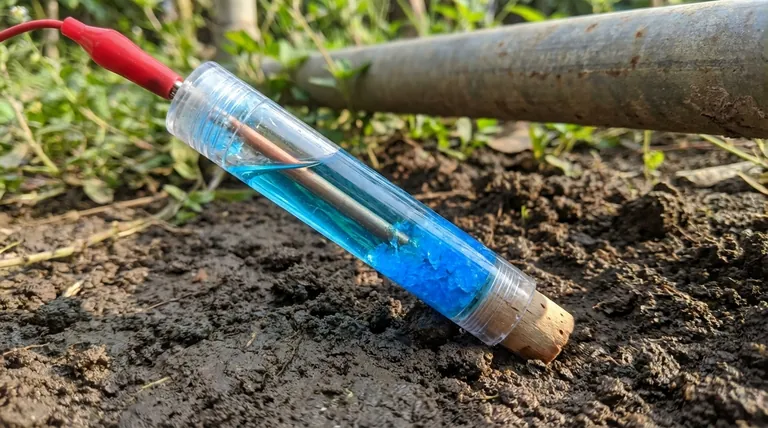
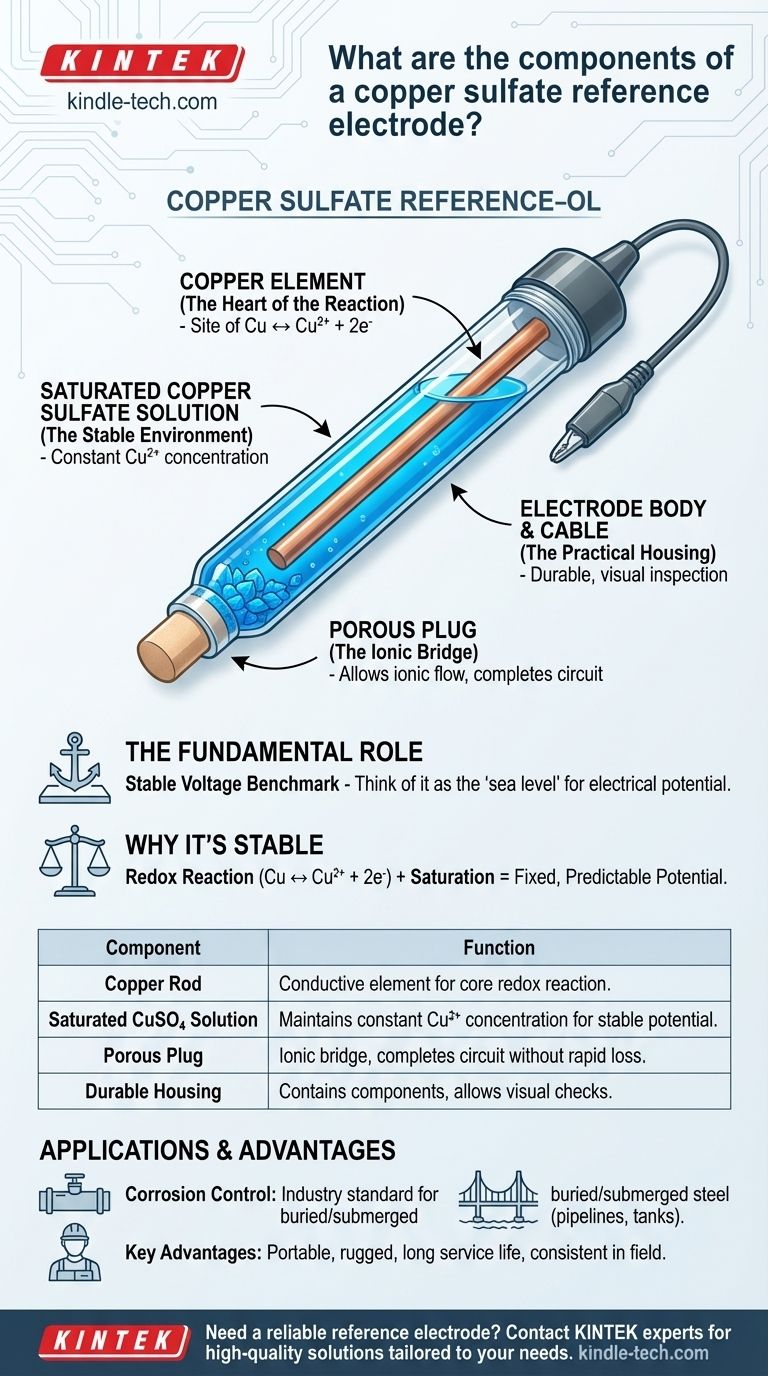
At its core, a copper sulfate reference electrode is a simple and rugged device designed to provide a stable voltage benchmark. Its main components are a high-purity copper rod immersed in a saturated solution of copper sulfate, all contained within a durable housing that features a porous plug to make ionic contact with the environment being measured.
