At its core, brazing is a highly versatile metal-joining process used in nearly every industry imaginable, from aerospace and automotive to electronics and plumbing. Its applications range from mass-producing millions of automotive air conditioning components to creating highly specialized, single-piece assemblies like rocket engine nozzles. Brazing is the go-to method for creating strong, precise, and leak-proof joints, especially when joining dissimilar metals or in assemblies where high heat from welding would cause damage.
Brazing's true value is not just in joining metals, but in doing so without melting them. This fundamental difference from welding allows it to create strong, clean joints between a vast range of materials—including metals to ceramics—making it indispensable for complex and heat-sensitive designs.
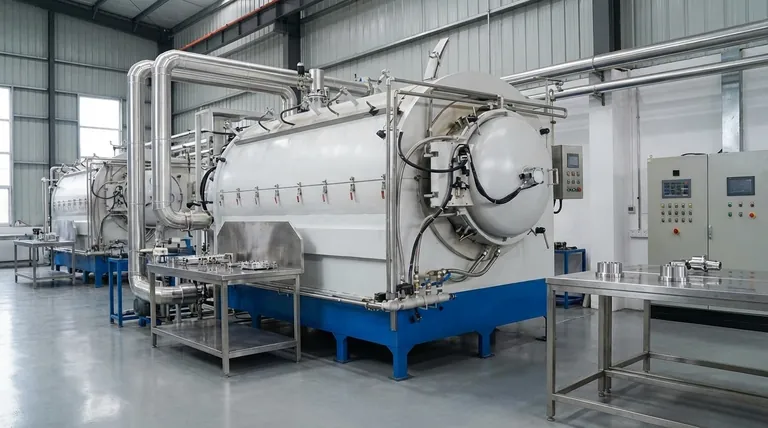

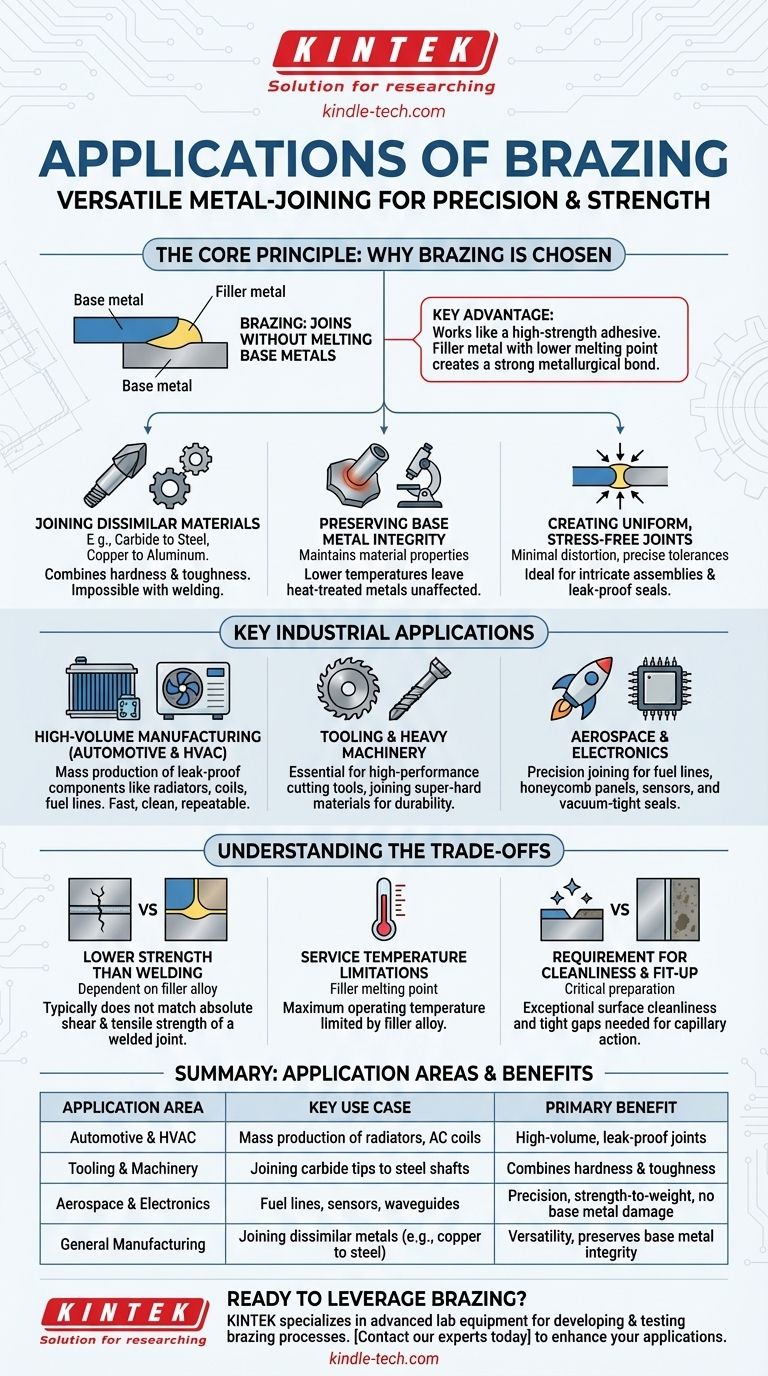
The Core Principle: Why Brazing Is Chosen
Unlike welding, which melts and fuses the base metals together, brazing works more like a high-strength adhesive. A filler metal with a lower melting point is heated, drawn into a tight-fitting joint by capillary action, and then solidifies to form a strong metallurgical bond. This principle is the source of its key advantages.
