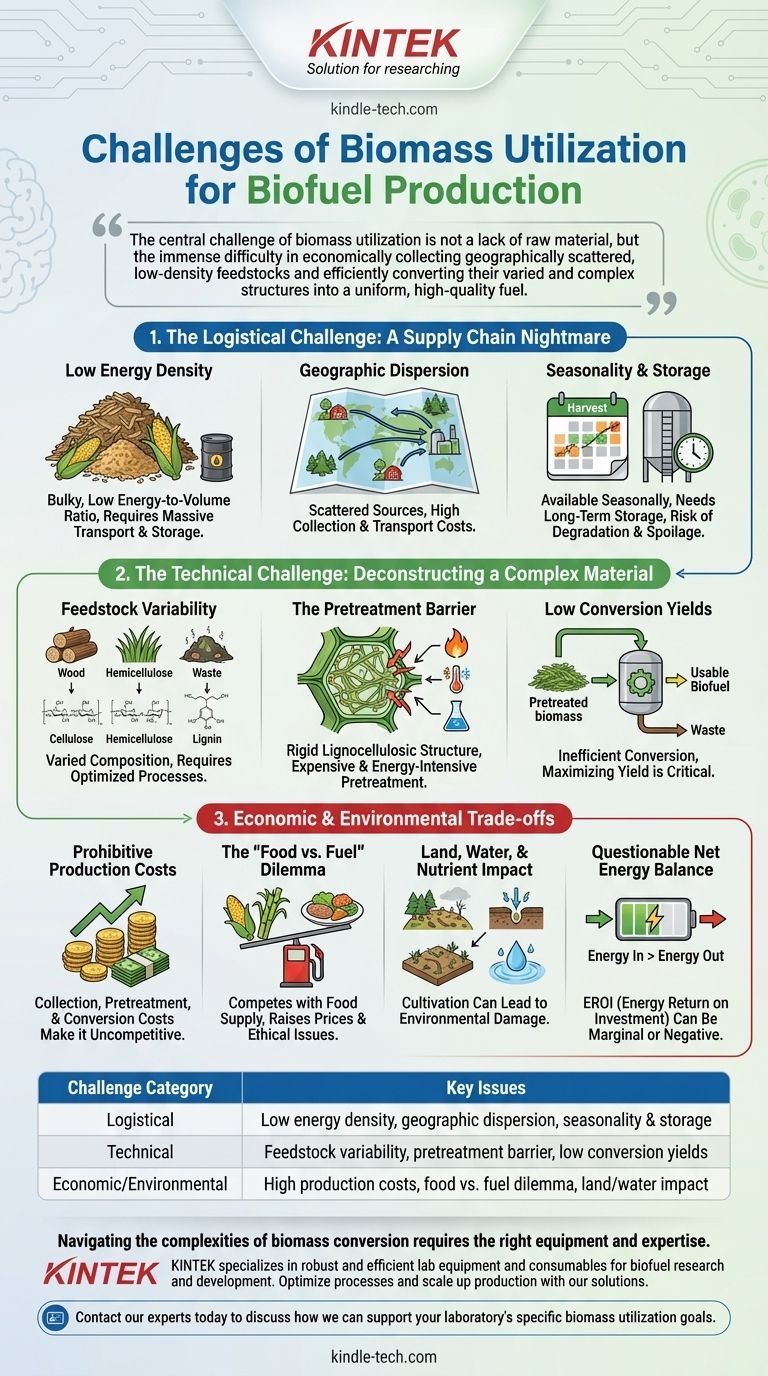
While promising in theory, utilizing biomass for biofuel production is fraught with significant logistical, technical, and economic challenges. The core difficulties stem from the inherent nature of biomass itself: it is bulky, dispersed, and chemically complex, making its efficient and cost-effective conversion into a high-density liquid fuel a formidable engineering problem.
The central challenge of biomass utilization is not a lack of raw material, but the immense difficulty in economically collecting geographically scattered, low-density feedstocks and efficiently converting their varied and complex structures into a uniform, high-quality fuel.

