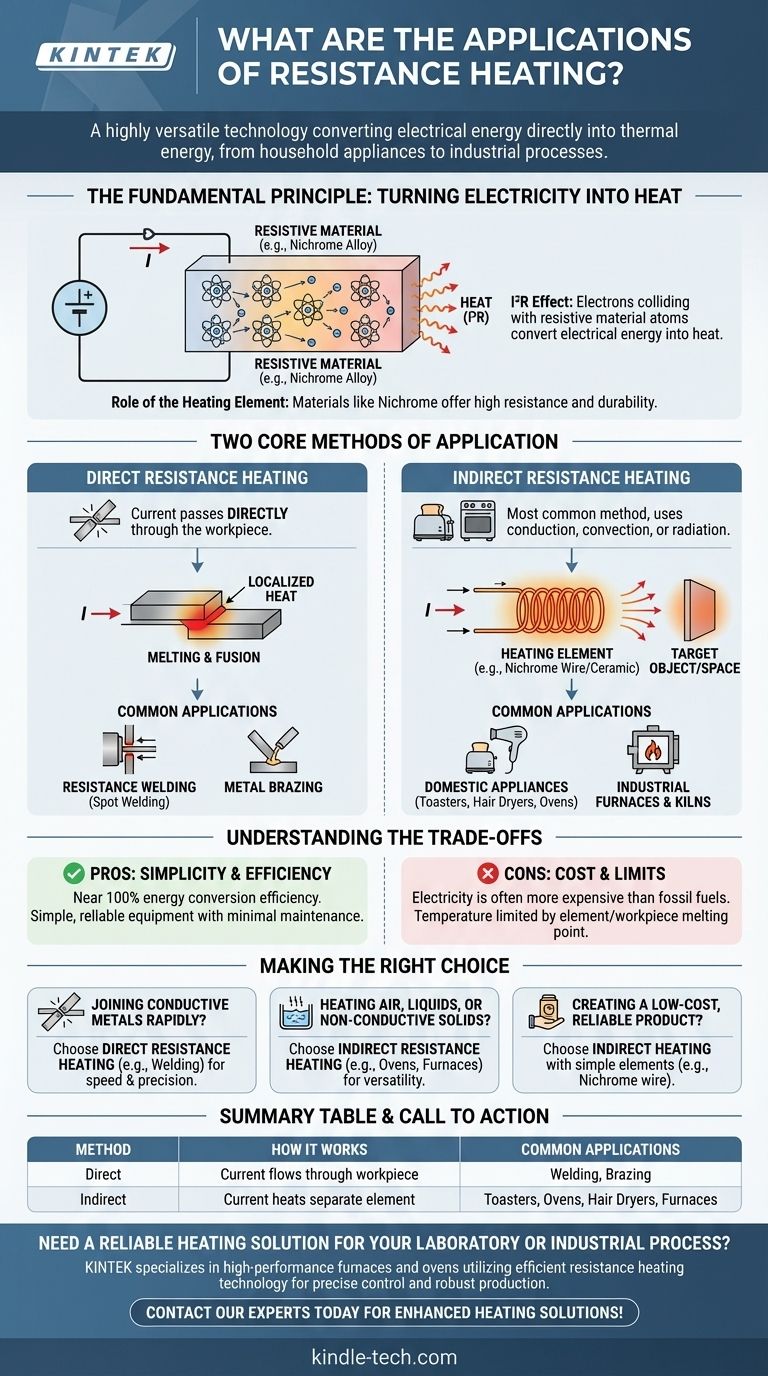
At its core, resistance heating is a highly versatile technology used in everything from common household appliances to demanding industrial processes. Its applications range from simple devices like toasters and hair dryers, which use nichrome wire elements, to industrial furnaces and specialized processes like resistance welding and brazing for joining metals.
The true power of resistance heating lies in its elegant simplicity: converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. Its vast range of applications stems from the two primary ways this principle is applied—either by heating a workpiece directly or by using a separate element to transfer heat indirectly.