### Joining Dissimilar Materials
Because the base metals are not melted, brazing excels at joining materials that cannot be welded together. This is one of its most powerful applications.
A classic example is brazing a carbide tip onto a steel tool shaft. The extreme hardness of carbide is joined to the toughness and lower cost of steel, creating a superior cutting tool. This is impossible with conventional welding.
Other common examples include joining copper to steel in refrigeration systems or aluminum to copper in electrical components.
### Preserving Base Metal Integrity
The lower process temperatures of brazing (though still very hot) leave the base metals largely unaffected.
This is critical for metals that have been heat-treated to achieve specific hardness or strength. Welding would ruin these properties, but brazing preserves them, maintaining the engineered characteristics of the components.
### Creating Uniform, Stress-Free Joints
The gentle heating and cooling cycles in brazing minimize the thermal distortion and residual stresses that are common in welding.
This results in dimensionally stable parts that meet precise tolerances, which is crucial for intricate assemblies in electronics and aerospace. The capillary action also ensures a complete, uniform bond line, creating a clean, leak-proof seal ideal for fluid or gas applications.
Key Industrial Applications
These principles translate directly into widespread use across multiple sectors, often leveraging automated processes for consistency and speed.
### High-Volume Manufacturing (Automotive & HVAC)
The automotive and HVAC industries rely heavily on brazing for components that must be leak-proof and produced efficiently.
Automatic and induction brazing are used for mass production of parts like vehicle radiators, air conditioning condenser and evaporator coils, and fuel lines. The process is fast, clean, and highly repeatable.
### Tooling and Heavy Machinery
Brazing is essential for manufacturing high-performance cutting tools, drill bits, and saw blades.
By joining super-hard materials like carbide, cermets, or industrial diamond to a tough steel body, manufacturers create tools that are both effective and economical.
### Aerospace and Electronics
In aerospace, brazing is used to join fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and even honeycomb panels where strength-to-weight ratio is paramount.
In electronics, its precision and low-heat input are perfect for creating vacuum-tight seals on components like vacuum tubes, sensors, and waveguides without damaging sensitive internal parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations of brazing.
### Lower Strength Than Welding
While a properly designed brazed joint is very strong (often stronger than the weaker of the two metals being joined), it typically does not match the absolute shear and tensile strength of a welded joint. The bond is dependent on the strength of the filler alloy.
### Service Temperature Limitations
The maximum temperature a brazed part can operate at is limited by the melting point of the filler alloy. If the service temperature gets too close to that point, the filler will soften and the joint will fail.
### Requirement for Cleanliness and Fit-Up
For capillary action to work effectively, the surfaces to be joined must be exceptionally clean and have a consistent, tight gap between them. This adds a critical preparation step and requires tighter manufacturing control than some welding processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if brazing is the correct choice, evaluate your primary design goal.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (like carbide to steel): Brazing is often the superior or only viable method, allowing you to combine the best properties of each material.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex or delicate parts: Automated processes like furnace or induction brazing offer unmatched repeatability and precision without distorting the components.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength for a high-temperature structural application: You should evaluate different welding methods as a potentially stronger alternative.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine where brazing offers a distinct advantage in your own engineering and manufacturing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Case | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & HVAC | Mass production of radiators, AC coils | High-volume, leak-proof joints |
| Tooling & Machinery | Joining carbide tips to steel shafts | Combines hardness & toughness |
| Aerospace & Electronics | Fuel lines, sensors, waveguides | Precision, strength-to-weight, no base metal damage |
| General Manufacturing | Joining dissimilar metals (e.g., copper to steel) | Versatility, preserves base metal integrity |
Ready to leverage brazing for your precision manufacturing needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing brazing processes. Whether you are joining dissimilar materials, creating complex assemblies, or optimizing for mass production, our solutions help ensure strong, reliable, and leak-proof joints.
Let KINTEK be your partner in precision. Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our equipment can enhance your brazing applications and improve your manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer



















