At its core, a high-resistance heating element is a material specifically designed to convert electrical energy into heat. The most common material used for this purpose, especially in everyday appliances, is an alloy of nickel and chromium called Nichrome (typically 80% nickel, 20% chromium), valued for its high electrical resistance and its ability to withstand repeated heating cycles without degrading.
The selection of a high-resistance heating element is not just about its ability to get hot. The crucial factor is its ability to survive at high temperatures by resisting oxidation, which would otherwise cause it to quickly burn out.
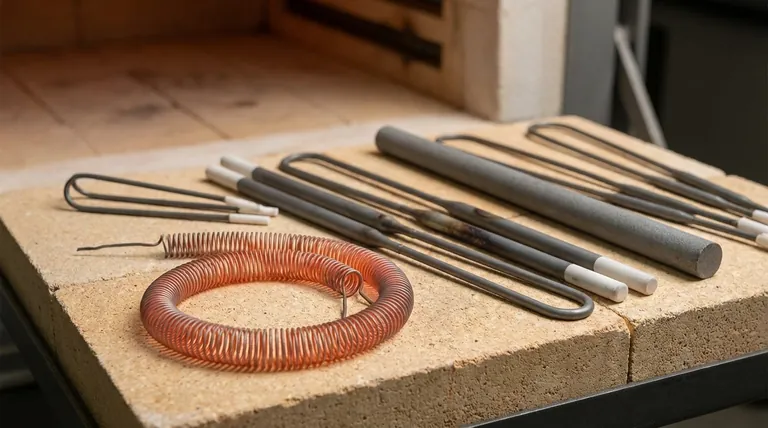

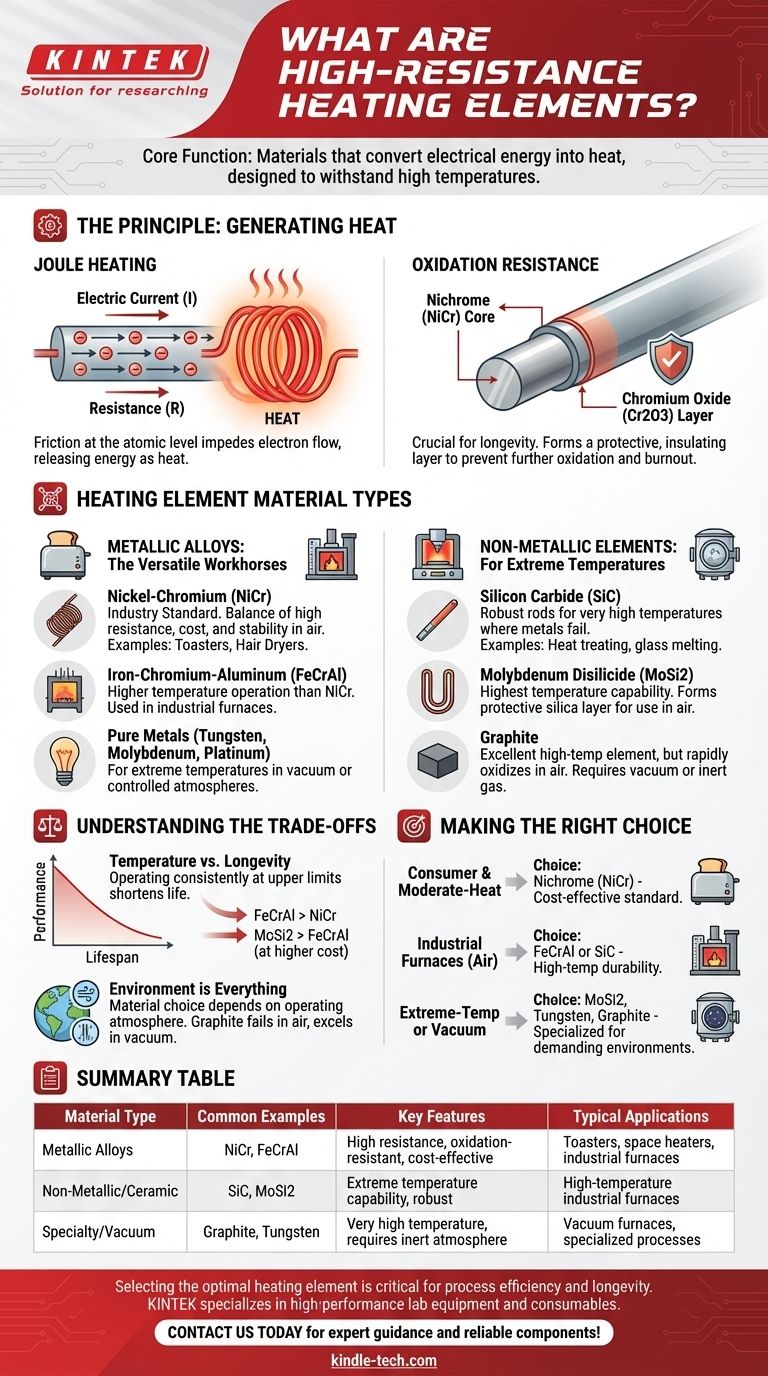
The Principle: How Resistance Generates Heat
Joule Heating
All resistance heating elements operate on a principle known as Joule heating. When an electric current passes through a material with high electrical resistance, the flow of electrons is impeded. This friction at the atomic level releases energy in the form of heat.
