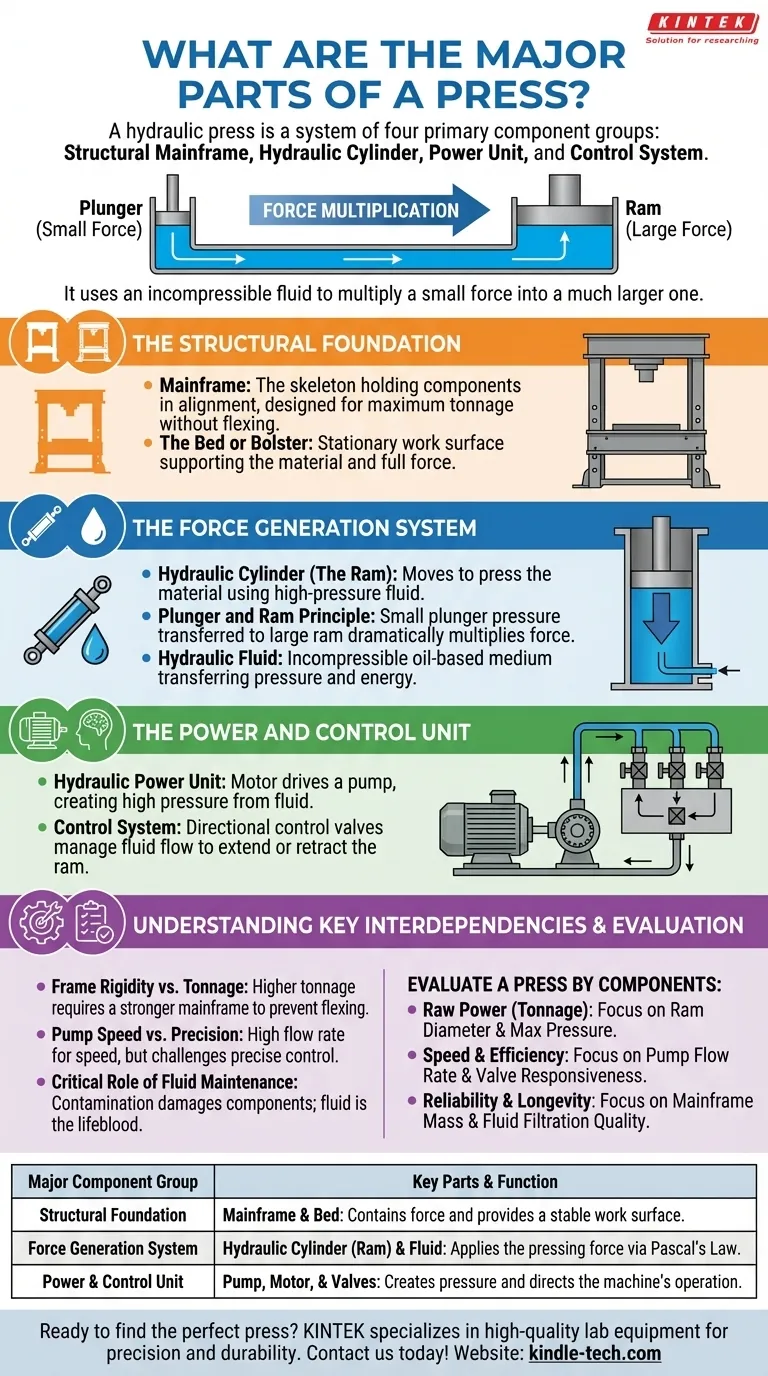
At its core, a hydraulic press is a system of four primary component groups. These are the structural mainframe that contains the force, the hydraulic cylinder that applies the force, a power unit that creates fluid pressure, and a control system that directs the operation. Every other part serves to support one of these fundamental functions.
A press operates on a simple principle: it uses an incompressible fluid to multiply a small force into a much larger one. Understanding how the frame, cylinders, and power unit interact is the key to understanding how the entire machine generates and controls immense power.
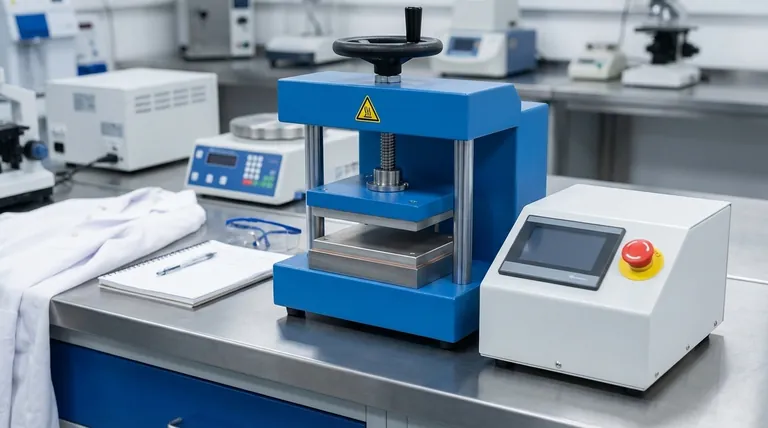

The Structural Foundation
The entire purpose of the press's structure is to safely contain the massive forces generated during operation. It provides the rigidity and stability necessary for precision work.