The purpose of combining these specific components—copper, copper sulfate, and a porous junction—is to create a self-contained electrochemical system with a highly stable and well-known potential, making it a reliable reference point for measuring unknown voltages in other materials.

The Fundamental Role of a Reference Electrode
To understand the design of a copper sulfate electrode, we must first understand the purpose of any reference electrode. In electrochemical measurements, we need a stable, unchanging benchmark against which to measure a fluctuating or unknown potential.
Establishing a Zero Point
Think of a reference electrode as the "sea level" for electrical potential. It provides a constant, known voltage, allowing you to accurately measure the "altitude" (potential) of another electrode, known as the working electrode.
The Need for Stability
The key to a good reference electrode is its stability. This is achieved by using a specific chemical reaction (a redox system) where the concentrations of the reactants are kept constant, typically by using a saturated solution. This ensures the electrode's potential does not drift over time or with small changes in temperature.
Deconstructing the Copper Sulfate Electrode
Each component of the copper sulfate electrode plays a critical role in creating and maintaining its stable reference potential.
The Copper Element (The Heart of the Reaction)
The central component is a copper rod or tube. This element is a direct participant in the electrode's core chemical reaction. It acts as the site where copper ions in the solution can either deposit as copper metal or where the rod itself can release new copper ions into the solution.
The Saturated Copper Sulfate Solution (The Stable Environment)
The copper rod is immersed in a solution saturated with copper sulfate crystals. Saturation is non-negotiable because it ensures the concentration of copper ions (Cu²⁺) in the solution remains constant. This constant concentration is what locks in the electrode's potential, making it stable and predictable.
The Porous Plug (The Ionic Bridge)
At the tip of the electrode is a porous plug, often made of wood or ceramic. This component, known as a liquid junction, is essential. It allows ions to flow between the internal copper sulfate solution and the external environment (e.g., soil or water), which completes the electrical circuit without allowing the internal solution to drain out quickly.
The Electrode Body and Cable (The Practical Housing)
The components are held in a durable body, often made of transparent plastic so the user can visually confirm that the solution is still saturated (i.e., that solid crystals are present). An attached cable with a clip provides the simple electrical connection to the measuring device (voltmeter).
Understanding the Electrode's Stability
The reliability of the copper sulfate electrode comes from the predictable electrochemical equilibrium between the copper metal and the copper ions.
The Underlying Redox Reaction
A constant, reversible reaction occurs at the surface of the copper rod: Cu ↔ Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻. The electrode's potential is generated by the tendency of this reaction to proceed in one direction or the other.
Why Saturation Creates Stability
By keeping the copper sulfate solution saturated, the concentration of Cu²⁺ ions is held at a fixed maximum. This prevents the equilibrium from shifting, which in turn keeps the electrode's potential exceptionally stable. Any copper ions consumed or produced by the reaction are immediately replaced from the solid crystals or precipitate out, maintaining a constant environment.
Practical Advantages and Common Applications
The design of the copper sulfate electrode makes it exceptionally well-suited for certain tasks but less so for others.
Key Advantages
This electrode is known for its portability, small size, and ruggedness. Its design allows for a long service life, as the solution can be easily refilled. The on-site potential difference between individual units is typically very low, ensuring consistent and reliable measurements in the field.
Where It Excels
Because of its durability and stable nature, the copper-copper sulfate electrode is the industry standard for measuring the potentials of buried or submerged steel structures. It is primarily used in cathodic protection systems for pipelines, storage tanks, and bridges, especially in soil or freshwater environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right reference electrode depends entirely on your application.
- If your primary focus is field measurement for corrosion control: The copper sulfate electrode is the ideal choice due to its ruggedness, stability in soil, and portability.
- If your primary focus is high-precision lab research in chloride-rich solutions: You would likely choose a different electrode, such as a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) model, which is designed for that specific chemical environment.
Ultimately, the components of a copper sulfate electrode are engineered for one primary purpose: to provide a dependable and stable voltage reference for demanding field applications.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Copper Rod | The conductive element where the core redox reaction (Cu ↔ Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻) occurs. |
| Saturated Copper Sulfate Solution | Maintains a constant concentration of Cu²⁺ ions, ensuring a stable and predictable reference potential. |
| Porous Plug | Acts as an ionic bridge, allowing ion flow to complete the electrical circuit without rapid solution loss. |
| Durable Housing | Contains the components, often transparent to allow visual inspection of the saturated solution. |
Need a reliable reference electrode for your corrosion control or field measurement applications? The copper sulfate electrode's design is proven for stability and durability. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including robust reference electrodes tailored for your specific environmental testing needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the expected lifespan of a copper sulfate reference electrode? Maximize Longevity with Proper Maintenance
- Is there a difference in performance between wood plug and ceramic core copper sulfate electrodes? Speed vs. Durability Explained
- What are the pre-treatment steps before using a portable copper sulfate reference electrode? Ensure Accurate Corrosion Potential Measurements
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of the ceramic core type copper sulfate reference electrode?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of the wood plug type copper sulfate reference electrode? Speed vs. Durability Explained



