The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
Simply having high resistance is not enough. When a metal is heated to high temperatures in the presence of air, it rapidly oxidizes, becoming brittle and failing.
The genius of materials like Nichrome is that when heated for the first time, they form a thin, adherent outer layer of chromium oxide. This layer is electrically insulating but, more importantly, it protects the underlying metal from further oxidation, dramatically extending the element's operational life.
A Breakdown of Heating Element Materials
Heating elements are broadly categorized into metallic and non-metallic types, chosen based on the required operating temperature and environment.
Metallic Elements: The Versatile Workhorses
These are the most common elements found in consumer and industrial applications.
- Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) Alloys: As mentioned, this is the industry standard for devices like toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters. It offers an excellent balance of high resistance, cost-effectiveness, and stability in air.
- Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys: This is another major class of resistance alloys. They can often operate at even higher temperatures than Nichrome and are frequently used in industrial furnaces.
- Pure Metals: In highly specialized applications, pure metals like tungsten, molybdenum, and platinum are used. Their extremely high melting points make them suitable for vacuum furnaces or other controlled-atmosphere heating.
Non-Metallic Elements: For Extreme Temperatures
When temperatures exceed the capabilities of common metal alloys, non-metallic ceramic or carbon-based elements are required.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): These rigid, robust rods are used extensively in industrial furnaces for processes like heat treating and glass melting, operating at very high temperatures where metal alloys would fail.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): For the most demanding, highest-temperature applications, these elements are the top choice. They form a protective silica layer that allows them to function reliably at extreme temperatures in air.
- Graphite: Graphite is an excellent high-temperature heating element, but it has a significant limitation: it will rapidly oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen. Therefore, it can only be used in vacuum or inert-gas atmosphere furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature vs. Longevity
The primary trade-off is performance versus lifespan. While an element might be rated for a very high temperature, operating it consistently at its upper limit will shorten its life. FeCrAl alloys can handle higher temperatures than NiCr, but MoSi2 outperforms them both, albeit at a significantly higher cost.
Environment is Everything
The choice of material is critically dependent on the operating atmosphere. NiCr and FeCrAl are designed to work in open air. In contrast, using a graphite element in an air-filled furnace would lead to immediate failure, while it would perform exceptionally in a vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is consumer appliances or moderate-heat applications: A Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) alloy is almost always the correct and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is industrial furnaces operating in air: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements provide the high-temperature durability required.
- If your primary focus is extreme-temperature or vacuum furnaces: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), Tungsten, or Graphite are the specialized materials designed for these demanding environments.
Ultimately, selecting the right element means matching the material's properties to the specific temperature and atmospheric conditions of your task.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nichrome (NiCr), FeCrAl | High resistance, oxidation-resistant, cost-effective | Toasters, space heaters, industrial furnaces |
| Non-Metallic/Ceramic | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Extreme temperature capability, robust | High-temperature industrial furnaces |
| Specialty/Vacuum | Graphite, Tungsten | Very high temperature, requires inert atmosphere | Vacuum furnaces, specialized processes |
Selecting the optimal heating element is critical for your process efficiency and equipment longevity. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and reliable components for all your laboratory heating needs. Contact us today to ensure you have the right element for your specific temperature and atmospheric requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs



