The Mainframe
The mainframe is the skeleton of the press. It holds all other components in their correct alignment and is engineered to withstand the machine's maximum rated tonnage without flexing or failing.
The Bed or Bolster
This is the stationary work surface of the press. The material to be pressed is placed on the bed, which is built to support the full force exerted by the cylinder from above.
The Force Generation System
This is the heart of the press, where hydraulic principles are translated into physical movement and power. The system is based on Pascal's Law, where pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished.
The Hydraulic Cylinder (The Ram)
The ram is the large cylinder and piston assembly that moves to press the material. High-pressure hydraulic fluid is pumped into this cylinder, pushing the piston down with significant force.
The Plunger and Ram Principle
Most presses use two connected cylinders: a small one (the plunger) and a large one (the ram). The power unit applies pressure to the fluid in the small plunger cylinder. This same pressure is then transferred to the ram cylinder, which has a much larger surface area, dramatically multiplying the output force.
The Hydraulic Fluid
Typically an oil-based fluid, this is the medium that transfers pressure. It must be incompressible to work effectively, meaning it does not shrink in volume under pressure, allowing for the efficient transfer of energy from the pump to the ram.
The Power and Control Unit
This system is the "engine and brain" of the press. It creates the power and tells the machine when and how to apply it.
The Hydraulic Power Unit
This unit consists of a motor that drives a pump. The pump is responsible for drawing hydraulic fluid from a reservoir and forcing it into the system's cylinders, creating the high pressure required for operation.
The Control System
A series of directional control valves manage the flow of the hydraulic fluid. By opening and closing these valves, an operator can direct the high-pressure fluid to extend or retract the ram, controlling the entire press cycle.
Understanding the Key Interdependencies
The effectiveness of a press is not just about the quality of individual parts, but how they work together. A change in one component directly impacts the performance of the others.
Frame Rigidity vs. Tonnage
A press designed for higher tonnage requires a proportionally stronger and more rigid mainframe. A weak frame will flex under load, leading to inaccurate pressing and potential equipment failure.
Pump Speed vs. Precision
The pump's flow rate determines how fast the ram can move. While a high flow rate enables faster cycle times, it can make very slow, precise movements more difficult to control without a sophisticated valve system.
The Critical Role of Fluid Maintenance
The hydraulic fluid is the lifeblood of the system. Contamination from dirt or debris can quickly damage the tight tolerances inside the pump and control valves, leading to pressure loss, erratic operation, and costly breakdowns.
How to Evaluate a Press by Its Components
By understanding these core parts, you can better assess a machine's capabilities based on its specifications.
- If your primary focus is raw power (tonnage): The diameter of the ram cylinder and the maximum pressure rating of the power unit are your most important metrics.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: The pump's flow rate (often in gallons per minute) and the responsiveness of the control valves are what you need to examine.
- If your primary focus is reliability and longevity: The mass and construction of the mainframe, coupled with the quality of the system's fluid filtration, are the best indicators of a durable machine.
Ultimately, knowing these major parts transforms a complex machine into a logical system of interconnected components working to achieve a single goal.
Summary Table:
| Major Component Group | Key Parts & Function |
|---|---|
| Structural Foundation | Mainframe & Bed: Contains force and provides a stable work surface. |
| Force Generation System | Hydraulic Cylinder (Ram) & Fluid: Applies the pressing force via Pascal's Law. |
| Power & Control Unit | Pump, Motor, & Valves: Creates pressure and directs the machine's operation. |
Ready to find the perfect press for your application?
Understanding the components is the first step. The next is selecting a machine with the right tonnage, speed, and reliability for your specific laboratory or industrial needs. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including hydraulic presses, designed for precision and durability.
Let our experts help you:
- Match the specifications (tonnage, pump speed, frame rigidity) to your process.
- Ensure long-term reliability with systems built for performance.
- Optimize your workflow with the right equipment.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover the difference the right press can make!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Can you use a hydraulic press for blacksmithing? Unlock the Power of Controlled Force
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used for all-solid-state batteries? Achieve 240 MPa for Peak Ion Transport
- What are three ways to reduce production time in compression molding? Optimize Design, Preheat, and Automate
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in ceramic green body preparation? Ensure Data Accuracy in Expansion.
- What is the alternative to XRF? Choose the Right Elemental Analysis for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of using stainless steel molds and laboratory hydraulic presses? Ensure Precise Ionic Conductivity
- What size are extrusion pellets? Mastering Pellet Geometry for Optimal Extrusion Performance
- Is compression molding a fast process? A Guide to Faster Time-to-Market for Low-Volume Production



















