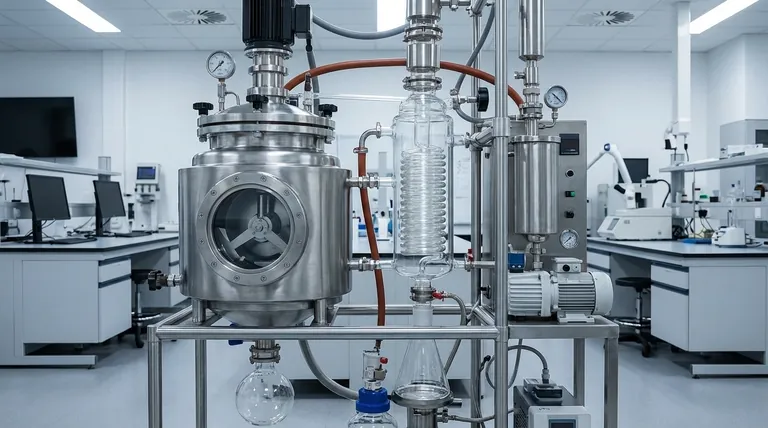
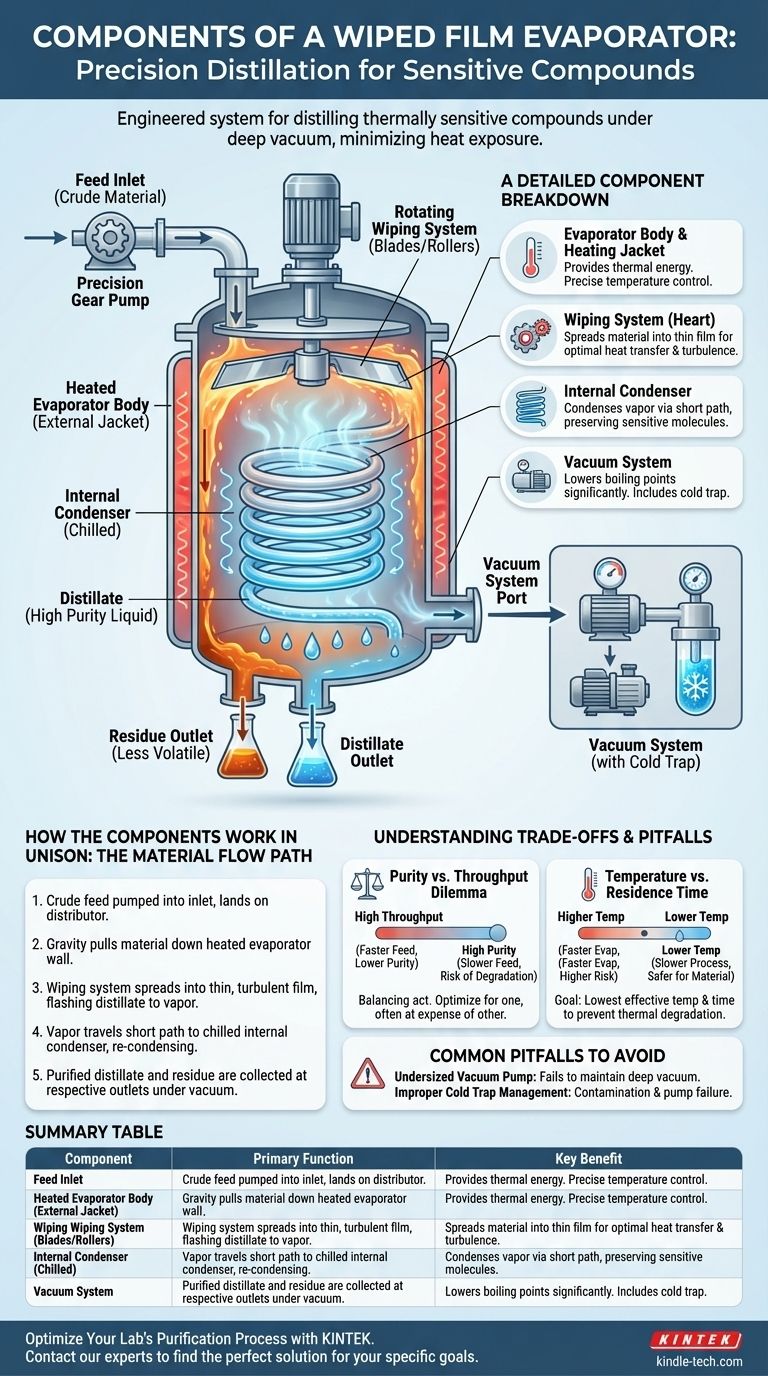
At its core, a wiped film evaporator is a system of precisely engineered components designed to distill thermally sensitive compounds under deep vacuum. Its primary components include the heated evaporator body, a rotating internal wiping system, an internal condenser, a vacuum system, and dedicated inlets and outlets for material flow. These parts work in concert to create a thin, agitated film of material, enabling rapid evaporation at temperatures far below the atmospheric boiling point.
