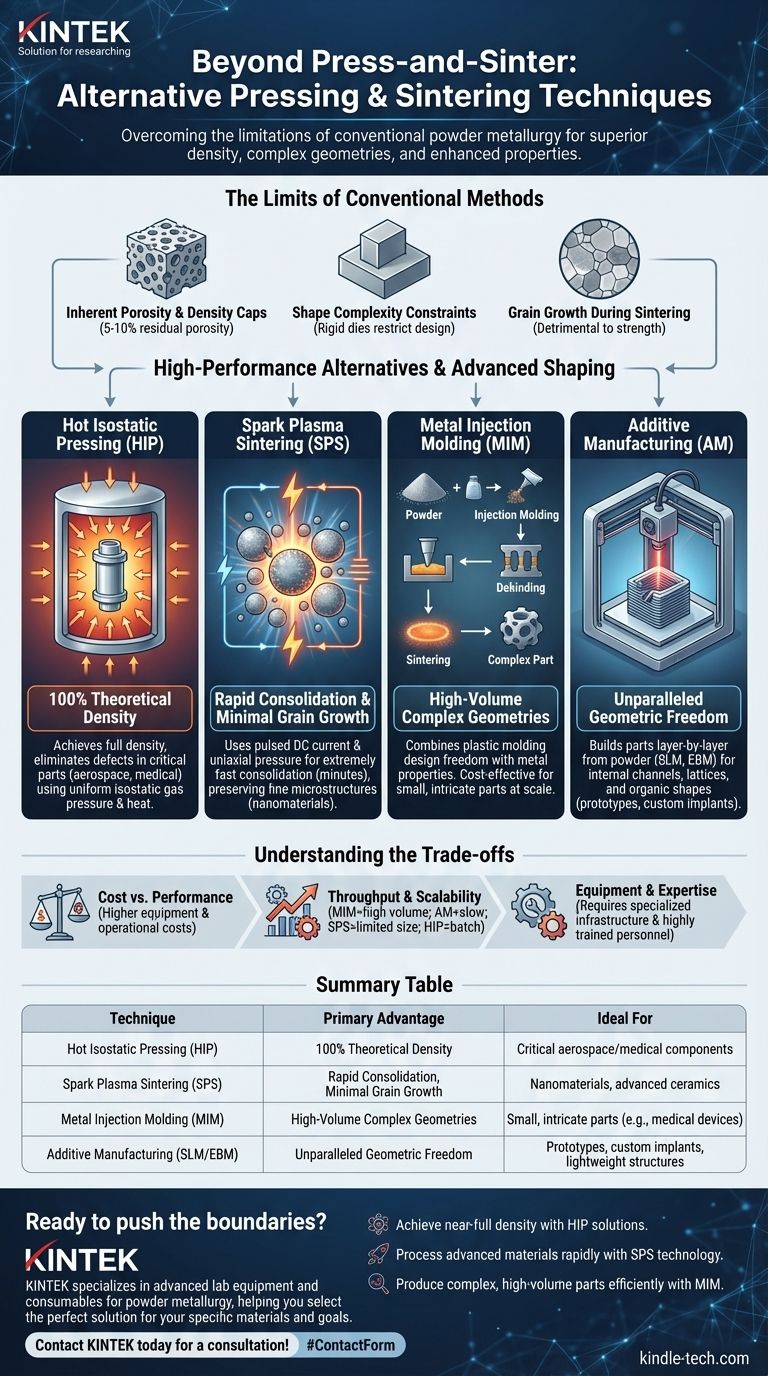
Beyond conventional press-and-sinter, a range of advanced techniques exist to overcome the inherent limitations of traditional powder metallurgy. These alternatives, such as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), and Metal Injection Molding (MIM), use sophisticated methods of applying heat and pressure to create components with superior density, more complex geometries, and enhanced mechanical properties.
The core challenge with conventional powder processing is the trade-off between density, shape complexity, and cost. Alternative techniques solve this by fundamentally changing how pressure and temperature are applied, enabling the fabrication of near-fully dense, intricate parts from high-performance materials.

The Limits of Conventional Methods
Traditional "press-and-sinter" involves compacting powder in a rigid die (pressing) and then heating it in a furnace (sintering). While effective and economical, this approach has fundamental constraints.
Inherent Porosity and Density Caps
Conventional sintering relies on atomic diffusion to bond particles, which often leaves 5-10% residual porosity in the final part. This porosity acts as a stress concentrator, significantly degrading mechanical properties like strength and fatigue life.
Shape Complexity Constraints
The use of rigid dies for pressing limits part geometry. Features like undercuts, cross-holes, or internal threads are impossible to produce directly, restricting design freedom.
Grain Growth During Sintering
The long duration at high temperatures required for conventional sintering can cause grains within the material to coarsen. This excessive grain growth is detrimental to the material's strength and toughness, a principle described by the Hall-Petch relationship.
High-Performance Alternatives: Combining Pressure and Temperature
These techniques apply pressure during the heating cycle to dramatically improve consolidation and densification, producing parts with properties that can rival those of wrought materials.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP places a component in a high-pressure vessel and subjects it to elevated temperature and uniform, isostatic gas pressure (typically using argon). This immense pressure, applied from all directions, effectively collapses and welds shut any internal voids or porosity.
