At its core, a furnace is a tool for controlled thermal processing. Its applications span nearly every major industry and scientific field, used for everything from melting metals and curing ceramics to synthesizing new chemical compounds and testing the physical properties of advanced materials. The specific application depends entirely on the furnace's scale, precision, and operating environment.
A furnace's purpose is to apply a precise amount of heat for a specific duration to manipulate a material's physical or chemical properties. The key distinction in its application lies in the required scale—either for high-volume industrial production or for high-precision laboratory research.

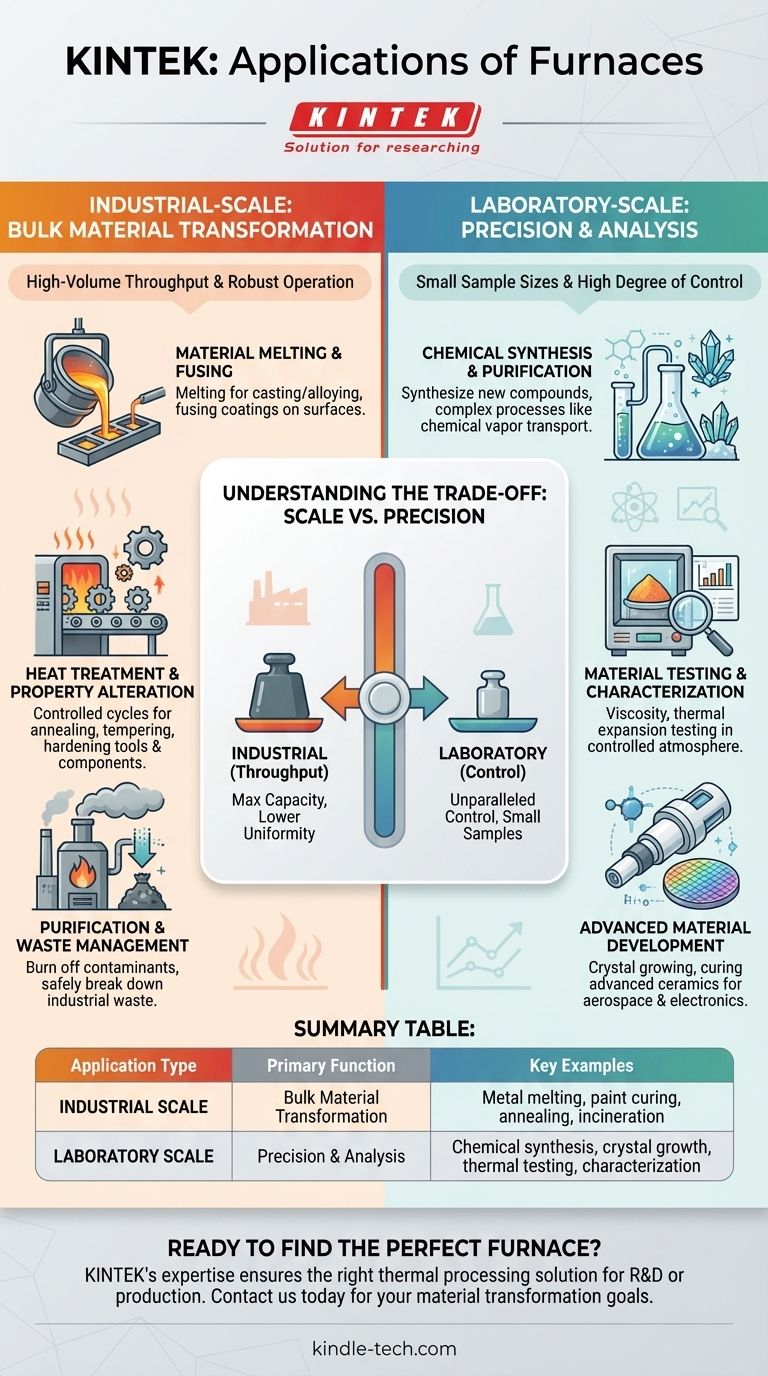
Industrial-Scale Applications: Bulk Material Transformation
Industrial furnaces are the workhorses of manufacturing, designed for high-volume throughput and robust, continuous operation. Their primary function is to process large quantities of material efficiently.
