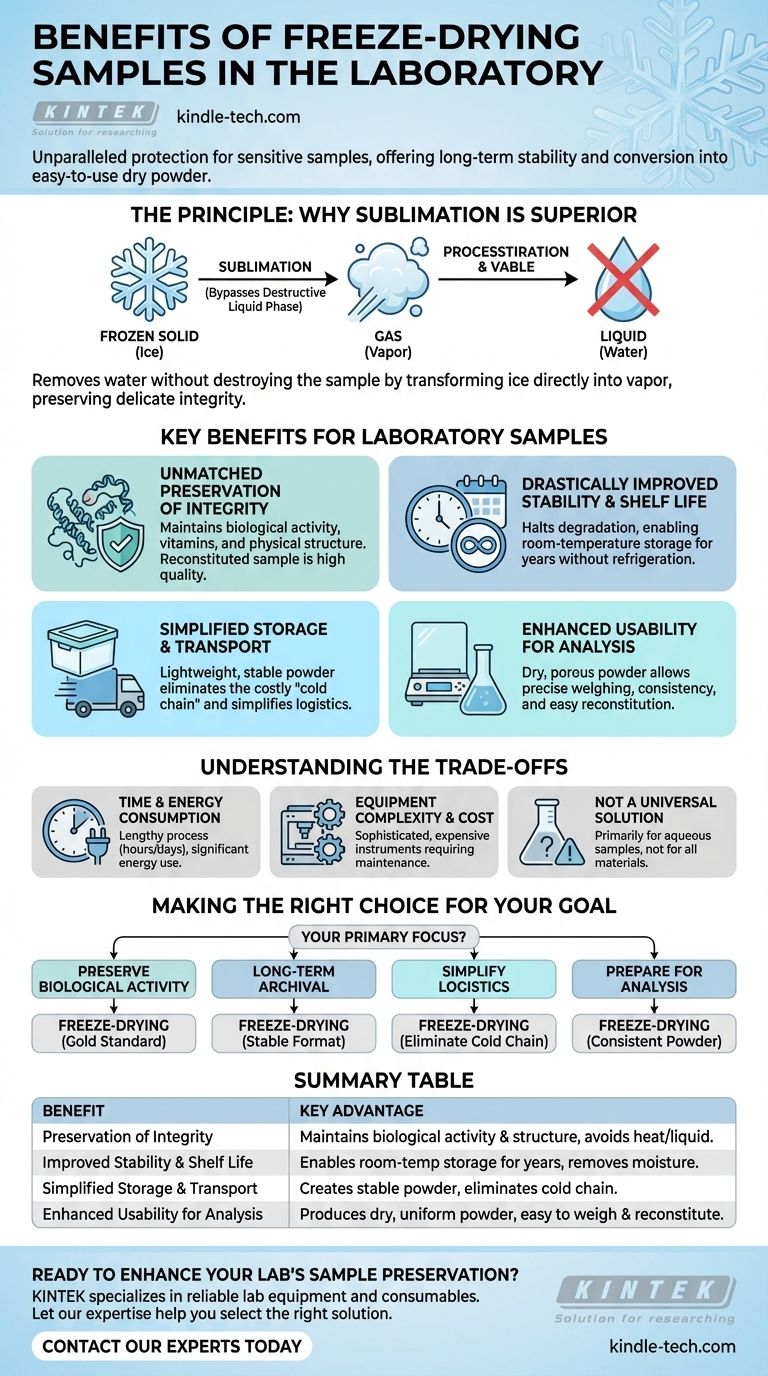
In short, freeze-drying offers unparalleled benefits for preserving sensitive laboratory samples. The primary advantages are the protection of a sample's active ingredients and physical structure, a dramatic improvement in long-term stability and shelf life, and the conversion of the material into a dry powder that is easy to store, transport, and use for analysis.
The core value of freeze-drying is not simply drying a sample, but removing water without destroying it. By transforming ice directly into vapor (sublimation), it bypasses the destructive liquid water phase, preserving the delicate biological and chemical integrity of the material in a way no other method can.
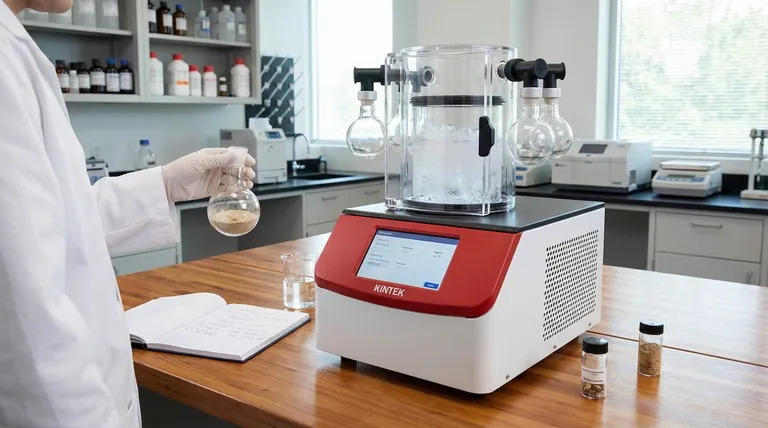

The Principle: Why Sublimation is Superior
The Freeze-Drying Process
Freeze-drying, or lyophilization, is a low-temperature dehydration process. It involves first freezing the material and then reducing the surrounding pressure to allow the frozen water in the material to sublimate directly from a solid to a gas.