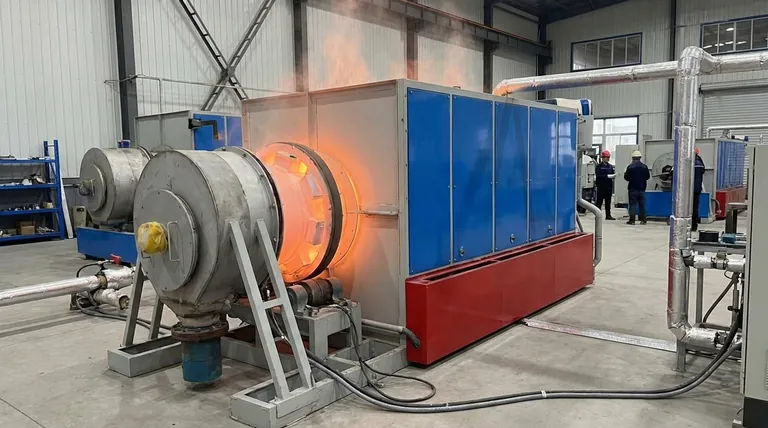

The Fundamental Principle: Turning Electricity into Heat
Resistance heating is governed by one of the most basic laws of electricity. Understanding this principle is key to seeing why it's so widely adopted.
The I²R Effect
The foundation of resistance heating is the Joule effect, often expressed as the I²R loss. When an electric current (I) flows through a material with electrical resistance (R), a portion of the electrical energy is converted into heat.
This conversion happens as electrons flowing in the current collide with the atoms of the resistive material. These collisions transfer kinetic energy, causing the atoms to vibrate more intensely, which we perceive as an increase in temperature.
The Role of the Heating Element
For this effect to be useful, a material is needed that can resist the flow of electricity efficiently without degrading. This is why alloys like nichrome (nickel-chromium) are so common.
These materials have high electrical resistance, generating significant heat even with a moderate current. They also possess a high melting point and form a protective oxide layer that prevents them from breaking down at high operating temperatures.
Two Core Methods of Application
All applications of resistance heating fall into one of two categories: direct or indirect. The choice between them depends entirely on what is being heated.
Direct Resistance Heating
In this method, the electric current is passed directly through the material to be heated. The object itself serves as the electrical resistor.
This is an incredibly efficient method of heating because the heat is generated within the object itself, minimizing energy loss. However, it only works on materials that can conduct electricity.
Applications of Direct Heating
The most prominent example of direct resistance heating is resistance welding. To join two pieces of metal, a high current is passed through them at the point of contact. The resistance at this junction generates intense, localized heat that melts and fuses the metals together.
Indirect Resistance Heating
This is the most common method. The current passes through a dedicated heating element, such as a nichrome wire or ceramic heater. This element becomes very hot and then transfers its thermal energy to the target object or space.
Heat transfer in this method occurs through conduction, convection, or radiation. For example, an oven uses a heating element to heat the air inside (convection), which then cooks the food.
Applications of Indirect Heating
Nearly all domestic heating appliances use this method. Toasters use radiant heat from glowing wires to brown bread. Hair dryers use a fan to blow air over a hot coil. Electric furnaces and kilns use robust heating elements to heat an insulated chamber for industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful and simple, resistance heating is not the ideal solution for every scenario. Its effectiveness is a balance of benefits and limitations.
Pro: Simplicity and Efficiency
The primary advantage of resistance heating is its near 100% efficiency in converting electrical energy into thermal energy at the point of use. The equipment is often simple, reliable, and requires minimal maintenance compared to combustion-based systems.
Con: Cost of Electricity
The main drawback is that electricity is often a more expensive energy source than fossil fuels like natural gas. For large-scale industrial heating, the operational cost can be a significant factor.
Con: Temperature and Material Limits
The maximum achievable temperature is limited by the melting point and durability of the heating element (in indirect heating) or the workpiece itself (in direct heating). This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring extremely high temperatures that other methods can achieve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating approach depends entirely on the material you need to heat and your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is joining conductive metals rapidly: Direct resistance heating, as used in spot welding, offers unparalleled speed and localized precision.
- If your primary focus is heating air, liquids, or non-conductive solids: Indirect resistance heating, found in ovens, water heaters, and furnaces, is the necessary and most versatile approach.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-cost, reliable consumer product: The simplicity of an indirect nichrome wire heating element is often the most practical solution.
Ultimately, the wide-ranging success of resistance heating is a testament to how a fundamental physical principle can be applied in brilliantly simple yet effective ways.
Summary Table:
| Method | How It Works | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Resistance Heating | Current flows directly through the material to be heated. | Resistance welding, metal brazing. |
| Indirect Resistance Heating | Current heats a separate element (e.g., nichrome wire), which then transfers heat. | Toasters, ovens, hair dryers, industrial furnaces. |
Need a reliable heating solution for your laboratory or industrial process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens that utilize efficient resistance heating technology. Whether you require precise temperature control for materials testing or a robust system for your production line, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your heating applications with reliable, efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















