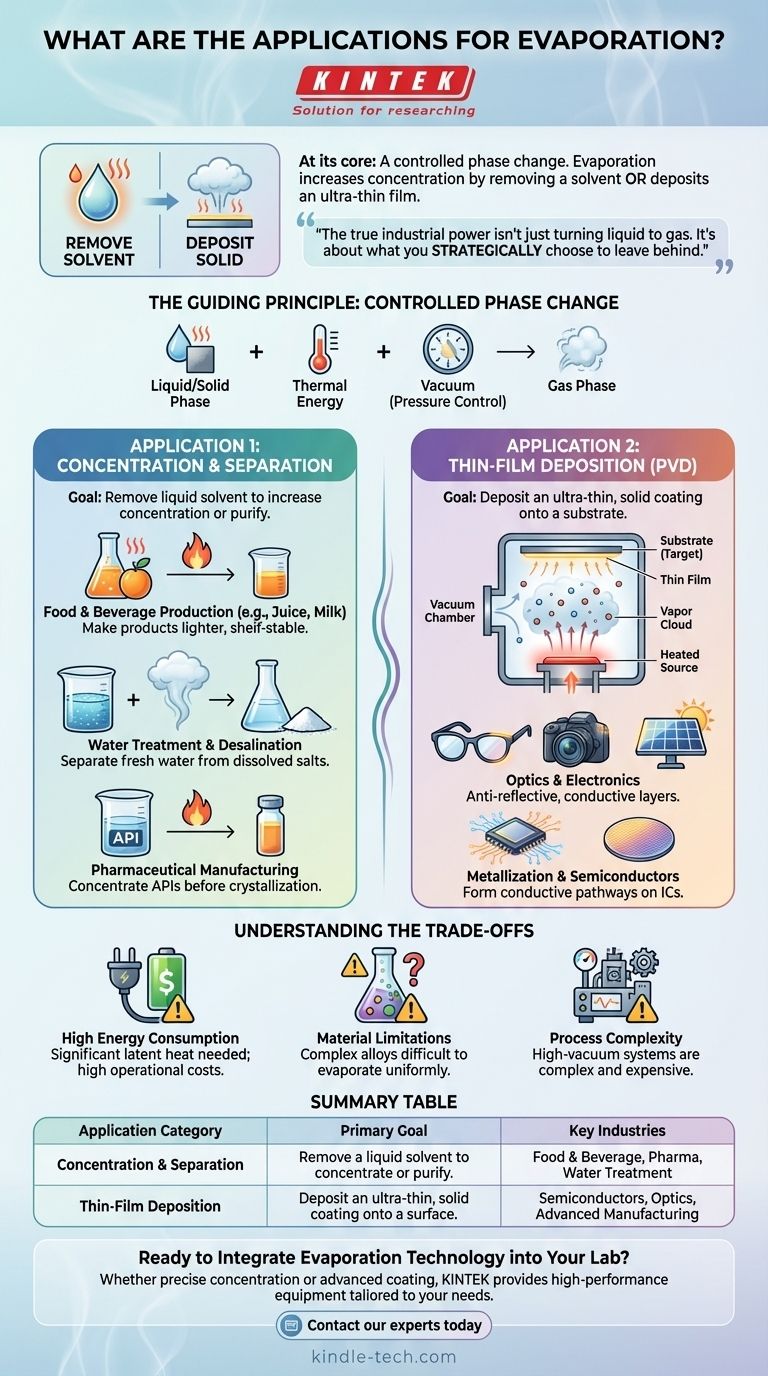
At its core, evaporation is a fundamental physical process with two distinct and powerful industrial applications. It is used either to increase the concentration of a solution by removing a liquid solvent or to deposit an ultra-thin film of a solid material onto a surface for advanced manufacturing.
The true industrial power of evaporation isn't just about turning a liquid into a gas. It's about what you strategically choose to leave behind: either a more concentrated solution or a precisely engineered solid coating.