Avoiding the Damage of Heat and Liquid
Standard heat-based drying can denature proteins, degrade vitamins, and destroy the physical structure of a sample. Even air-drying at room temperature is problematic, as the presence of liquid water can facilitate chemical reactions that degrade the sample. Freeze-drying avoids both of these issues entirely.
Key Benefits for Laboratory Samples
Unmatched Preservation of Integrity
Because it operates at low temperatures and avoids the liquid phase, freeze-drying maintains the essential properties of the original material. This includes preserving the biological activity of proteins and microbes, retaining vitamins, and keeping the physical structure intact.
A properly freeze-dried sample, when reconstituted with water or another solvent, is considered the closest you can get to the fresh material in terms of quality.
Drastically Improved Stability and Shelf Life
Water is a primary driver of chemical and biological degradation. By removing moisture to residual levels, freeze-drying effectively halts these degradation pathways.
This allows for highly unstable or sensitive materials to be stored for years at room temperature without significant loss of quality, eliminating the need for constant refrigeration or freezing.
Simplified Storage and Transport
Freeze-dried materials are lightweight, compact, and stable at ambient temperatures. This makes them significantly easier and cheaper to handle, store, and transport.
The need for a "cold chain"—a costly and logistically complex system of uninterrupted refrigeration—is completely eliminated. This is a critical advantage for distributing pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and research reagents.
Enhanced Usability for Analysis
The process results in a dry, often porous powder. This format is ideal for laboratory work because it can be easily and precisely weighed for experiments.
Its uniform nature ensures that each portion taken from the sample is consistent, and it readily reconstitutes, making it simple to prepare for analysis or other applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Time and Energy Consumption
Freeze-drying is not a fast process. The cycle, which includes pre-freezing, primary drying under deep vacuum, and secondary drying to remove residual moisture, can take many hours or even days depending on the sample. The equipment also consumes a significant amount of energy.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Laboratory freeze dryers are sophisticated and expensive instruments. They require a powerful vacuum pump and a very low-temperature cold trap, both of which demand regular maintenance and careful operation to function correctly and avoid damage.
Not a Universal Solution
Freeze-drying is primarily designed for aqueous-based samples. While it is exceptionally versatile for pharmaceuticals, biologicals, and food, it is not the optimal preservation method for all materials, particularly those that do not contain water or are sensitive to the freezing process itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding on a preservation method, your primary objective will guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: Freeze-drying is the gold standard for proteins, enzymes, microbes, and vaccines, as it prevents the denaturation caused by heat.
- If your primary focus is long-term archival: Freeze-drying creates an exceptionally stable format that resists degradation for years, making it ideal for creating reference materials or archiving unique samples.
- If your primary focus is simplifying logistics: Freeze-drying is the best choice to eliminate the cost and complexity of cold-chain shipping and storage.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for analysis: Freeze-drying produces a stable, homogenous powder that is perfect for ensuring consistent and repeatable experimental results.
Ultimately, choosing freeze-drying is an investment in the long-term integrity and usability of your most sensitive samples.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Preservation of Integrity | Maintains biological activity and physical structure by avoiding heat and liquid water. |
| Improved Stability & Shelf Life | Enables room-temperature storage for years by removing moisture. |
| Simplified Storage & Transport | Creates a lightweight, stable powder, eliminating the need for a cold chain. |
| Enhanced Usability for Analysis | Produces a dry, uniform powder that is easy to weigh and reconstitute. |
Ready to enhance your lab's sample preservation and analysis?
Freeze-drying is an investment in the long-term integrity of your most sensitive materials. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Our expertise can help you select the right freeze-drying solution to protect your proteins, vaccines, and reagents, simplify your logistics, and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the three phases of freeze drying? Mastering Lyophilization for Perfect Preservation
- What is the recommended approach to selecting features for a lab freeze dryer? Match Core Performance to Your Application
- Where are evaporators used in food industry? Concentrate Products & Reduce Costs
- What can I use instead of rotavap? Find the Perfect Solvent Removal Tool for Your Lab
- In what ways does freeze drying improve pharmaceutical product quality? Extend Shelf-Life and Preserve Drug Efficacy


