The genius of a wiped film system is not in any single component, but in how they combine to minimize the time and temperature a molecule is exposed to heat. By creating a mechanically agitated thin film opposite a close-proximity condenser, it enables the purification of materials that would be destroyed by traditional distillation.

How the Components Work in Unison
A wiped film evaporator (often called a short-path still when it includes an internal condenser) operates as a continuous process. Understanding the material's journey clarifies the function of each part.
The Material Flow Path
First, the crude feed material is pumped into the evaporator through a dedicated feed inlet, landing on a distributor plate.
Gravity pulls the material down the inner wall of the evaporator body, which is heated by an external jacket.
The wiping system (rollers or blades) spreads this material into an extremely thin, turbulent film against the hot surface, causing the most volatile compounds (the "distillate") to flash into vapor.
This vapor travels an extremely short distance—the "short path"—to the internal condenser, which is chilled. Upon contact, the vapor re-condenses into a high-purity liquid.
The purified distillate liquid runs down the condenser and is collected at the distillate outlet. The less volatile material (the "residue") that did not evaporate continues down the heated wall and is collected at the residue outlet.
A Detailed Component Breakdown
Each component is critical for controlling the separation process. A failure or misconfiguration in one part will compromise the entire system's efficiency.
The Evaporator Body and Heating Jacket
The evaporator body is the main cylindrical vessel, typically made of stainless steel or borosilicate glass.
It is surrounded by a heating jacket through which a thermal fluid (like oil or water) is circulated. This jacket provides the energy required for evaporation, and its temperature is a primary control parameter.
The Wiping System
This is the heart of the machine. A motor drives a central rotor assembly fitted with wipers—often spring-loaded PTFE blades or rolling cylinders.
The wipers serve two functions: they maintain a consistently thin film for optimal heat transfer and create turbulence to ensure fresh material is constantly exposed to the heated surface.
The Internal Condenser
In a short-path configuration, a large condenser coil is placed inside the center of the evaporator body. A chilled fluid is circulated through it.
Its central location drastically reduces the distance vapor must travel, which minimizes pressure drop and prevents sensitive molecules from degrading during their journey from the hot wall to the cold surface.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system is not part of the evaporator itself but is essential for its operation. It connects to the main body via a large port.
A strong vacuum (typically from 0.001 to 1 mbar) dramatically lowers the boiling point of the target compounds. This system usually includes a cold trap to freeze vapors before they can damage the expensive vacuum pumps.
Feed and Discharge Systems
The feed inlet is often connected to a high-precision pump (like a gear pump) to ensure a stable and controllable feed rate.
The distillate and residue outlets are located at the bottom of the unit, allowing the separated fractions to be continuously removed from the vacuum environment, often via pumps or collection flasks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Operating a wiped film system is a balancing act. Optimizing for one parameter, such as throughput, often comes at the expense of another, like purity.
The Purity vs. Throughput Dilemma
Increasing the feed rate can boost throughput, but it may also thicken the film on the evaporator wall, reducing evaporation efficiency and lowering the final purity of the distillate.
Conversely, a very slow feed rate can maximize purity but may lead to thermal degradation if material stays on the hot surface for too long, even as a thin film.
Temperature vs. Residence Time
Higher evaporator temperatures increase the rate of evaporation but also increase the risk of thermally degrading your target compound.
The goal is to find the lowest possible temperature that achieves effective separation at your desired vacuum level and feed rate.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Failing to properly size the vacuum pump is a common mistake. An undersized pump will be unable to maintain the deep vacuum needed to lower boiling points sufficiently.
Another pitfall is improper cold trap management. If the trap is not cold enough or fills up, volatile compounds will pass through to the vacuum pump, causing contamination and eventual failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational parameters should be dictated by your primary objective for the distillation run.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Operate at the deepest possible vacuum, use a slower feed rate, and find the lowest effective evaporator temperature.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Increase the feed rate and wiper speed, accepting a potential small trade-off in final purity.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive material: Prioritize a deep, stable vacuum and a very low evaporator temperature, even if it significantly slows down the process.
By understanding how each component contributes to the delicate balance of time, temperature, and pressure, you can effectively control the separation of your most valuable compounds.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporator Body & Heating Jacket | Provides the thermal energy for evaporation | Precise temperature control for sensitive materials |
| Wiping System (Rotors/Blades) | Spreads material into a thin, agitated film | Maximizes heat transfer and minimizes thermal exposure |
| Internal Condenser | Condenses vapor back into liquid over a short path | Preserves compound integrity by reducing vapor travel distance |
| Vacuum System | Dramatically lowers the boiling points of compounds | Enables distillation at temperatures safe for sensitive materials |
| Feed & Discharge Systems | Controls the continuous input and output of material | Allows for a stable, controlled separation process |
Optimize Your Lab's Purification Process with KINTEK
Are you struggling to purify thermally sensitive compounds without degradation? The precise engineering of a wiped film evaporator is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including distillation systems designed for maximum efficiency and purity.
We can help you select the right system to meet your specific goals, whether your priority is maximizing purity, increasing throughput, or processing highly sensitive materials. Our expertise ensures you get the performance and reliability your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect wiped film evaporator solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