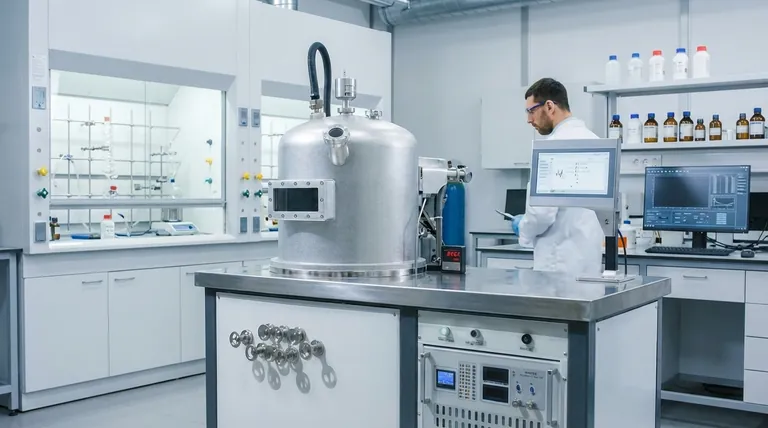

The Guiding Principle: A Controlled Phase Change
Before exploring its applications, it's crucial to understand the mechanism that makes evaporation so versatile in an industrial setting.
How Evaporation Works
Evaporation is the transition of a substance from a liquid or solid phase into a gas phase. This occurs when the atoms or molecules of a material gain enough thermal energy to overcome the forces binding them together.
The Role of Control
Industrial applications rely on precisely controlling this process. By manipulating factors like temperature and pressure (often creating a vacuum), engineers can significantly speed up evaporation or allow materials with very high boiling points to be evaporated efficiently.
Application 1: Concentration and Separation
The most intuitive application of evaporation is removing a liquid solvent (like water) to increase the concentration of the substances dissolved within it.
Food and Beverage Production
This is widely used to concentrate products like fruit juices and milk. Removing water makes these products lighter, more shelf-stable, and less expensive to transport before being reconstituted later.
Water Treatment and Desalination
In large-scale desalination plants, evaporation is a key method for separating fresh water from dissolved salts. The water is evaporated, collected as vapor, and then condensed back into pure liquid, leaving the salts and minerals behind.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In drug production, evaporation is often used to concentrate a solution containing an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) after it has been synthesized or extracted, preparing it for crystallization or drying.
Application 2: Thin-Film Deposition
A less obvious but highly advanced application is using evaporation to create ultra-thin coatings on a substrate. This process, often called physical vapor deposition (PVD), involves heating a solid material in a high vacuum until it evaporates.
The Deposition Process
In a vacuum chamber, the evaporated atoms or molecules travel in a straight line and condense on a cooler target surface, or substrate. This builds up a film that can be anywhere from a few atoms to several micrometers thick.
Optics and Electronics
This technique is critical for manufacturing precision optical coatings. Anti-reflective coatings on eyeglasses and camera lenses, reflective layers on mirrors, and conductive layers on solar panels are all created using evaporation.
Metallization and Semiconductors
In the semiconductor industry, evaporation is used to deposit thin layers of metal (like aluminum or gold) to form the conductive pathways and connections on integrated circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, evaporation is not a universal solution and comes with important considerations that determine its suitability for a given task.
High Energy Consumption
Changing a substance's phase from liquid to gas requires a significant amount of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. On an industrial scale, this can translate to high operational costs.
Material Limitations
For thin-film deposition, not all materials are suitable. Complex alloys can be difficult to evaporate uniformly, as different components may vaporize at different rates, changing the composition of the final film.
Process Complexity
High-vacuum deposition systems are complex and expensive to build and maintain. Achieving the pristine, low-pressure environment required for high-quality coatings demands specialized equipment and rigorous operational procedures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" application of evaporation depends entirely on whether your goal is to remove a liquid or deposit a solid.
- If your primary focus is concentration or purification: Your goal is to efficiently remove a liquid solvent, making thermal or vacuum evaporation of the liquid itself your key process.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced surfaces or coatings: You will use high-vacuum deposition techniques to evaporate a solid material and deposit it onto a substrate.
Understanding which form of evaporation to apply—separating a liquid or depositing a solid—is the key to unlocking its vast industrial potential.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Primary Goal | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration & Separation | Remove a liquid solvent to concentrate a solution or purify a substance. | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Water Treatment |
| Thin-Film Deposition | Deposit an ultra-thin, solid coating onto a substrate surface. | Semiconductors, Optics, Advanced Manufacturing |
Ready to Integrate Evaporation Technology into Your Lab?
Whether your goal is precise solution concentration or advanced thin-film coating, KINTEK provides the high-performance lab equipment you need. Our expertise in evaporation and vacuum deposition systems ensures you get reliable, efficient, and scalable solutions tailored to your specific application in pharmaceuticals, materials science, or electronics.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results and accelerate your R&D or production processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth

