The primary benefit of HIP is its ability to achieve 100% theoretical density. It is widely used to eliminate defects in critical castings or to consolidate powder into fully dense, near-net shape parts for aerospace, medical, and energy applications.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST), SPS is a revolutionary technique that uses a combination of uniaxial pressure and a pulsed high-amperage, low-voltage DC current. The current passes directly through the powder and tooling, generating rapid, localized heating at the particle contact points.
This process enables extremely fast consolidation—often in minutes instead of hours. The speed minimizes grain growth, making SPS ideal for processing nanomaterials, advanced ceramics, and functionally graded materials where preserving a fine microstructure is critical.
Hot Pressing (HP)
Hot Pressing is a simpler variant where uniaxial pressure is applied to a powder in a die while it is heated. It is more effective than pressureless sintering for achieving high density but is less powerful than HIP.
HP is best suited for producing simple, dense shapes like plates, discs, or sputtering targets from materials that are difficult to sinter conventionally.
Advanced Shaping for Complex Geometries
For components where geometric intricacy is the primary challenge, these methods separate the shaping and consolidation steps to enable new design possibilities.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
MIM combines the design freedom of plastic injection molding with the material properties of metal. The process involves mixing fine metal powder with a polymer binder to create a feedstock, which is then injection molded into a complex "green" part.
The binder is then removed through a thermal or chemical "debinding" process, and the fragile "brown" part is sintered in a furnace to high density. MIM is exceptionally cost-effective for producing small, highly complex metal parts in high volumes.
Additive Manufacturing (Powder Bed Fusion)
Methods like Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) build parts layer-by-layer directly from a bed of powder. A high-energy beam (laser or electron) selectively melts the powder according to a 3D CAD model.
This approach offers unparalleled geometric freedom, allowing for the creation of internal channels, lattice structures, and organic shapes that are impossible to make with any other method. It is the go-to technique for prototypes, customized medical implants, and lightweight aerospace components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an advanced technique requires a careful evaluation of its costs, benefits, and limitations. These are not direct replacements for conventional methods but tools for specific, demanding applications.
Cost vs. Performance
The superior performance and capabilities of these alternative methods come at a price. The equipment for HIP, SPS, and Additive Manufacturing is significantly more expensive, and operational costs are higher. The performance gains must justify the investment.
Throughput and Scalability
MIM and conventional press-and-sinter are designed for high-volume manufacturing. In contrast, Additive Manufacturing is often slow for mass production, and SPS is typically limited to smaller parts or lab-scale quantities. HIP is a batch process, with cycle times measured in hours.
Equipment and Expertise
Operating these advanced systems requires specialized infrastructure and highly trained personnel. The process parameters are complex and must be carefully developed and controlled for each specific material and part geometry.
Choosing the Right Alternative for Your Goal
The best method depends entirely on your specific material, geometry, and performance targets. Your decision should be guided by your primary engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and eliminating all porosity: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the definitive solution, especially for critical performance components.
- If your primary focus is rapid consolidation of novel or nano-structured materials while preventing grain growth: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS/FAST) offers unmatched speed and microstructural control.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, intricate metal parts: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) provides the best balance of geometric complexity and cost-effectiveness at scale.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex, one-off, or customized parts with near-unlimited design freedom: Additive Manufacturing methods like SLM or EBM are the ideal choice.
Understanding these powerful alternatives empowers you to select the right tool to fabricate parts that meet performance and complexity demands far beyond the reach of conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Primary Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | 100% Theoretical Density | Critical aerospace/medical components |
| Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Rapid Consolidation, Minimal Grain Growth | Nanomaterials, advanced ceramics |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | High-Volume Complex Geometries | Small, intricate parts (e.g., medical devices) |
| Additive Manufacturing (SLM/EBM) | Unparalleled Geometric Freedom | Prototypes, custom implants, lightweight structures |
Ready to push the boundaries of your materials?
The right pressing and sintering technique is critical for achieving the density, complexity, and performance your application demands. The experts at KINTEK specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for powder metallurgy, helping you select the perfect solution for your specific materials and goals.
We provide the tools and expertise to help you:
- Achieve near-full density with HIP solutions.
- Process advanced materials rapidly with SPS technology.
- Produce complex, high-volume parts efficiently with MIM.
Let's discuss how our specialized lab equipment can optimize your R&D and production. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why is Platinum Foil used to wrap samples during the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) of ZnS crystals? Enhance Optical Purity
- What are the applications of thin films in semiconductors? Powering Modern Electronics from Transistors to Solar Cells
- What is condensation tubing? Prevent Costly HVAC Shutdowns and Water Damage
- What are the factors affecting heat transfer efficiency? Optimize Your Thermal Management System
- What is the role of a magnetic stirrer in npAu catalyst preparation? Ensure Uniform Coating and Deep Diffusion
- What are the factors of powder metallurgy? Master the Key to High-Performance Parts
- Do diamond testing machines work? Choose the Right Tester for Accurate Results
- How does a constant temperature magnetic stirrer contribute to electroless plating quality? Enhancing Surface Integrity



