The Logistical Challenge: A Supply Chain Nightmare
The first major hurdle appears before any conversion process begins. Unlike crude oil, which is highly concentrated in specific locations, biomass is diffuse and difficult to manage.
Low Energy Density
Biomass, whether it's wood chips, corn stover, or switchgrass, is bulky. It has a very low energy-to-volume ratio compared to fossil fuels, meaning vast quantities must be transported and stored to produce a meaningful amount of energy.
Geographic Dispersion
Biomass sources like agricultural residues are spread over wide areas. The cost and energy required to collect this material from countless fields and forests and transport it to a central processing facility are often prohibitively high.
Seasonality and Storage
Most agricultural biomass is only available during specific harvest seasons. This necessitates massive, long-term storage facilities to ensure a year-round supply for a biofuel plant, introducing risks of material degradation, spoilage, and storage costs.
The Technical Challenge: Deconstructing a Complex Material
Once collected, converting the tough, fibrous structure of biomass into liquid fuel presents another set of complex technical problems.
Feedstock Variability
Biomass is not a uniform commodity. The chemical composition—specifically the ratios of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—varies dramatically between wood, grasses, and agricultural waste, requiring different and highly optimized conversion processes.
The Pretreatment Barrier
The rigid structure of lignocellulosic biomass (the woody, non-food parts of plants) is naturally resistant to decomposition. Breaking it down requires an aggressive pretreatment step using heat, pressure, or harsh chemicals, which is both expensive and energy-intensive.
Low Conversion Yields
The efficiency of converting the pretreated biomass into biofuel through enzymatic or chemical processes can be low. Maximizing the yield of usable fuel from each ton of raw feedstock remains a critical area of research and a major barrier to economic viability.
Understanding the Economic and Environmental Trade-offs
The logistical and technical hurdles culminate in significant economic and environmental questions that cannot be ignored.
Prohibitive Production Costs
The combined expenses of collection, transportation, pretreatment, and conversion often make the final biofuel product significantly more expensive than its petroleum-based equivalent, rendering it uncompetitive without substantial government subsidies.
The "Food vs. Fuel" Dilemma
Using first-generation feedstocks like corn and sugarcane for fuel production creates direct competition with the global food supply. This can lead to increased food prices and raises serious ethical questions about land and resource allocation.
Land, Water, and Nutrient Impact
Cultivating dedicated energy crops at scale can lead to deforestation, soil nutrient depletion, and significant water consumption. These factors can undermine the supposed environmental benefits of moving away from fossil fuels.
Questionable Net Energy Balance
A crucial metric is the Energy Return on Investment (EROI)—does the process yield more energy than it consumes? For some biofuel pathways, when you account for farming, transport, and processing, the net energy gain is marginal or even negative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Successfully leveraging biomass for fuel requires a clear-eyed assessment of these challenges and aligning your strategy with a specific, achievable objective.
- If your primary focus is local waste reduction: Concentrate on small-scale, decentralized conversion technologies that process a specific, readily available waste stream, such as agricultural residue from a single large farm or forestry operation.
- If your primary focus is large-scale energy production: The critical path involves investing heavily in advanced conversion technologies for non-food, lignocellulosic feedstocks and solving the complex "last-mile" collection logistics.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Prioritize feedstocks that do not compete with food, require minimal land-use change, and demonstrate a positive lifecycle energy and carbon balance.
Understanding these fundamental challenges is the essential first step in developing truly viable and sustainable biofuel solutions.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Logistical | Low energy density, geographic dispersion, seasonality & storage |
| Technical | Feedstock variability, pretreatment barrier, low conversion yields |
| Economic/Environmental | High production costs, food vs. fuel dilemma, land/water impact |
Navigating the complexities of biomass conversion requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in providing robust and efficient lab equipment and consumables for biofuel research and development. Whether you are optimizing pretreatment processes or scaling up production, our solutions are designed to help you overcome these challenges and improve your conversion yields. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific biomass utilization goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