Material Melting and Fusing
The most fundamental industrial use is melting raw materials for casting or alloying. This process is essential for creating metal parts and components.
Similarly, furnaces are used to fuse coatings to surfaces. This includes curing paint on automotive bodies, applying enamel to appliances, or bonding glass coatings to steel.
Heat Treatment and Property Alteration
Many materials, particularly metals, have their physical properties (like hardness or ductility) altered through heat treatment.
Furnaces provide the controlled heating and cooling cycles required for processes like annealing, tempering, and hardening, which are critical for manufacturing durable tools, structural components, and machine parts.
Purification and Waste Management
Furnaces are also used in purification and disposal processes. High temperatures can be used to burn off contaminants or unwanted residues from parts.
In a more specialized capacity, incinerator furnaces use extreme heat to safely break down and reduce industrial or municipal waste.
Laboratory-Scale Applications: Precision and Analysis
In research and development, furnaces are valued for precision, not volume. Laboratory furnaces, especially tube furnaces, are designed for small samples and offer a high degree of control over temperature and atmosphere.
Chemical Synthesis and Purification
Chemists and material scientists use lab furnaces to synthesize new compounds, particularly inorganic materials that require high temperatures to form.
Specialized tube furnaces with multiple temperature zones allow for complex processes like chemical vapor transport, where a material is purified by sublimating it in one zone and re-depositing it as a pure crystal in another, cooler zone.
Material Testing and Characterization
Furnaces are essential for understanding how materials behave under thermal stress. They are used for viscosity testing, measuring thermal expansion, and performing high-temperature calibrations.
By heating a small sample in a controlled environment, often within an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation, researchers can gather critical data on a material's performance limits.
Advanced Material Development
Creating next-generation materials often starts in a furnace. Processes like crystal growing for the semiconductor industry or curing advanced ceramics for aerospace applications require exact and sustained temperature profiles that only a precision laboratory furnace can provide.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Scale vs. Precision
The vast range of furnace applications is possible because of a fundamental design trade-off between throughput and control. Understanding this distinction is key to selecting the right thermal process.
Industrial Furnaces: Built for Throughput
These furnaces are designed for maximum capacity and efficiency. Their value lies in processing tons of material per hour. The trade-off is often a lower degree of temperature uniformity and atmospheric control compared to their lab-scale counterparts.
Laboratory Furnaces: Designed for Control
These furnaces prioritize precision above all else. They handle small sample sizes but offer unparalleled control over temperature (often to within a single degree), heating and cooling rates, and the composition of the gas atmosphere. This control is necessary for repeatable experiments and the development of sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines the type of furnace and process required.
- If your primary focus is mass production or bulk processing: You are in the realm of industrial furnaces, used for large-scale melting, coating, and heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a laboratory furnace that offers the precision for chemical synthesis, material analysis, and repeatable experiments.
- If your primary focus is creating new, high-performance materials: Specialized lab furnaces are critical for processes like crystal growth and ceramic sintering that demand absolute control.
Ultimately, the furnace is a foundational tool that empowers engineers and scientists to purposefully transform matter using heat.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Primary Function | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Scale | Bulk Material Transformation | Metal melting, paint curing, annealing, waste incineration |
| Laboratory Scale | Precision & Analysis | Chemical synthesis, crystal growth, thermal testing, material characterization |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your application?
Whether you are scaling up production or require precision for R&D, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right thermal processing solution. Our furnaces are designed for reliability, control, and performance to meet your specific industrial or laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project and let our specialists help you achieve your material transformation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs



















